Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Ectocarpales
Family Acinetosporaceae
Feldmannia irregularis (Kützing) G.Hamel 1939: XVII
Plants 0.5 to 6 cm long, sparsely branched, more so basally, with many erect axes arising from an entangled prostrate system. Filaments ca. 25 µm in diameter towards the base, tapering gradually towards the apex. Cells with numerous discoid plastids. Meristematic regions basal, with cells 0.5 – 1.0 times as long as broad; distally cells ca. 15 µm in diameter and commonly 2-3 times as long as broad. Lateral branches mostly short, often with meristematic zones near their bases. Plurilocular sporangia sessile, sometimes in secund series, cylindroconical, to 180 µm long x 40 µm in diameter. Unilocular sporangia not observed.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Mainly epiphytic on Codium spp. Recorded from Langebaan Lagoon on the west coast , then from False Bay along the entire south coast and coast of Kwazulu-Natal (17 – 58).
World distribution: Widespread on tropical and temperate coasts all over the world, including Namibia and Mozambique (Guiry & Guiry 2011).
Type locality: Adriatic Sea (Silva et al. 1996).
Note: According to Womersley (1987) this species shows characters somewhat intermediate between Feldmannia and Hincksia.
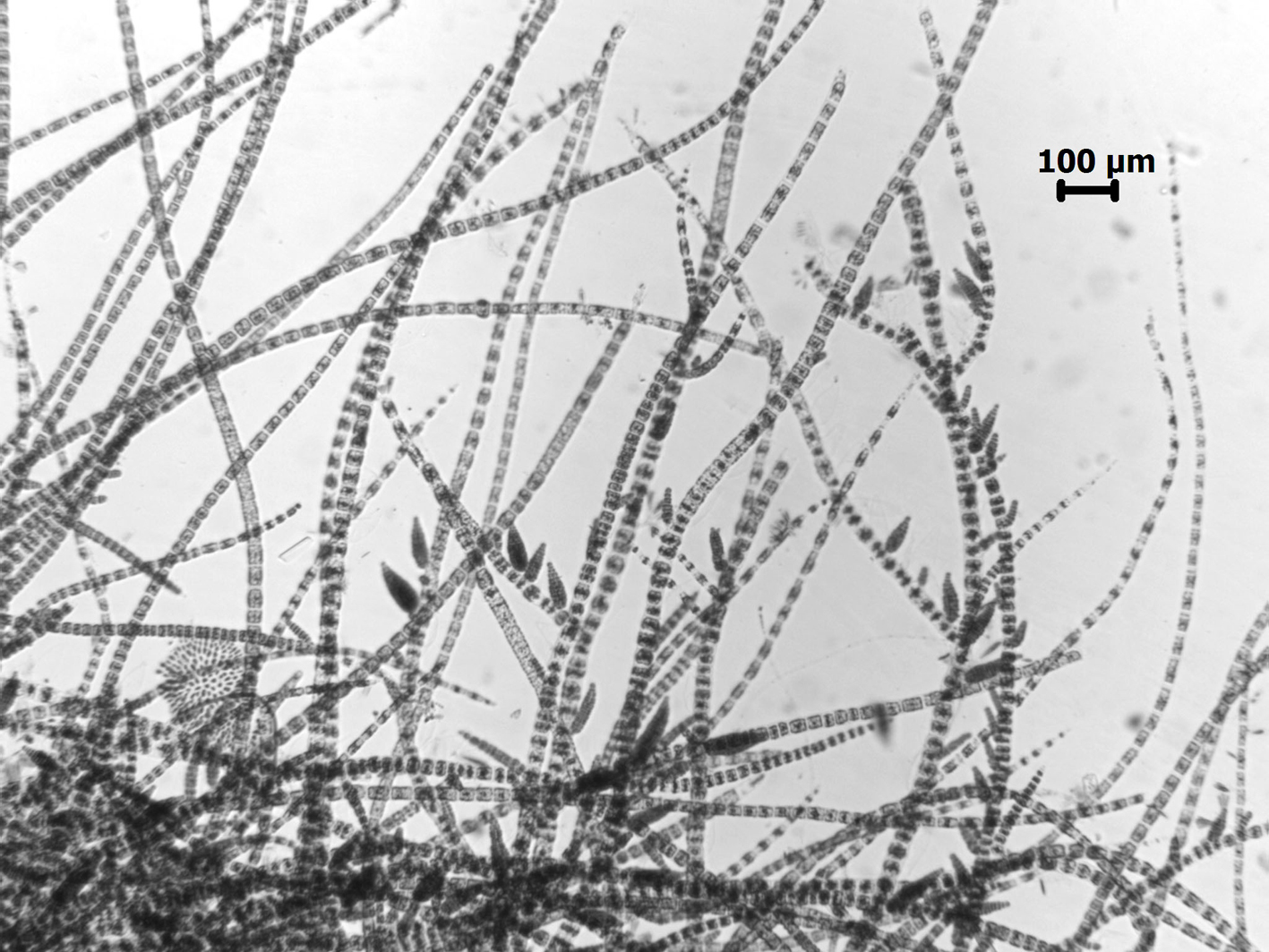

Feldmannia irregularis, with plurilocular sporangia.
