Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Ectocarpales
Family Acinetosporaceae
Hincksia mitchelliae (Harvey) P.C.Silva in P.C. Silva, Meñez & Moe 1987: 73, 130
Plants brown, epilithic or epiphytic, 0.5 – 4 (-10) cm long, uniseriate, filamentous, attached by entangled mass of rhizoids. Erect axes profusely branched , branching irregular to unilateral (secund) in distal regions. Filaments tapering gradually, cells in lower parts 30-60 µm in diameter and 1-2 times as long as broad, ultimate branches 20-60 µm in diameter , cells 4-6 times as long as broad. Meristematic regions scattered on main filaments and at bases of branches, scattered intercalary divisions sometimes present. Cells with many discoid plastids each with one pyrenoid. Plurilocular sporangia straight, sub-cylindrical, with rounded tapering ends; scattered but often unilateral/adaxial, sessile, 50-140 µm long x 20-40 µm in diameter. Sporangia often ripening in basipetal sequence. Unilocular sporangia not seen (reported in Australian specimens as ovoid and in similar positions to plurilocular sporangia).
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Recorded from De Hoop to northern Kwazulu-Natal (24-58). Specimens from Mkambati on Anthophycus longifolius, and from the Kowie on Codium tenue (all bearing plurilocular sporangia).
World distribution: widespread in temperate and tropical seas (Guiry & Guiry Sept 2011).
Type locality: Massachusetts, U.S.A. (Silva et al. 1996).
Note: This taxon is cited by Kim (2010) as belonging to the genus Feldmannia and cited by Guiry & Guiry (2017) as Feldmannia mitchelliae (Harvey) H.-S.Kim.
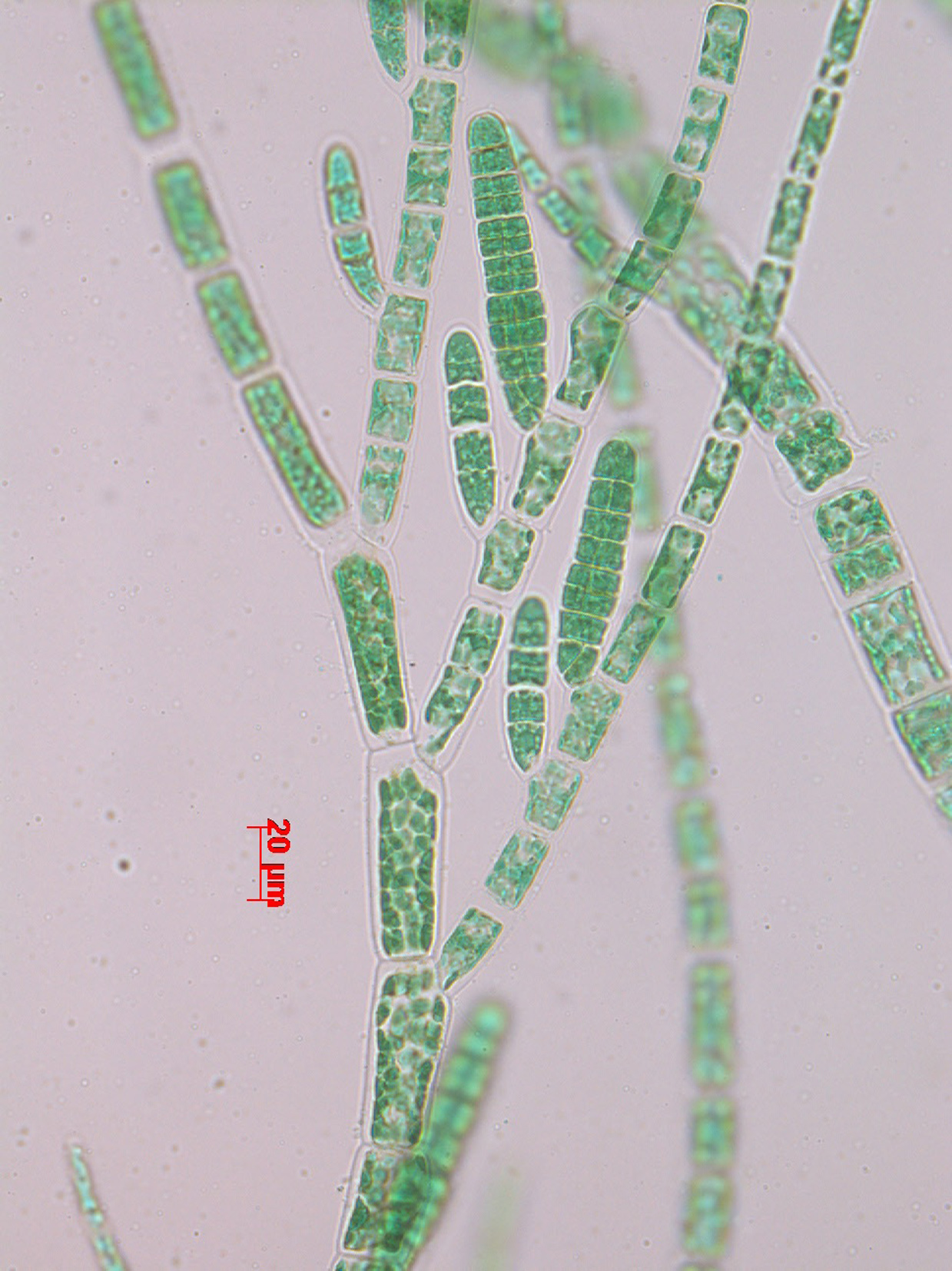
Hincksia mitchelliae, Mkambati, on Anthophycus longifolius (stained slide material).
