Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Ectocarpales
Family Adenocystaceae
Chordariopsis capensis (C.Agardh) Kylin 1940: 54, fig. 30
Plants brown to yellow-brown, branched and stringy, up to 40 cm long, comprising several erect thalli arising from a crustose base. Thallus comprising a number of terete indeterminate main axes, generally less than 1 mm in diameter, from which arise a profusion of terete, determinate secondary branches of varying lengths, irregularly inserted at wide angles. Laterals often unbranched, but may bear profuse, often short, branches. Structure of pigmented cortex of cells ca. 12-14 µm long x 5-8 µm in diameter, organised in radiating filaments of 3-5 cells (ca. 40 µm ) deep, grading below into an unpigmented medulla of a very compact pseudoparenchyma, with roundish cells ca. 25-30 µm in cross-sectional diameter; longitudinally elongated, older axes with a schizogenic cavity. In corss-section, medullary cells in a spiral pattern. Hairs absent in our material.
Unilocular sporangia embedded in paraphyses, in sori 50-60 µm deep; cylindroconical to ovate, ca. 25-50 µm long and 10 µm maximum) in diameter; paraphyses clavate, loosely arranged, unicellular (occasionally 2-celled), 25-40 µm long.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Abundant in intertidal rock-pools, particularly in the upper eulittoral zone. Recorded along the entire west coast to at least the Tsitsikamma region (1-32).
World distribution: Also recorded from Namibia and New Zealand, Macquarie Island, and Antarctica (Guiry & Guiry 2011).
Type locality: Cape of Good Hope, South Africa (Silva et al.1996).
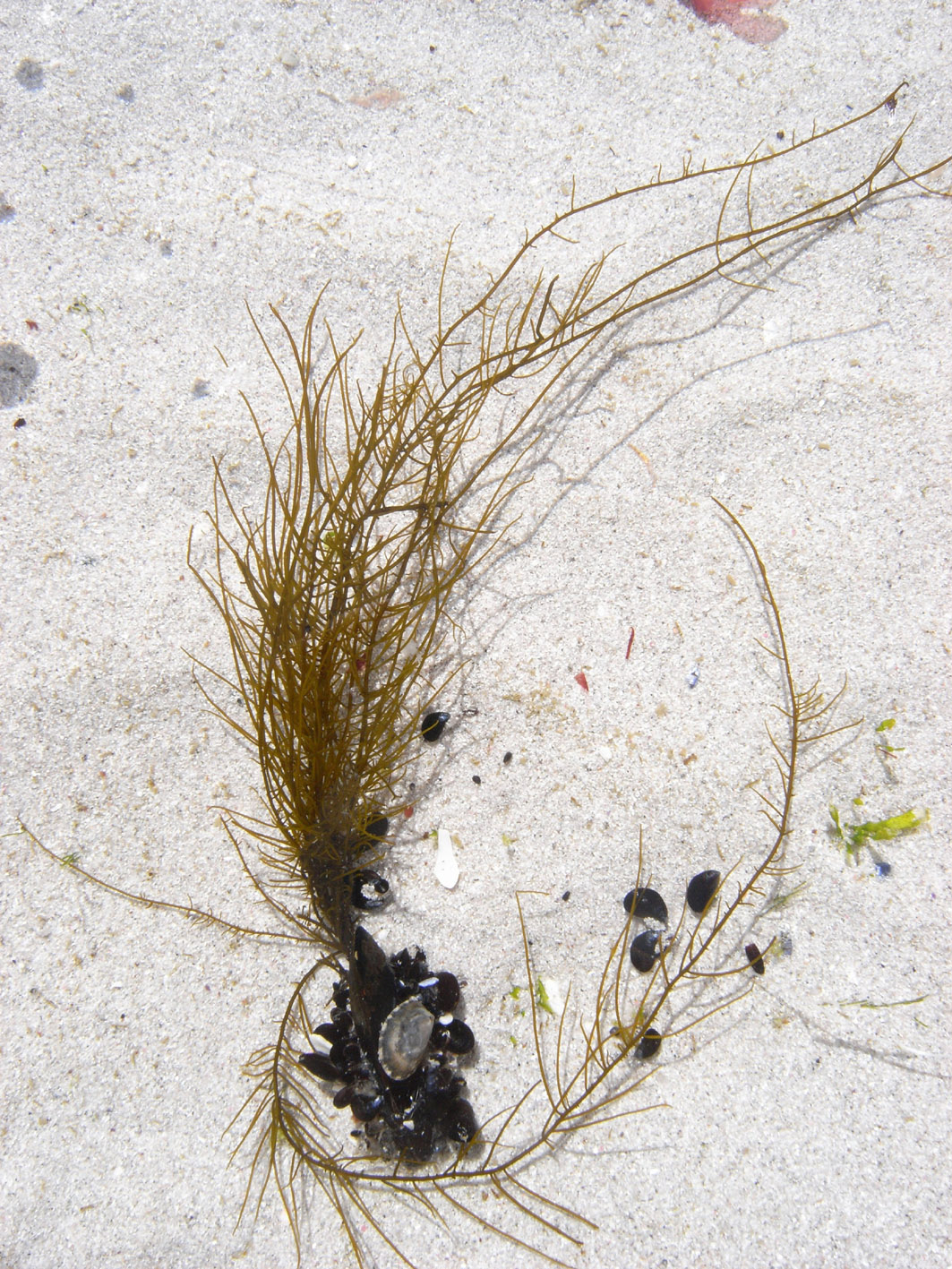

Chordariopsis capensis, attached to small mussel shells, Kommetjie, Western Cape.