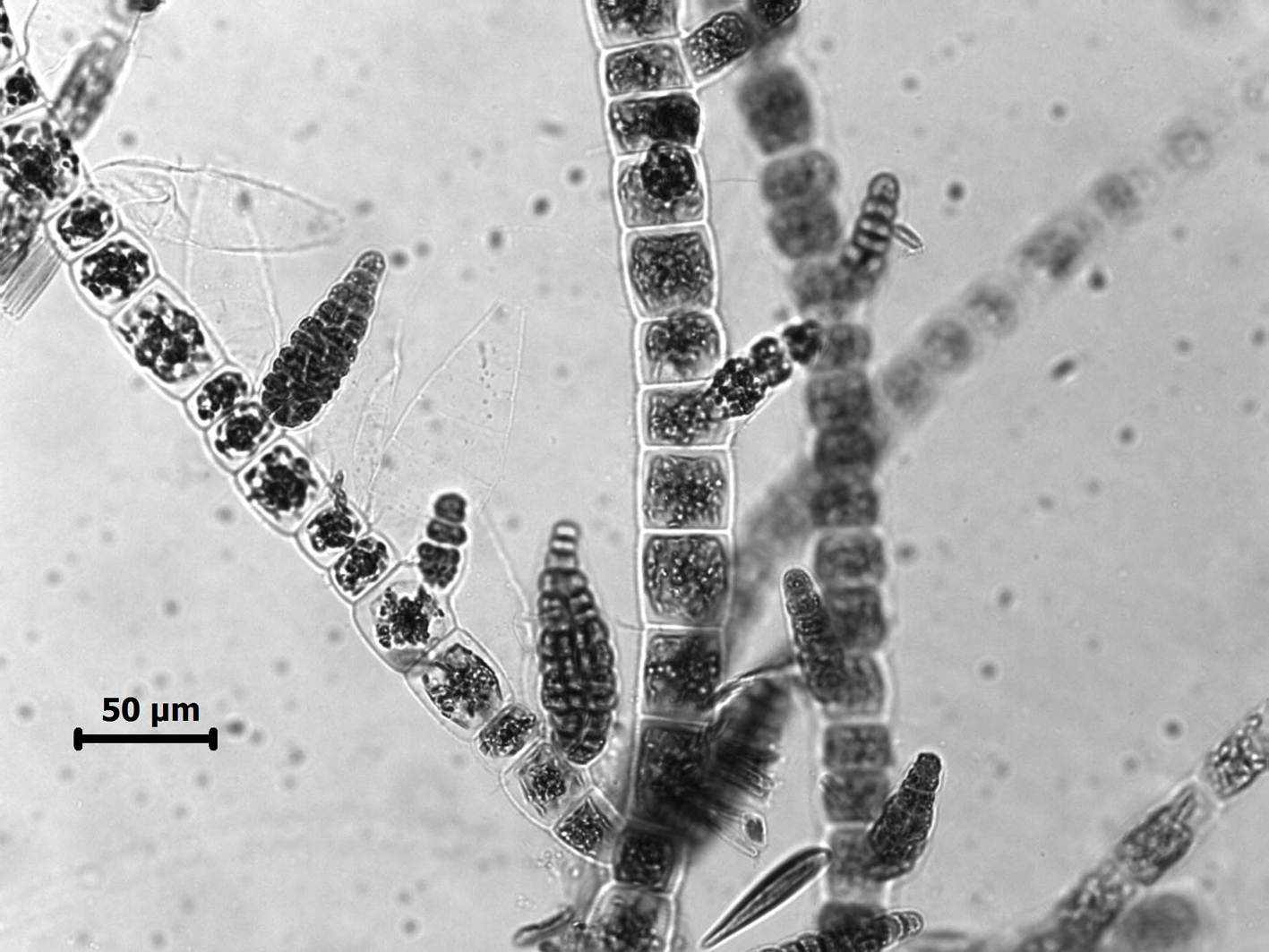

Feldmannia irregularis, conical plurilocular sporangia.
