Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Ectocarpales
Family Acinetosporaceae
Feldmannia globifera (Kützing) G.Hamel 1939: 67
Plants brown, 0.5 – 2 cm long, usually epiphytic, filamentous, uniseriate, irregularly branched close to the base; attached by entangled rhizoids. Filaments 25-50 (60) µm in diameter, cells 1-3 (-4) times as long as broad; filaments mainly of uniform diameter but gradually tapering distally. Meristematic zone of short cells at the base of each filament. Cells with numerous discoid plastids each with one pyrenoid. Plurilocular sporangia borne on 1-3 celled pedicels, rarely sessile; globular to ovoid with rounded apex, 60-100 µm long x 50-80 µm in diameter. Unilocular sporangia rarely seen; in same position as plurilocular sporangia, ovoid, sessile (35-60 µm diameter).
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Recorded from Tsitsikamma to Kenton-on –Sea (31-39). Epiphytic on larger algae such as Codium spp.
World distribution: Widespread in temperate regions (Guiry & Guiry 2011).
Type locality: Yugoslavia (Womersley 1987).
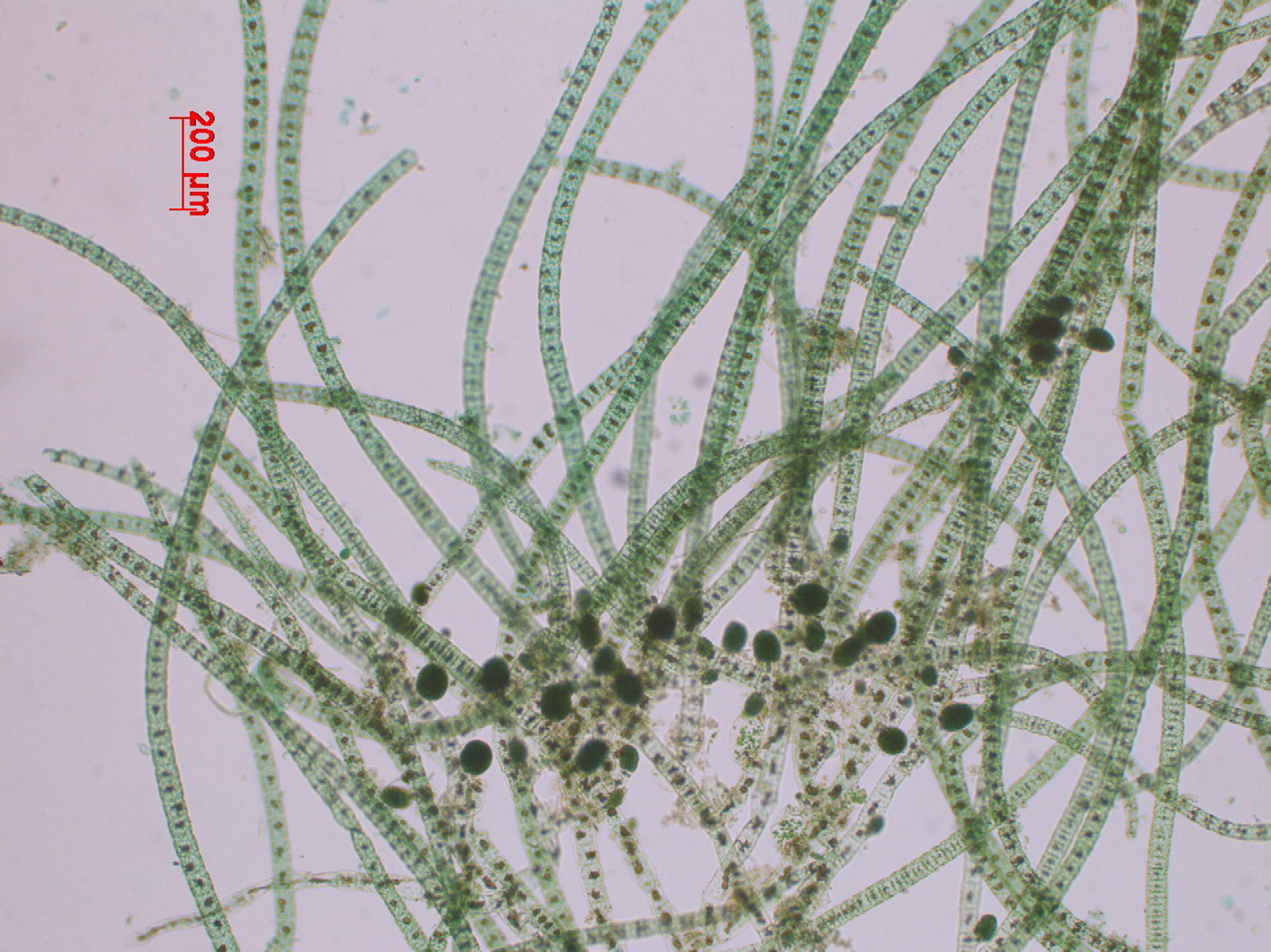
Feldmannia globifera, Tsitsikamma, sporangia near bases of filaments (stained slide material).