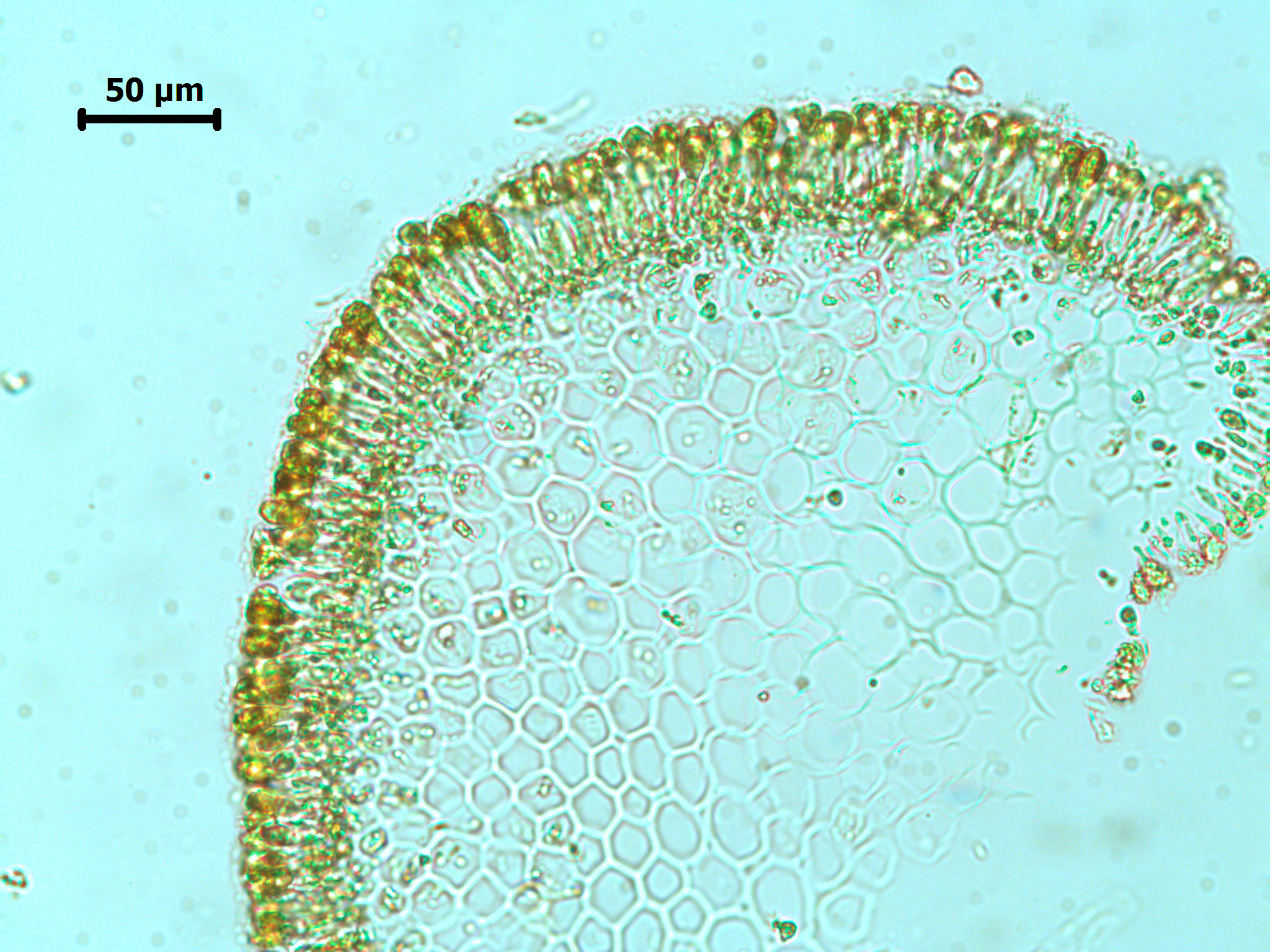
Chordariopsis capensis, xs showing filamentous cortex and parenchymatous medulla.
