Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Fucales
Family Sargassaceae
Cystophora fibrosa Simons 1970: 1, figs. 1, 2
Plants dark brown to yellowish-brown, branched, up to 50 cm (-1 m) high; fibrous in texture. Holdfast irregularly conical, up to 6 mm in diameter, bearing a single primary axis. Thallus comprising two distinct branching systems; primary system with 1-3 orders, flexuous, distichous, giving rise to a secondary system of branches producing fascicles of narrower branches by bifurcation in a radial, alternate fashion.
Receptacles formed from ultimate branches that become slightly distorted with numerous swellings and constrictions at intervals. Vesicles absent. Receptacles containing 2-3 rows of bisexual conceptacles; conceptacles sub-spherical, ca. 0.5 mm in diameter with 1 egg per oogonium. See Simons (1970) for further details of reproductive anatomy.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Recorded in a very restricted area from Die Walle, just west of Cape Agulhas, to Koppie Alleen, De Hoop (22-24) although Stegenga et al. (1997) reported that a few plants were found at Platboom on the Cape Peninsula.
World distribution: Also reported from the Canary Islands and Mauritania (Guiry & Guiry 2012).
Type locality: Die Walle, South Africa (Simons 1970).
Note: This species may be better placed in Cystoseira, on morphological grounds (Womersley 1987) and in terms of its chemistry (Laird & van Altena, 2006).
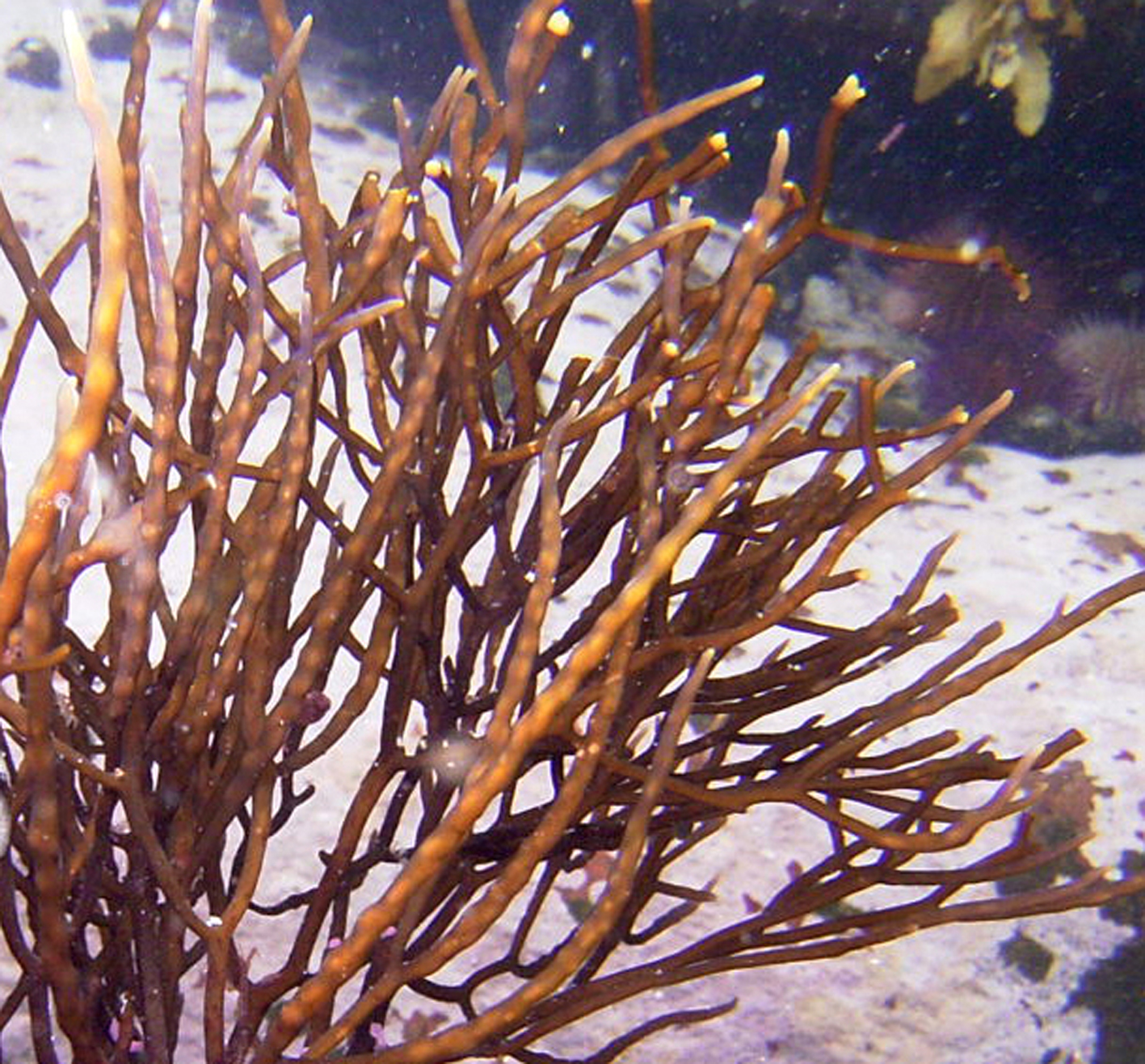

Cystophora fibrosa, Arniston, showing fertile receptacles.