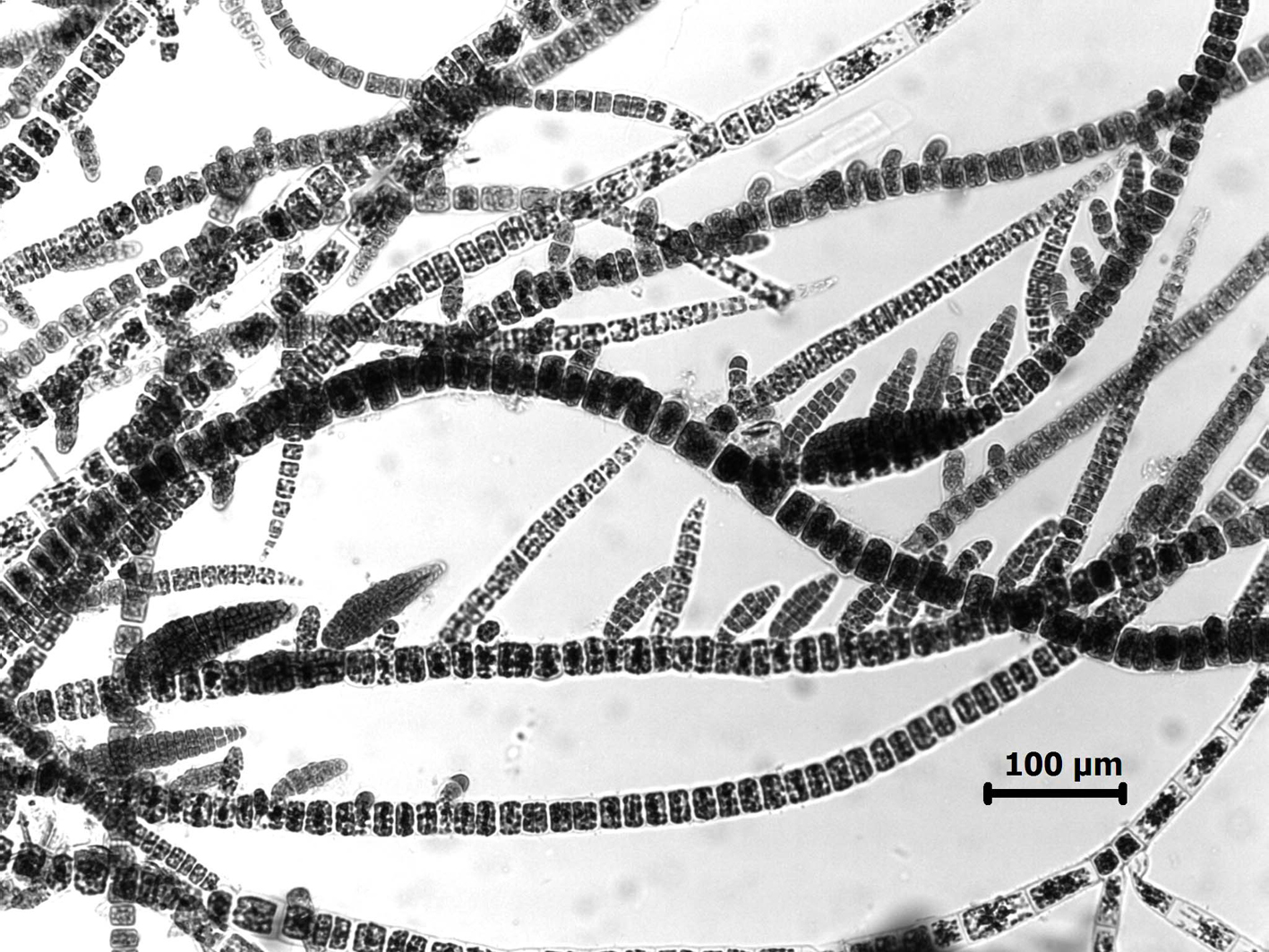
Feldmannia irregularis, with secund plurilocular sporangia.