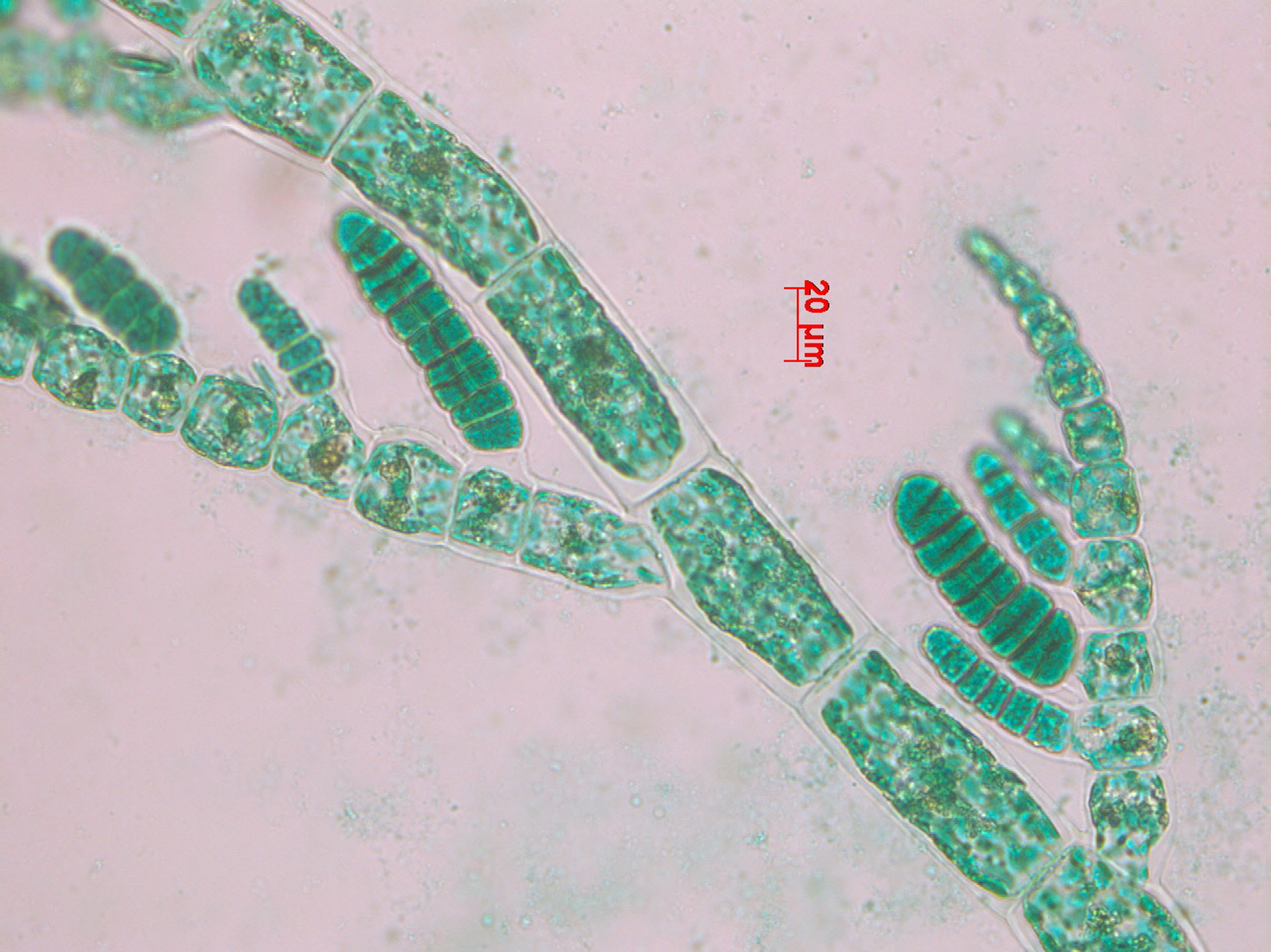
Hincksia mitchelliae, Mkambati, showing subcylindrical plurilocular sporangia (stained slide material).
References Hincksia mitchelliae
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. 2011. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched September 2011.
Guiry, M. D. in Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. 2017. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched on 13 October 2017.
Kim, H.-S. 2010. Ectocarpaceae, Acinetosporaceae, Chordariaceae. In: Algal flora of Korea. Volume 2, Number 1. Heterokontophyta: Phaeophyceae: Ectocarpales. Marine brown algae I. (Kim, H.-S. & Boo, S.-M. Eds), pp. [3]-137. Incheon: National Institute of Biological Resources.
Silva, P.C., Meñez, E.G. & Moe, R.L. (1987). Catalog of the benthic marine algae of the Philippines. Smithsonian Contributions to Marine Sciences 27: [i-ii] iii-iv, 1-179, 2 figs, 1 table.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. (1996). Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 09 March 2026.