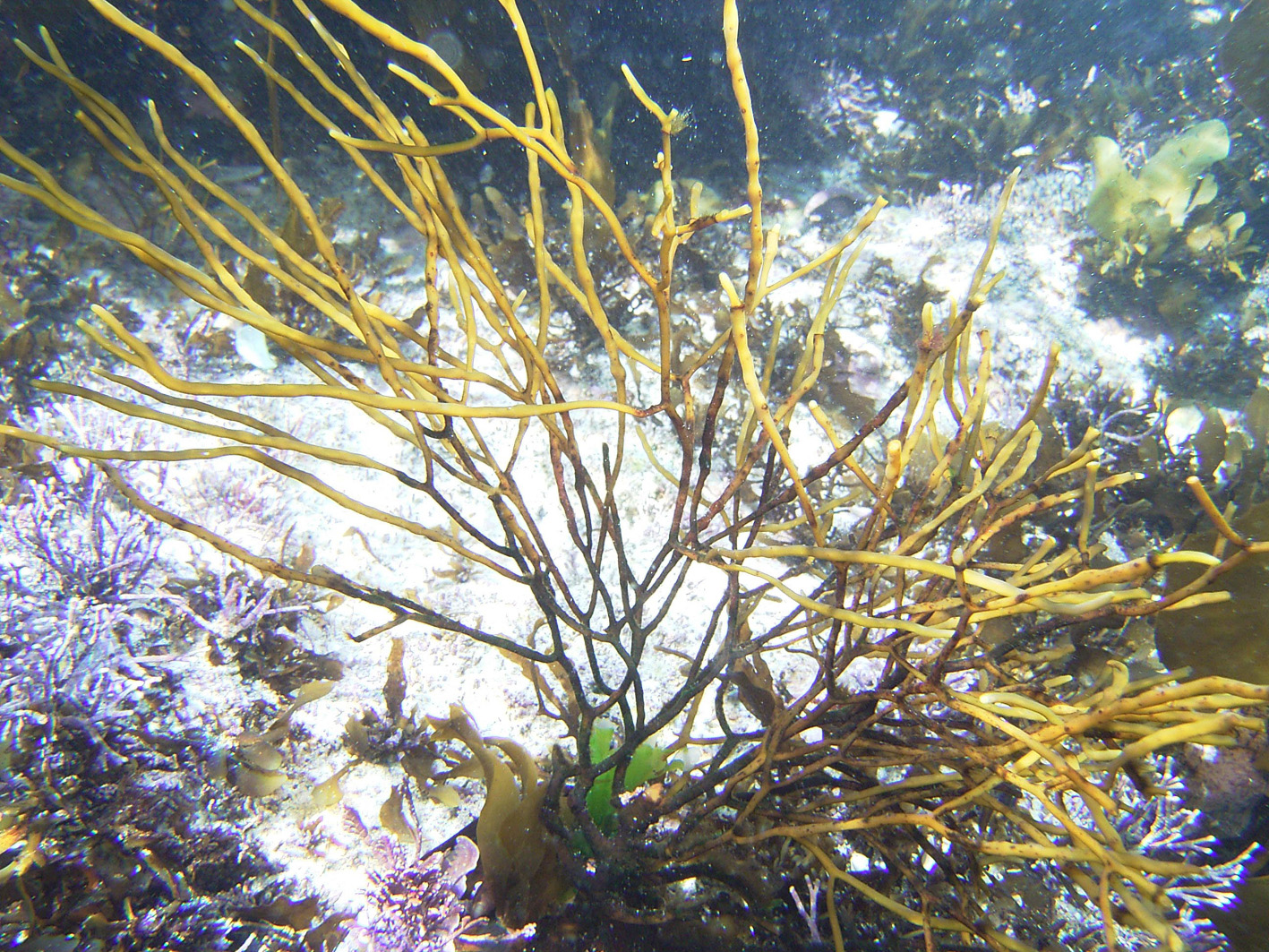

Cystophora fibrosa, De Hoop rock pool.