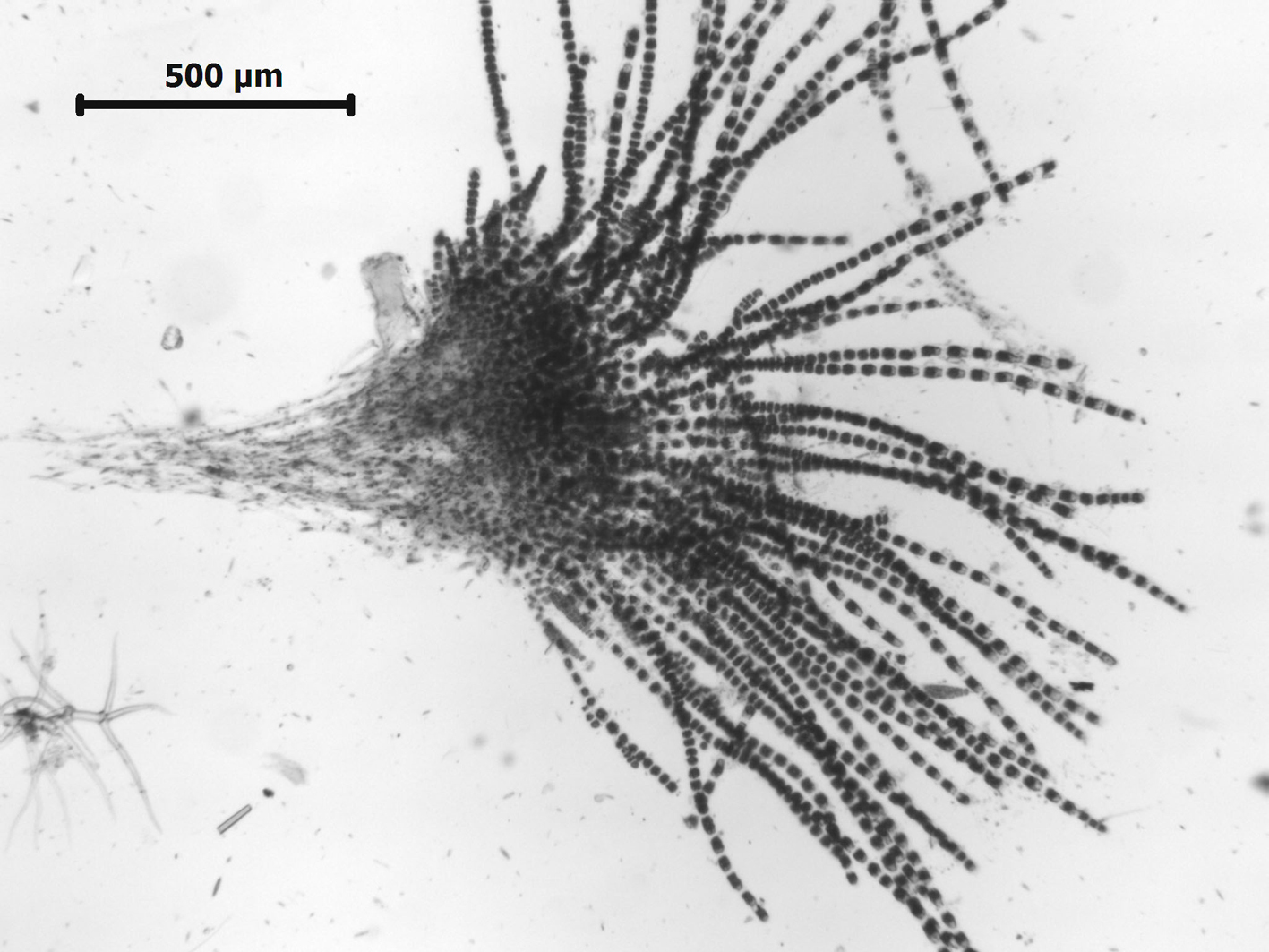
Feldmannia irregularis, whole thalli with rhizoidal mass on left.
