Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Sporochnales
Family Sporochnaceae
Carpomitra costata (Stackhouse) Batters 1902: 46
Plants medium brown, up to 20 (-40) cm tall, comprising robust conical holdfast with felty surface and one to several tough, wiry axes. Axes frequently irregularly branched, compressed, with more-or-less evident midrib. Structure parenchymatous, central medulla of thin-walled cells surrounded by mantle of thick-walled cells especially in region of midrib; cortex of isodiametric cells 5-10 µm in diameter. Meristematic zone at base of terminal tuft of trichothallic filaments.
Unilocular sporangia in subterminal sori surrounding the axis of branches below the terminal tuft of assimilatory filaments; sorus subtended by a cup-shaped vegetative structure. Sporangia borne on several cells of (branched) paraphyses; sporangia elongate ellipsoid, 35-45 x 15 µm ; terminal cells of paraphyses swollen, ovoid or truncate, 15-20 µm in diameter.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Recorded from Hout Bay to the Port Shepstone area of Kwazulu-Natal (16-49). A deep water species, found down to around 40 m.
World distribution: widely distributed in tropical and temperate waters (Guiry & Guiry 2012).
Type locality: Fowey, Cornwall, England (Womersley 1987).
Note: our entity was originally described as C. filiformis (Suhr) Papenfuss, with the type specimen from Algoa Bay, but we follow Stegenga et al. (1997) who agreed with Womersley (1987) in considering C. filiformis to belong within the widespread C. costata.
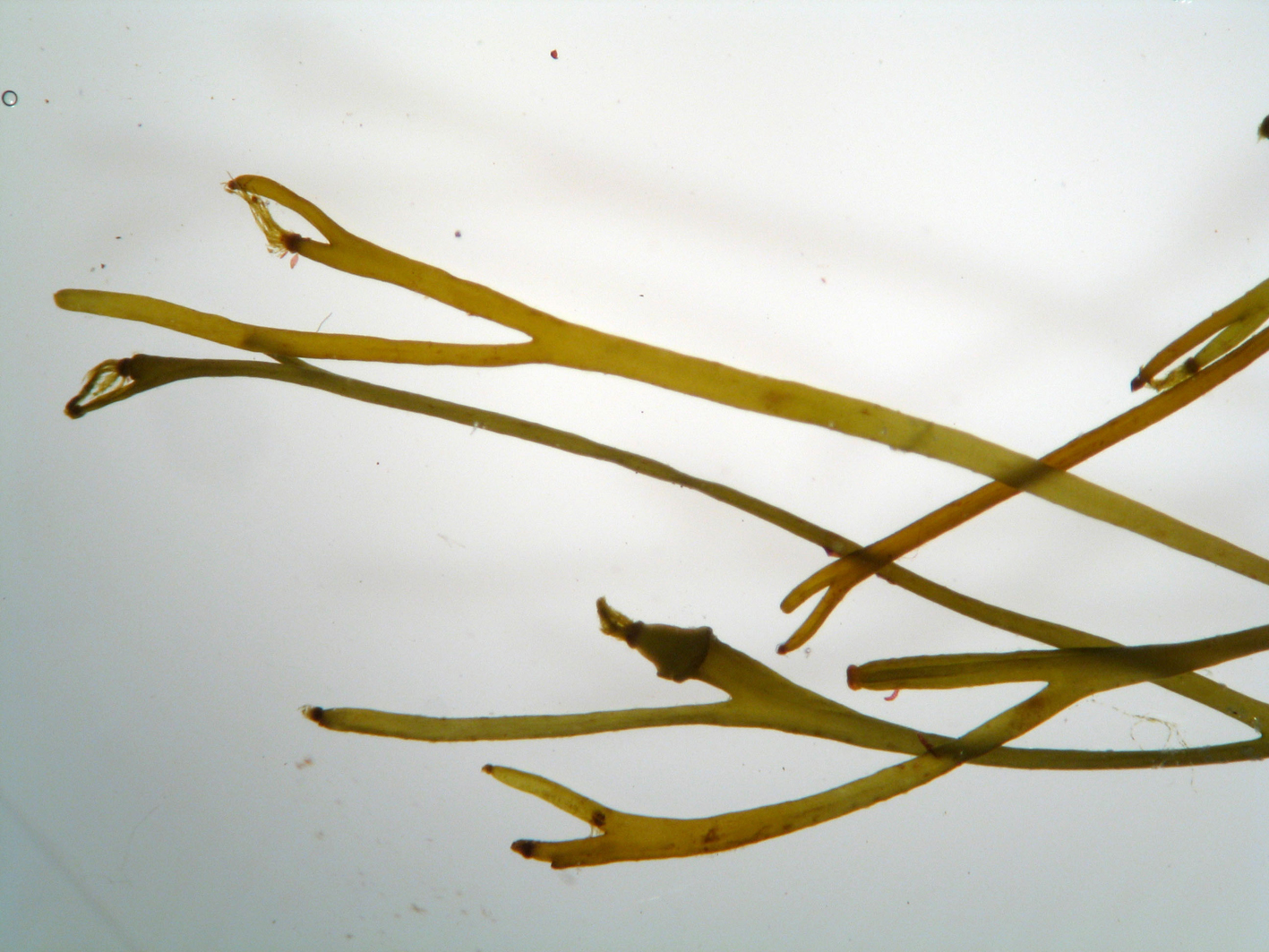

Carpomitra costata, ends of thalli (pressed specimen), ca 0.8-1.2 mm wide.