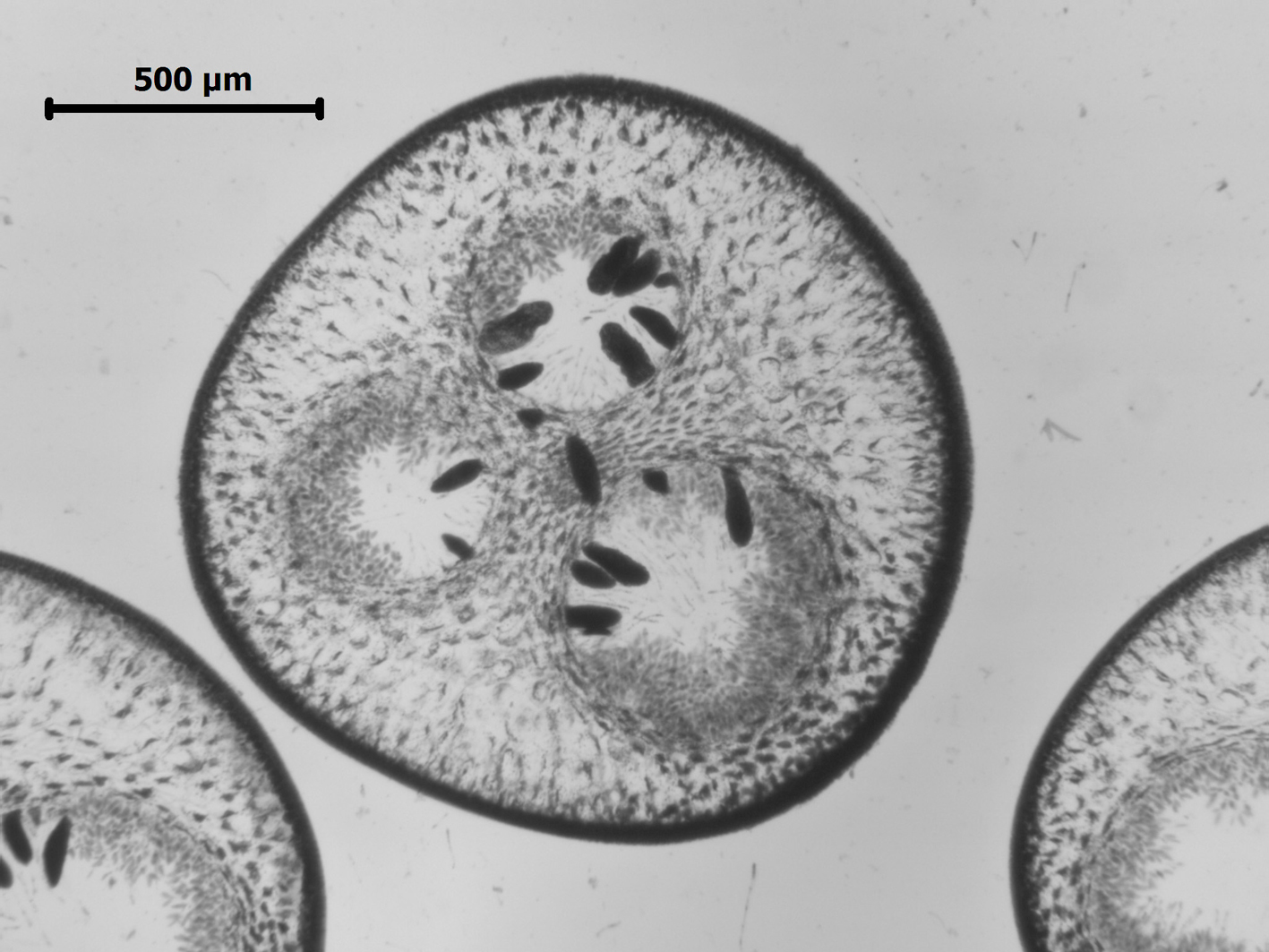
Cystophora fibrosa, XS of receptacles, showing three conceptacles.
