Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Ectocarpales
Family Scytosiphonaceae
Colpomenia sinuosa (Mertens ex Roth) Derbès & Solier in Castagne 1851: 95
Plants yellowish-brown, hollow, convoluted-globose, several to 10 cm in diameter, attached by rhizoids from broad base. Structure of ca. 4 layers of large colourless medullary cells becoming smaller towards the cortex, surrounded by cortex of 2-3 layers of small isodiametric cells, with surface cells ca. 7 µm in diameter; bundles of phaeophycean hairs ( ca. 8-9 µm in diameter) emerging through cortex from the medulla.
Plurilocular sporangia in raised sori, covered by cuticular membrane and often associated with hair bundles. Plurilocular sporangia uniseriate with ca. 6 locules ca. 20 µm long x 4 µm wide, with occasional unicellular paraphyses. Unilocular sporangia unknown.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Recorded along the whole South African coast (1-58), but see note 1 below. Found in rock pools and in the lower eulittoral zone, often epiphytic on larger algae.
Worldwide distribution: worldwide in tropical and temperate waters (Guiry & Guiry 2011).
Type locality: near Cádiz, Spain (Guiry & Guiry 2011).
Notes: 1. A second species, Colpomenia claytonii S.M.Boo, K.M.Lee, G.Y.Cho et W.Nelson, is recorded from Seaforth Beach in False Bay, Western Cape (Boo et al. 2011), and may be more widely distributed in South Africa. Unlike C. sinuosa, this species has a single layer of angular cortical cells (rather than 1-2 layers of cuboidal cells), and phaeophycean hairs that arise from the cortex (rather than the sub-cortical medulla). Mature plurilocular sporangia in C. claytonii have 6-8 locules compared to 8-12 locules in C. sinuosa.
2. Some specimens of C. sinuosa may appear superficially similar to Leathesia marina, but the latter species has a better-developed medulla and is spongy rather than completely hollow. Clusters of small Colpomenia plants may resemble Iyengaria stellata, but the latter species has solid thalli (at least in younger plants) and thicker walls - of at least 10 cell layers (Stegenga et al. 1997).
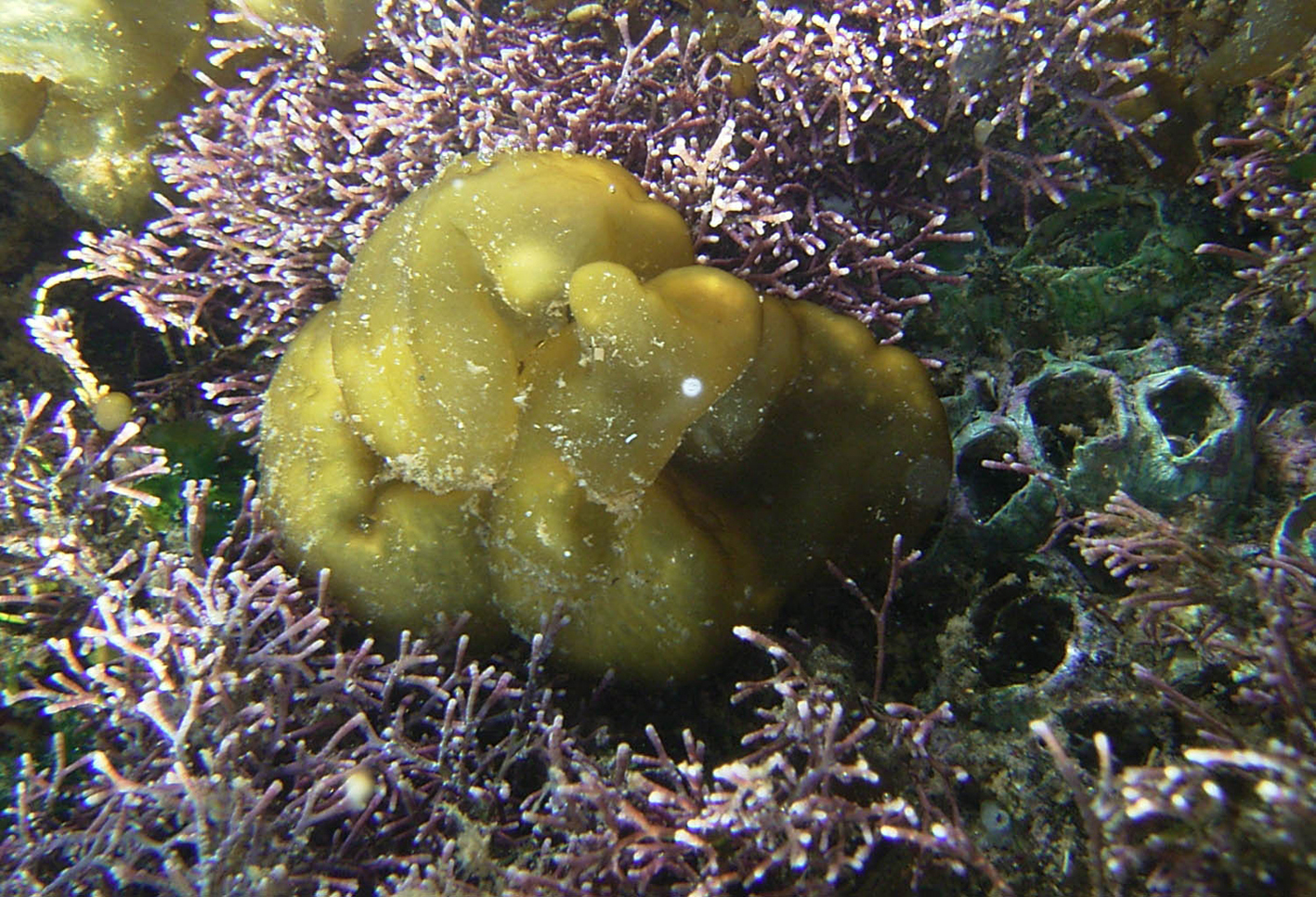

Colpomenia sinuosa, Haga Haga tidal pool, under water.