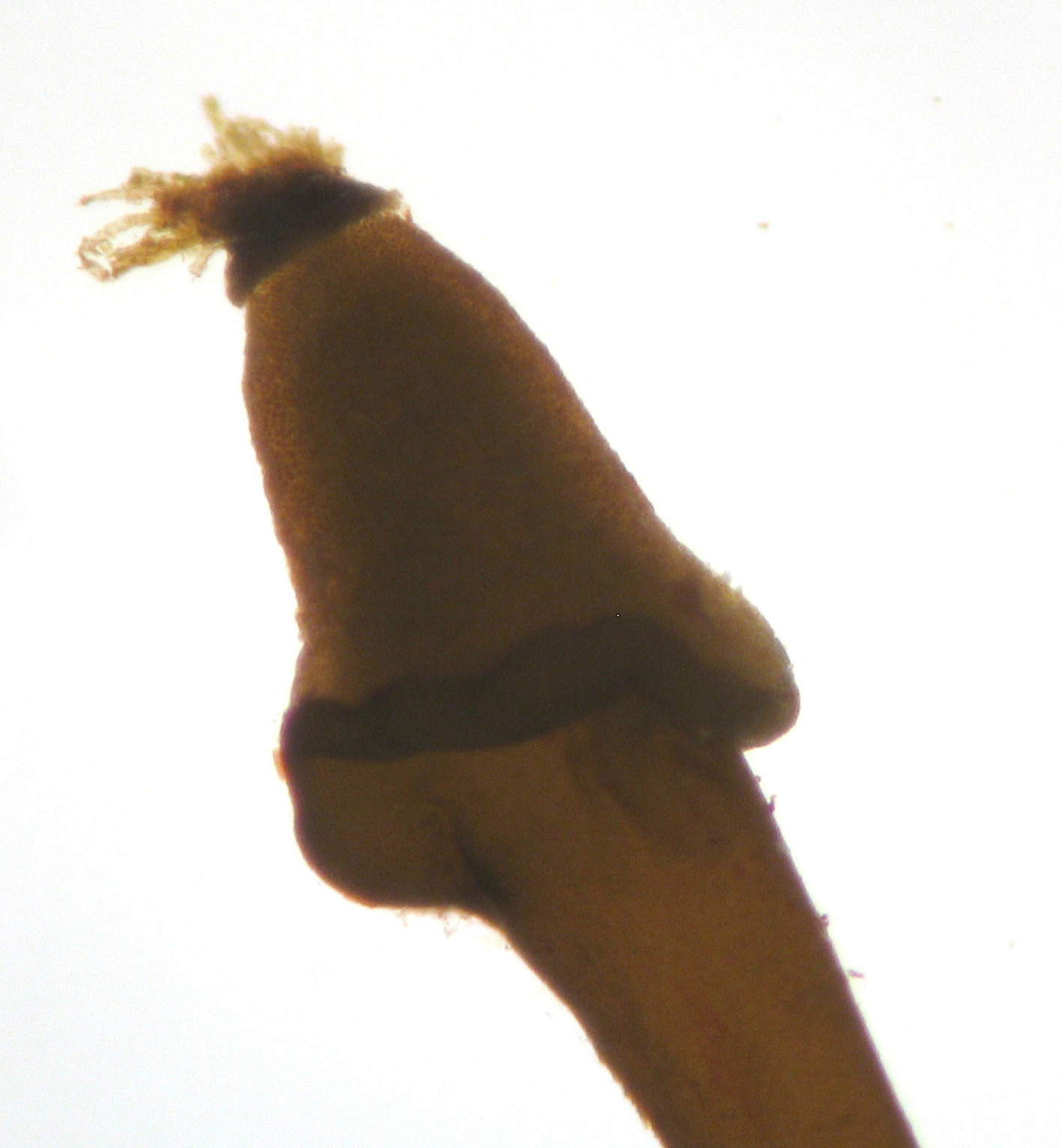

Carpomitra costata, fruiting body in which unilocular sporangia are produced in sori.