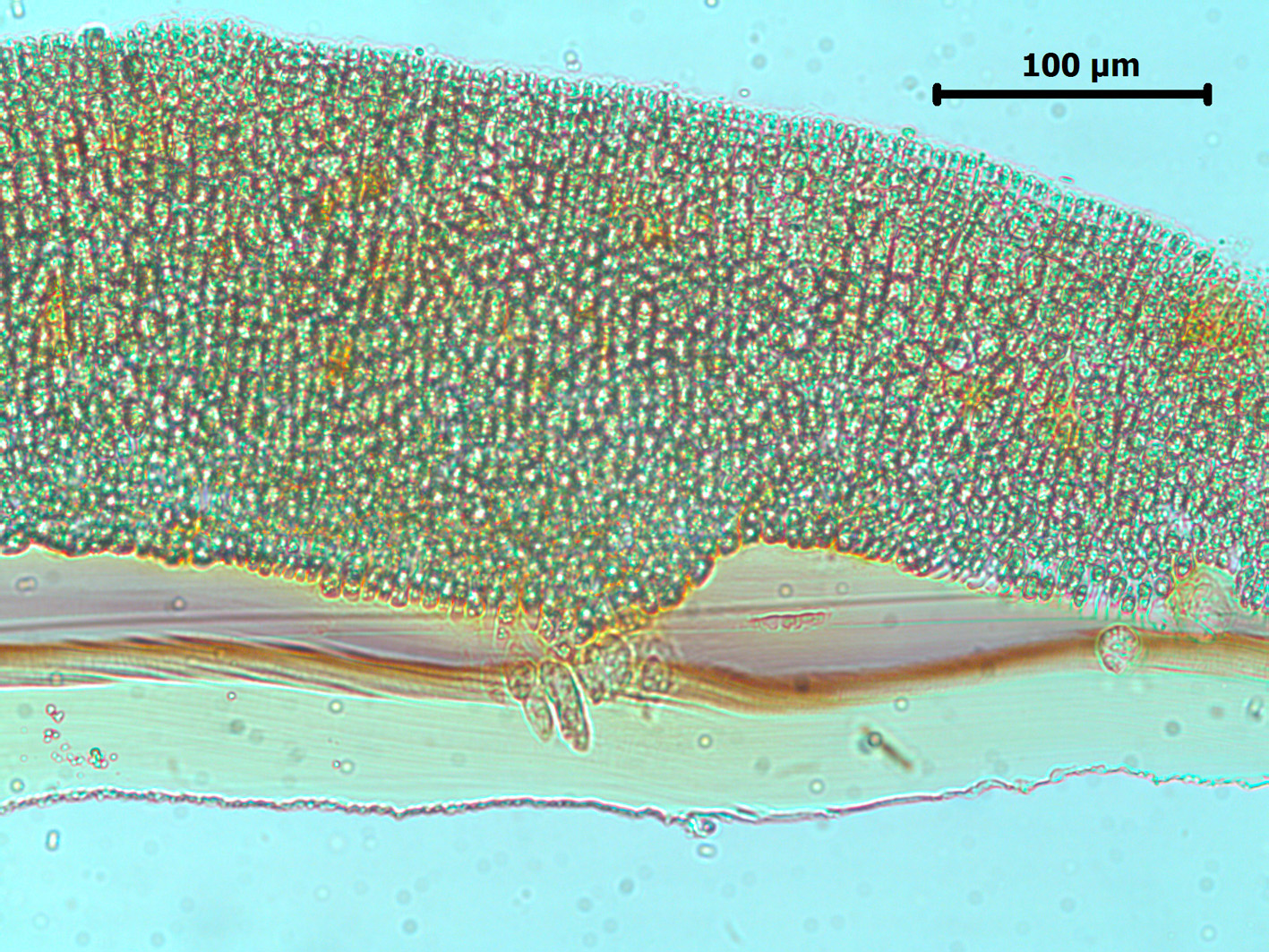

Chordariopsis capensis, xs of crustose base attached to piece of mussel shell.
