Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Ectocarpales
Family Chordariaceae
Leathesia marina (Lyngbye) Decaisne 1842: 370
Plants yellow-brown, globose, convoluted, slippery, a few to ca. 8 cm in diameter; firm becoming hollow. Thallus largely of a medulla of large cells forming a branched network. Outer medullary cells ca. 80-130 µm long. Thin cortex of assimilatory filaments 3-4 µm in diameter and a few cells long, with enlarged terminal cell up to ca. 10 µm in diameter. Plurilocular sporangia branching laterally from cell at base of assimilatory filament, generally in groups of 3-5, uniseriate, ca. 3-5 µm in diameter and 30-35 µm long, with 10-12 locules. Unilocular sporangia unknown in South African material.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Recorded along the west coast, south coast and into Kwazulu-Natal as far as Mission Rocks. Epilithic or epiphytic in the eulittoral zone (1-56).
World distribution: Widely distributed in temperate seas, including coast of Namibia (M.D. Guiry in Guiry & Guiry 2014).
Type locality: (“in Confervis maris occidentalis” (Silva et al. 1996).
Note: Superficially very similar to Colpomenia sinuosa, but the latter is much less firm and has a cortex that is obviously parenchymatous. Previously known as Leathesia difformis, but renamed for reasons of nomenclatural priority (MD Guiry in Guiry & Guiry 2014).
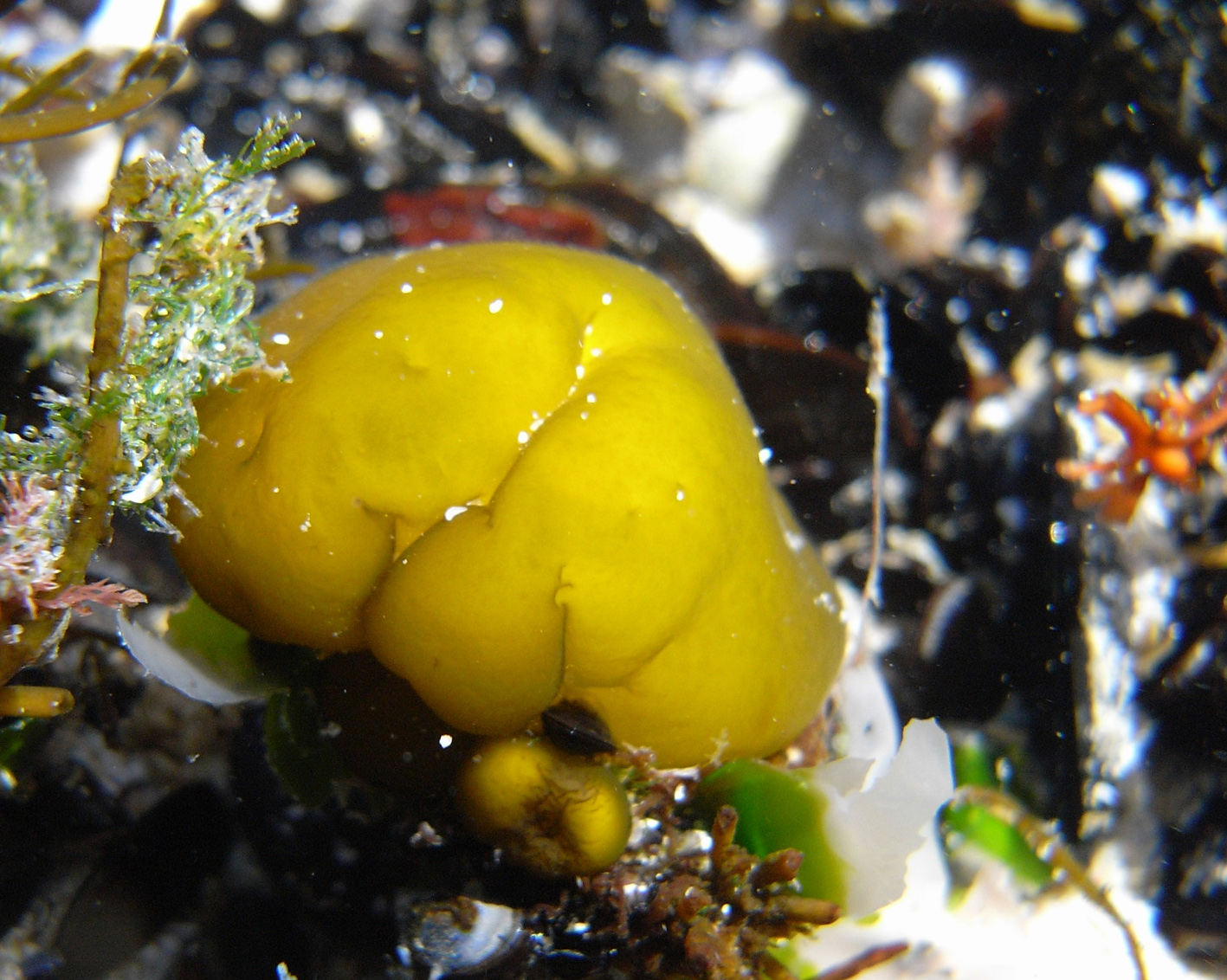

Leathesia marina in rock pool.