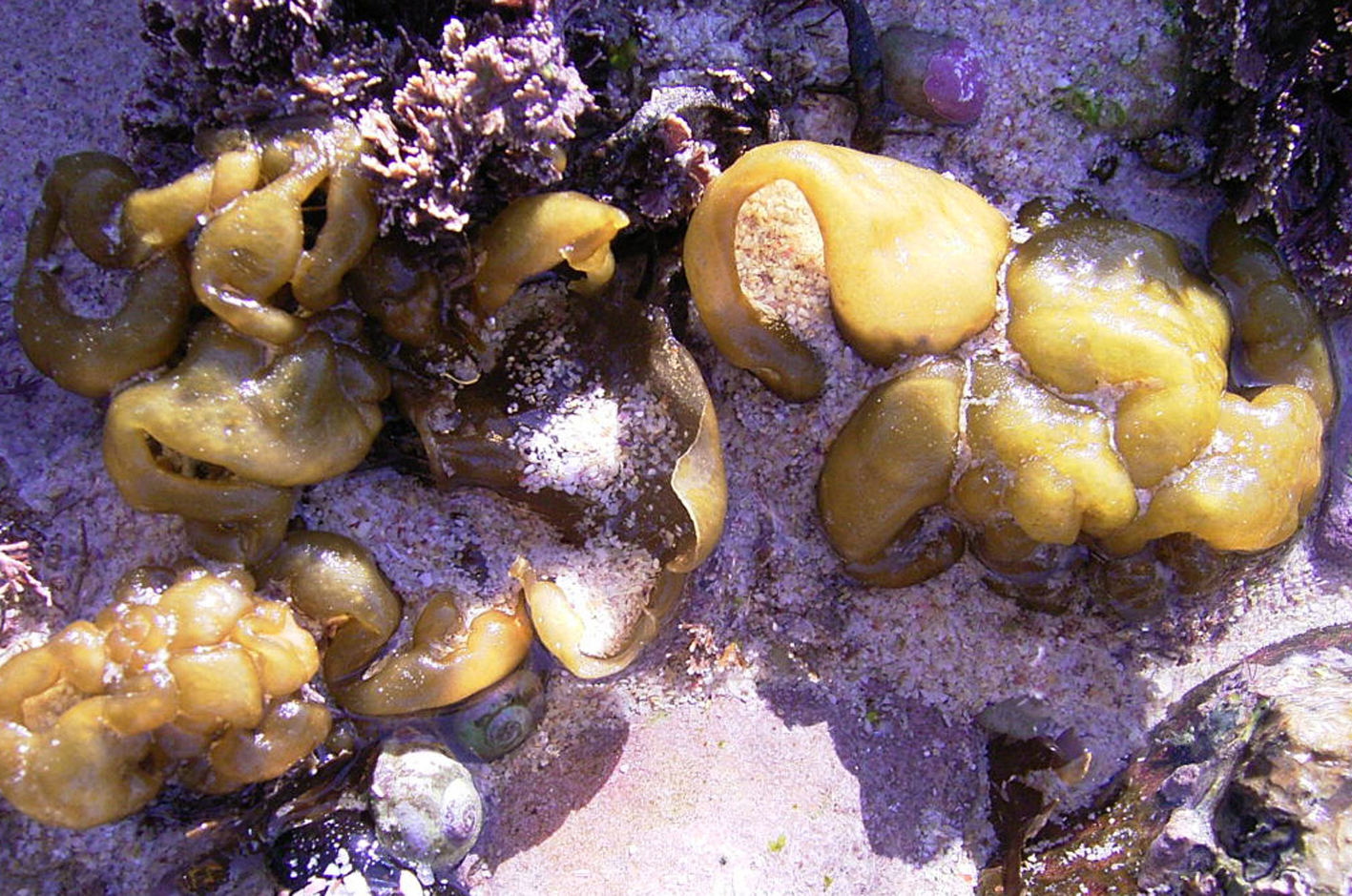

Colpomenia sinuosa, mid eulittoral zone, Struis Bay.