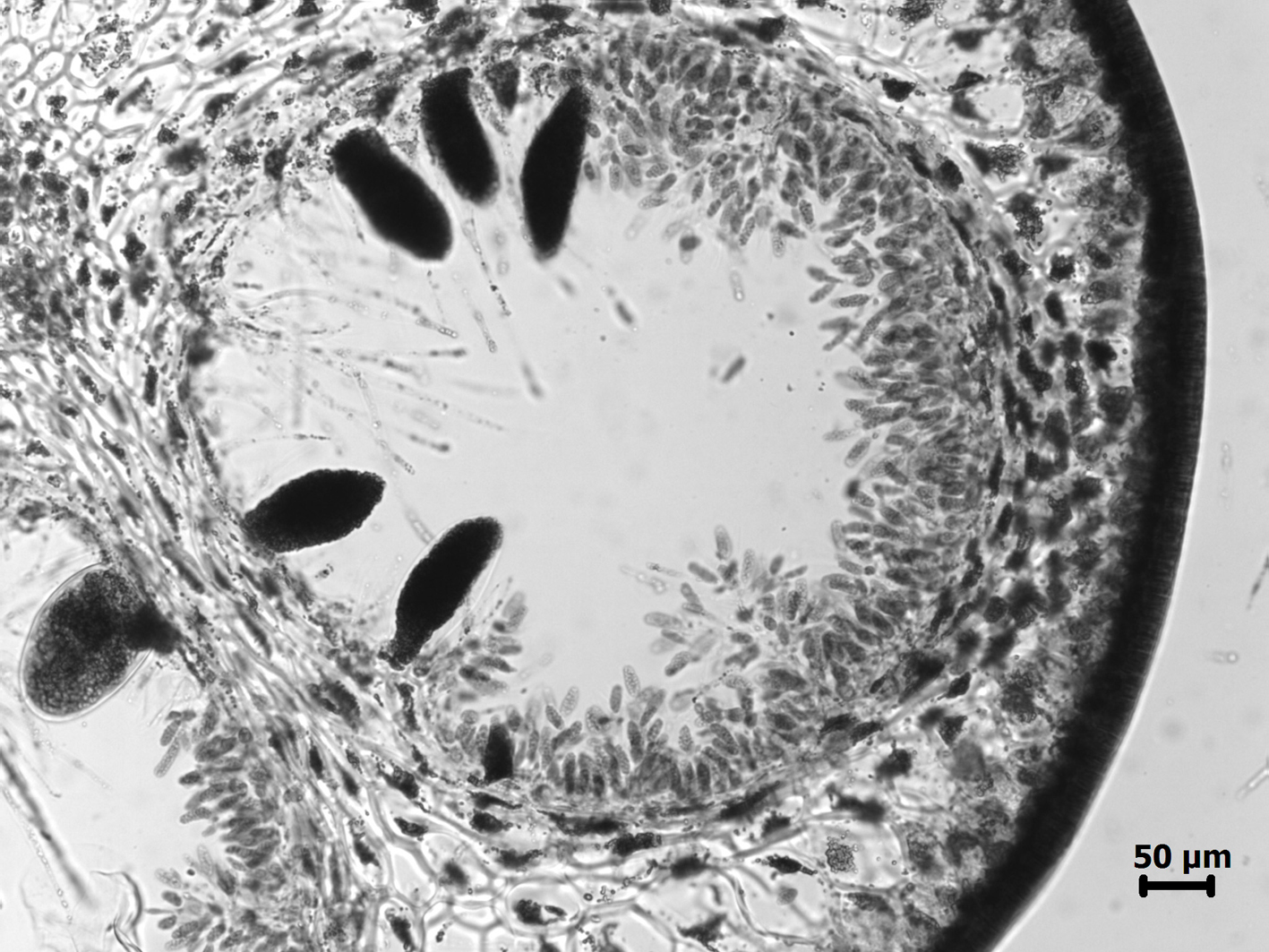
Cystophora fibrosa, XS of a receptacle, showing oogonia and antheridiophores.