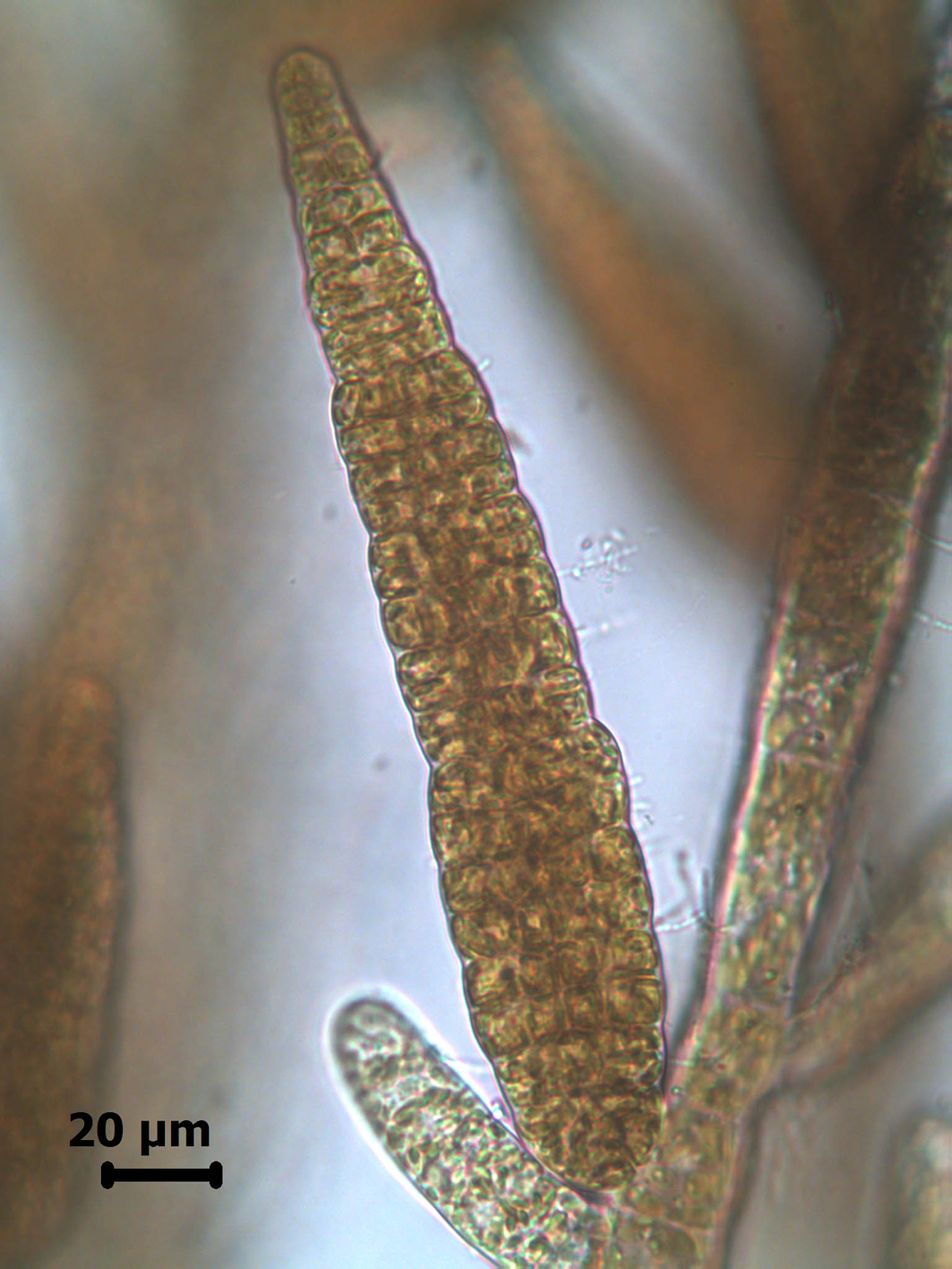

Feldmannia irregularis, a conical plurilocular sporangium (fresh material, Tsitsikamma).