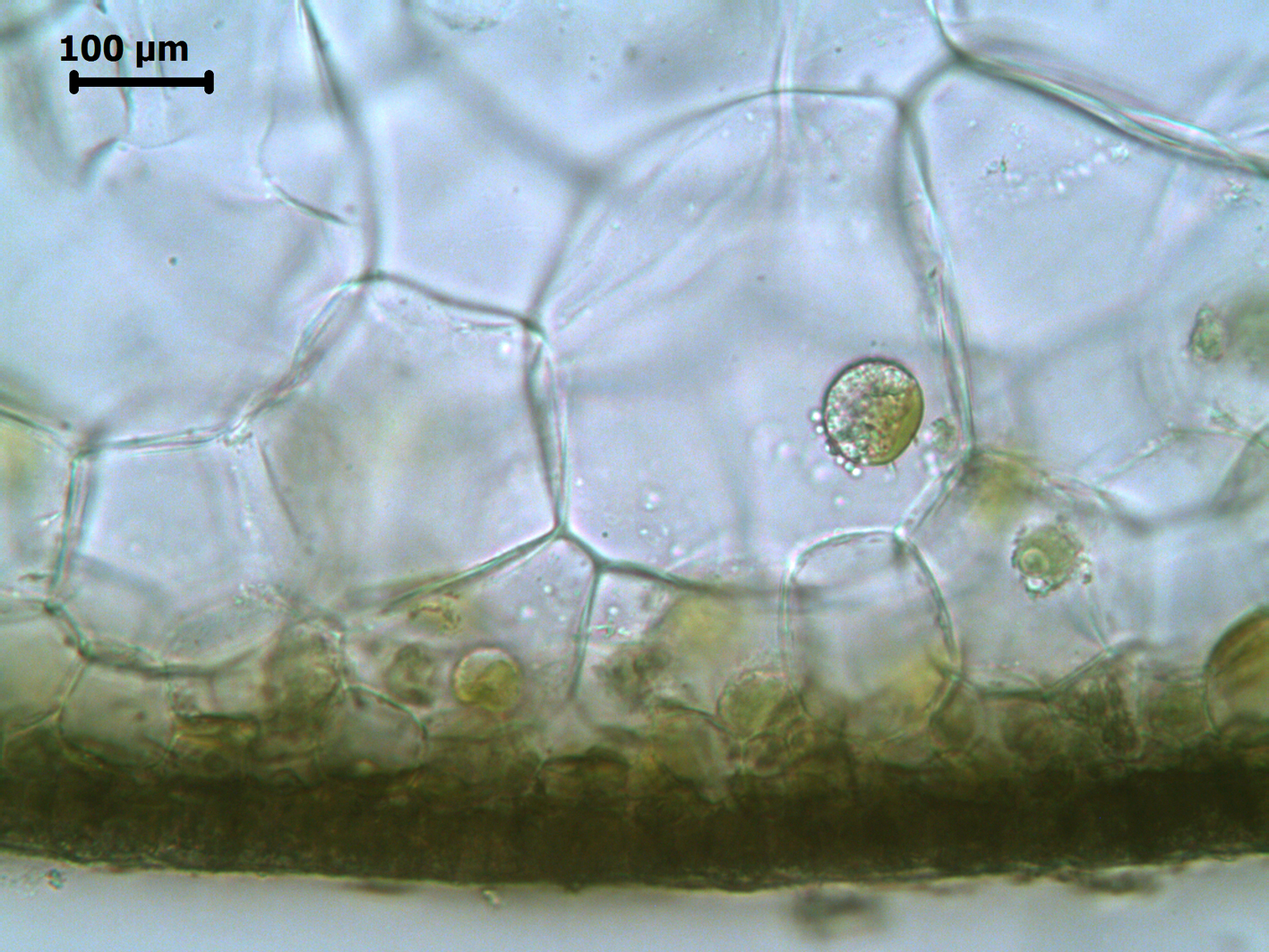
Colpomenia sinuosa, xs through cortex and outer medulla, Nature’s Valley material.