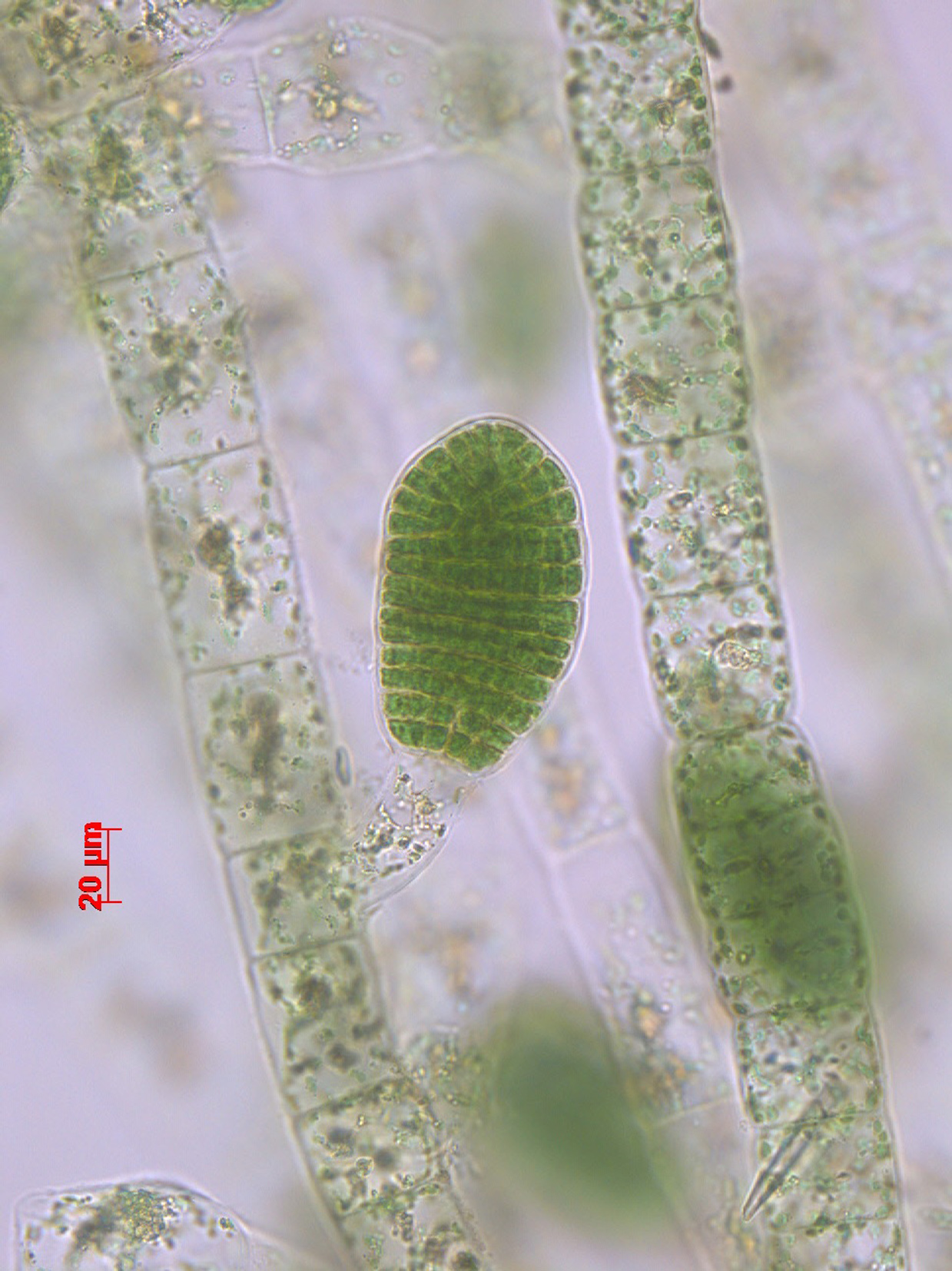

Feldmannia globifera, Tsitsikamma, plurilocular sporangium with pedicel (stained slide material).
References Feldmannia globifera
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. 2011. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched May 2011.
Hamel, G. (1939). Sur la classification des Ectocarpales. Botaniska Notiser 1939: 65-70.
Womersley, H.B.S. (1987). The marine benthic flora of southern Australia. Part II. pp. 481, 169 figs, 1 table, 8 plates, 4 maps. Adelaide: South Australian Government Printing Division.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 11 March 2026.