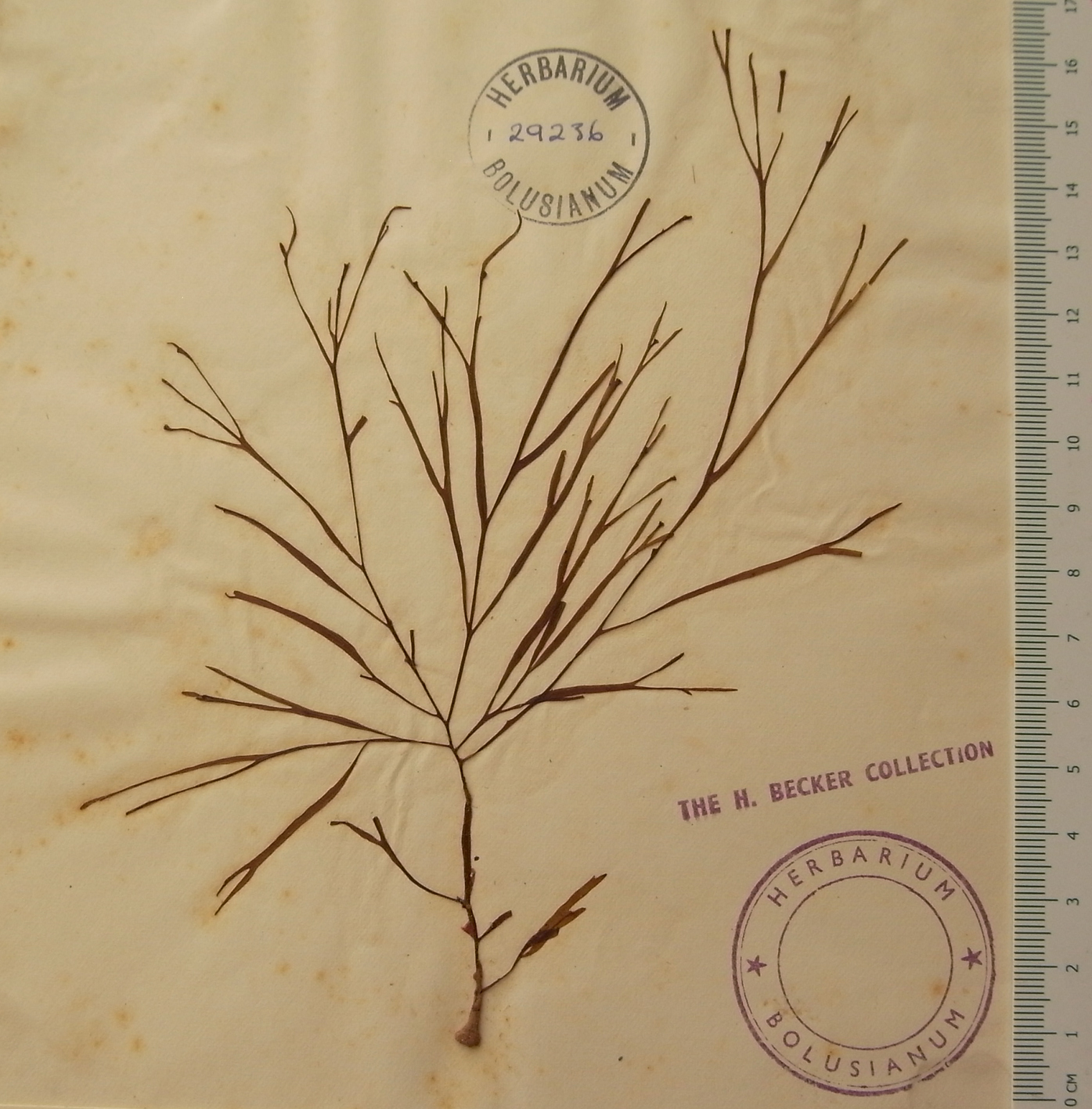

Carpomitra costata, herbarium specimen from the Lizard, England (BOL).