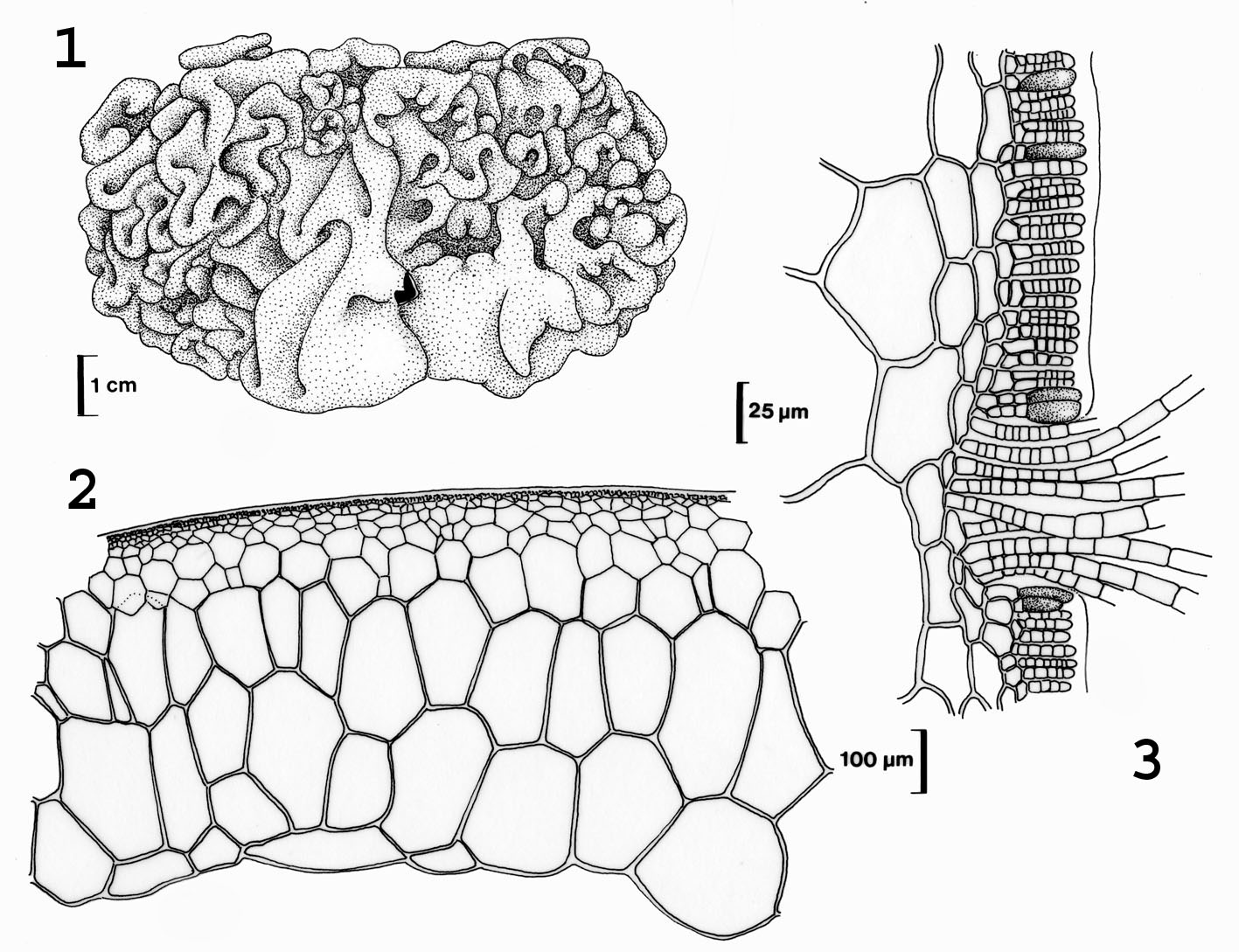
Colpomenia sinuosa. 1. Habit. 2. Cross section of sterile specimen. 3. Cross section with plurilocular sporangia, paraphyses and hair bundle. Drawings from Stegenga et al. (1997).
References Colpomenia
Boo, S.M., Lee, K.M., Cho, G.Y. & Nelson, W. (2011). Colpomenia claytonii sp. nov. (Scytosiphonaceae, Phaeophyceae) based on morphology and mitochondrial cox3 sequences. Botanica Marina 54(2): 159-167.
Derbès, A. & Solier, A.J.J. (1851). Algues. In: Supplément au catalogue des plantes qui croissant naturellement aux environs de Marseille. (Castagne, J.L.M. Eds), pp. 93-121. Aix: Nicot & Pardigon.
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. 2011. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched October 2011.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. and R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 09 March 2026.