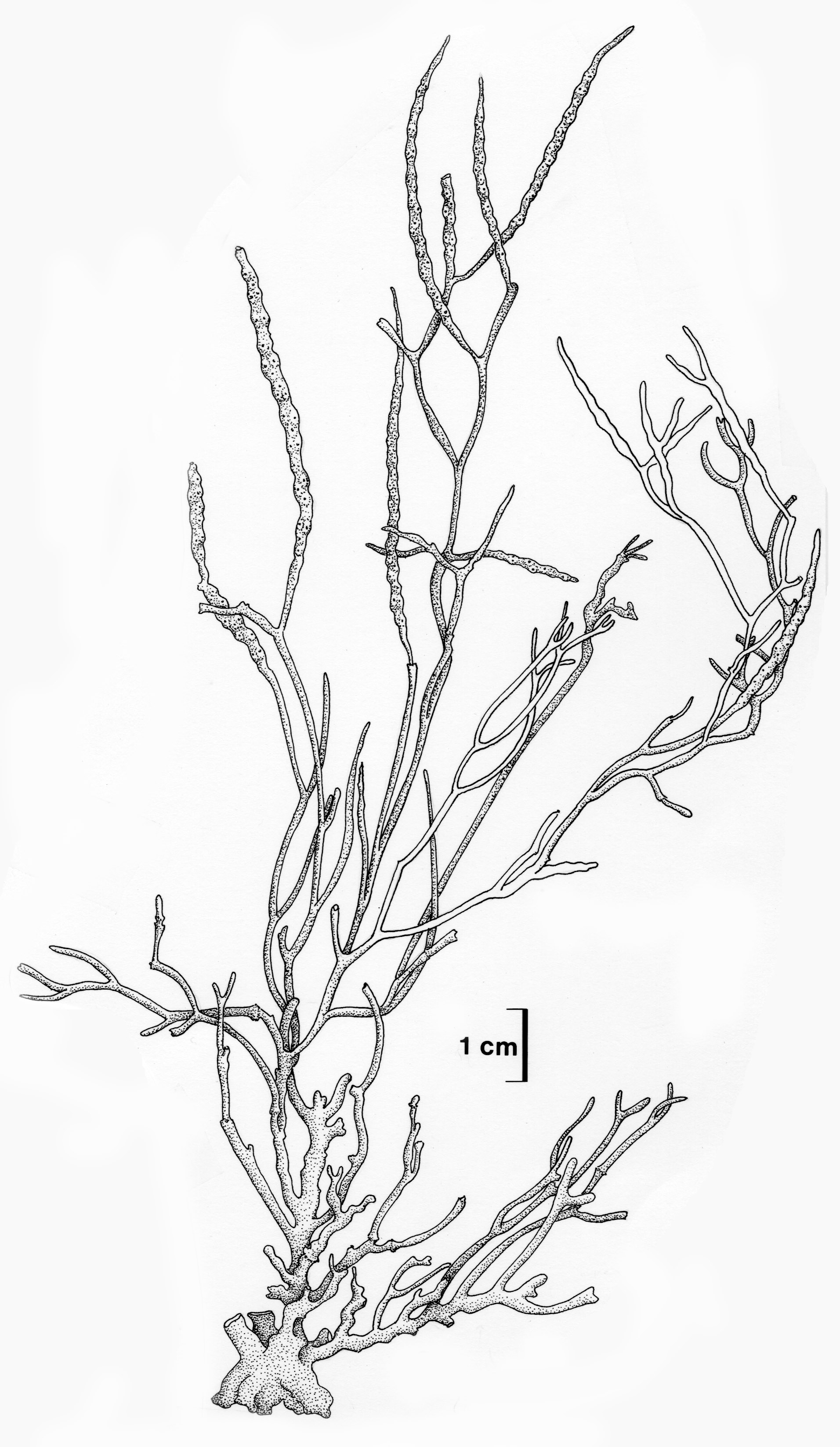
Cystophora fibrosa, habit of fertile plant. Reproduced from Stegenga et al. (1997).
References Cystophora
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. 2012. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched February 2012.
Laird, D.W. & van Altena I.A. (2006). Tetraprenyltoluquinols from the brown alga Cystophora fibrosa. Phytochemistry 67: 944-955.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. (1996). Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Simons, R.H. (1970). Marine algae from southern Africa. 1. Six new species from the inter- and infra-tidal zones. Republic of South Africa, Department of Industries, Division of Sea Fisheries Investigational Report 88: (iii +) 13, 11 figs.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. and R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Womersley, H.B.S. (1987). The marine benthic flora of southern Australia. Part II. pp. 481, 169 figs, 1 table, 8 plates, 4 maps. Adelaide: South Australian Government Printing Division.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 09 March 2026.