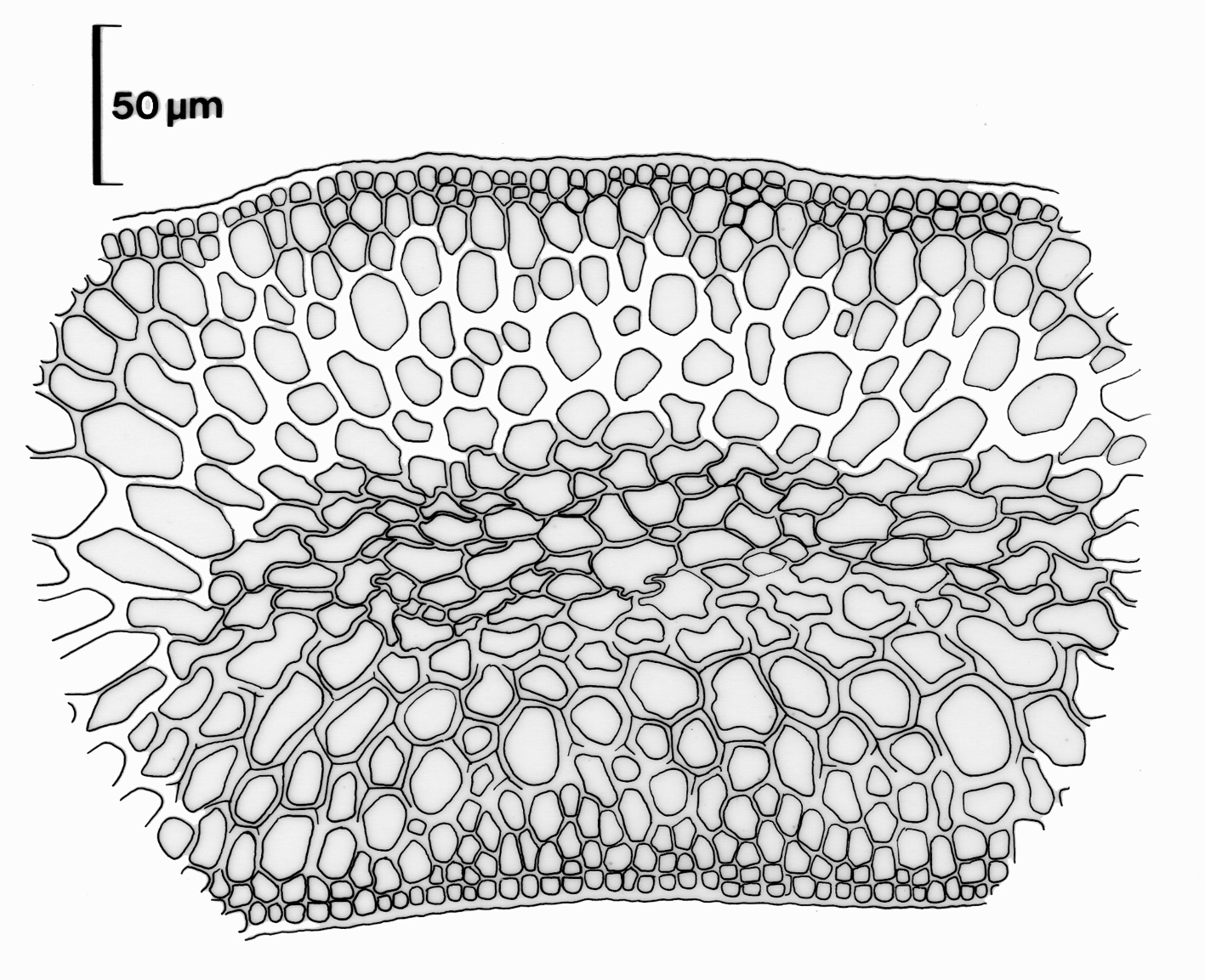
Carpomitra costata. 1. Section of main axis from herbarium material. Reproduced from Stegenga et al. (1997).
References Carpomitra costata
Batters, E.A.L. (1902). A catalogue of the British marine algae. Journal of Botany, British and Foreign 40(Supplement): 1-107.
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. 2012. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched February 2012.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. and R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Womersley, H.B.S. (1987). The marine benthic flora of southern Australia. Part II. pp. 481, 169 figs, 1 table, 8 plates, 4 maps. Adelaide: South Australian Government Printing Division.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 16 February 2026.