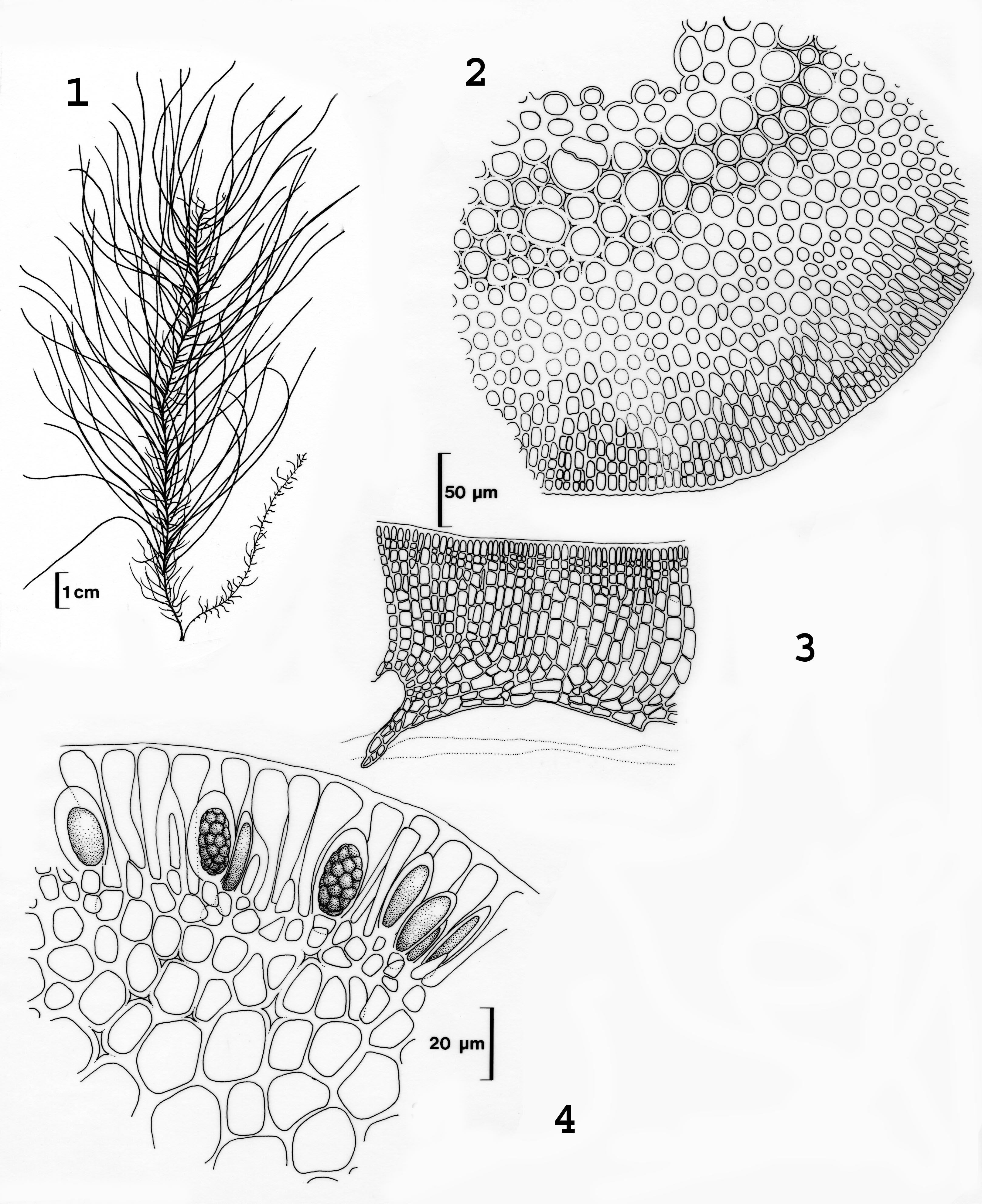
Chordariopsis capensis. 1. Habit. 2. Cross section. 3. Section of crustose base on mussel shell. 4. Unilocular sporangia in cross section of thallus. Drawings from Stegenga et al. (1997).
References Chordariopsis capensis
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. 2011. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched on 20 May 2011.
Kylin, H. (1940). Die Phaeophyceenordnung Chordariales. Acta Universitatis Lundensis 36(9): 1-67, 30 figs.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. (1996). Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. and R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 09 March 2026.