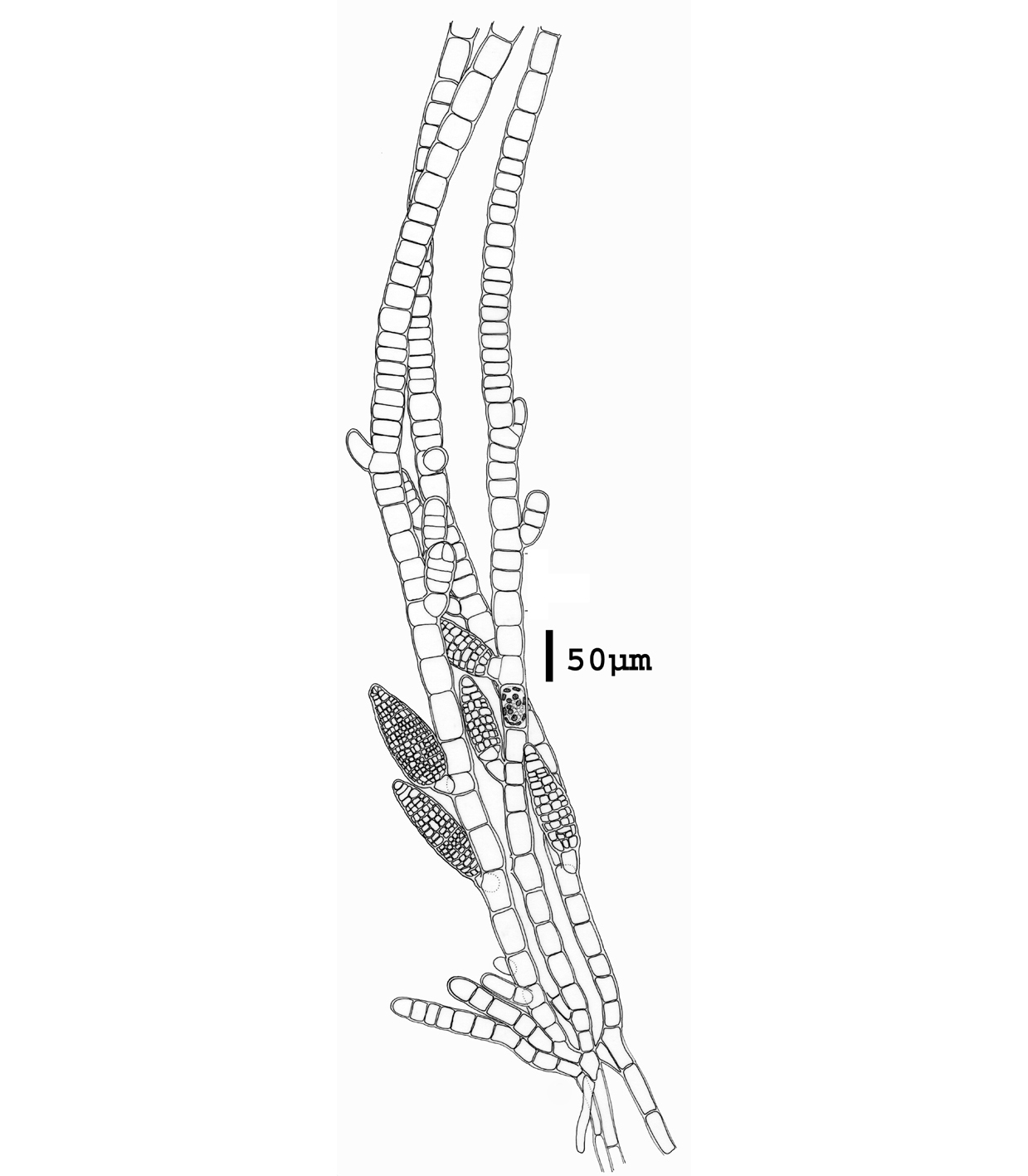
Feldmannia irregularis, detail of thallus showing meristematic zone, endophytic filaments and plurilocular sporangia (reproduced from Stegenga et al. 1997).
References Feldmannia irregularis
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. 2011. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched May 2011.
Hamel, G. (1939). Sur la classification des Ectocarpales. Botaniska Notiser 1939: 65-70.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. and R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Womersley, H.B.S. (1987). The marine benthic flora of southern Australia. Part II. pp. 481, 169 figs, 1 table, 8 plates, 4 maps. Adelaide: South Australian Government Printing Division.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 11 March 2026.