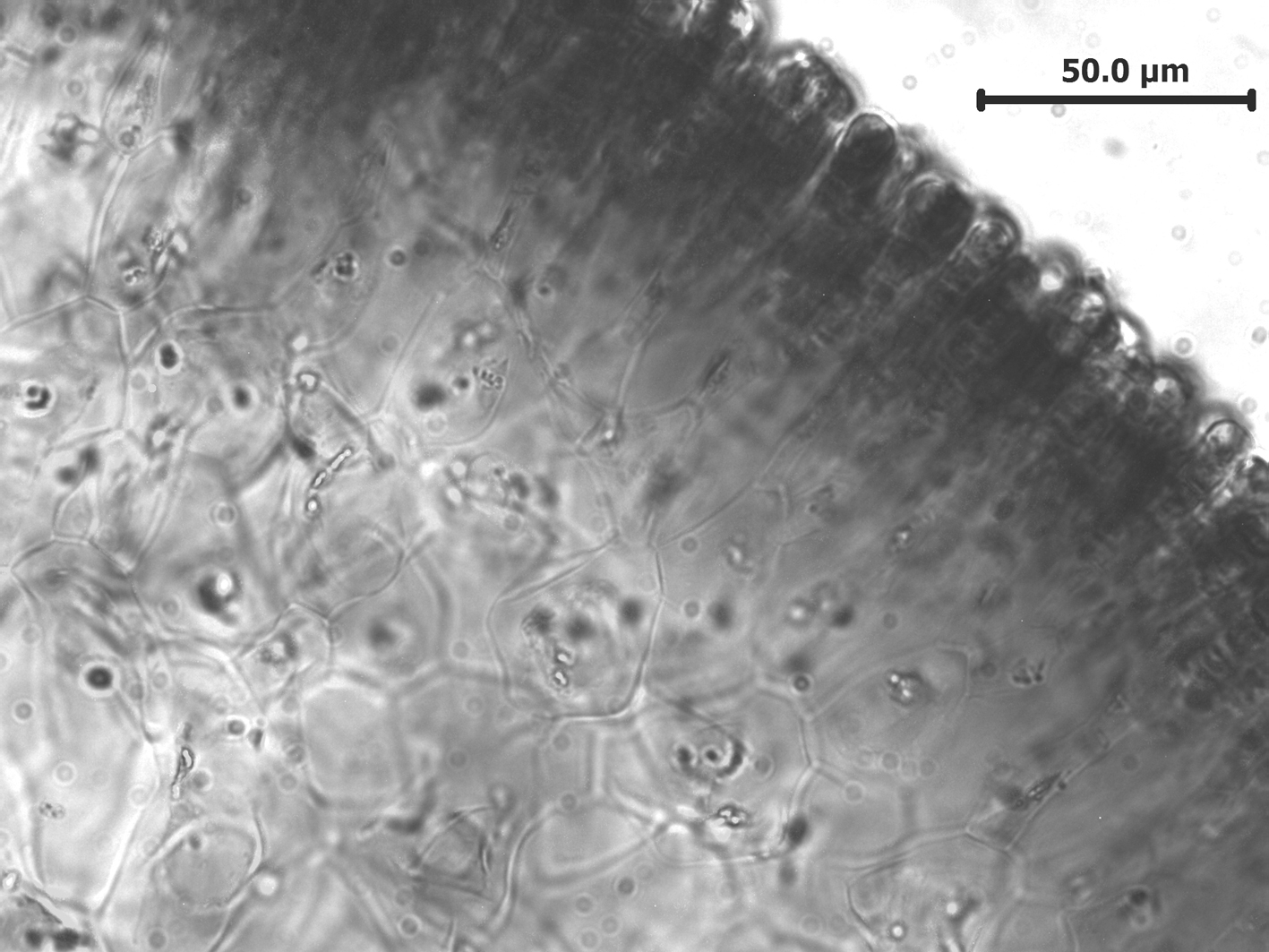
Leathesia marina, xs showing filamentous cortex underlain by medulla.
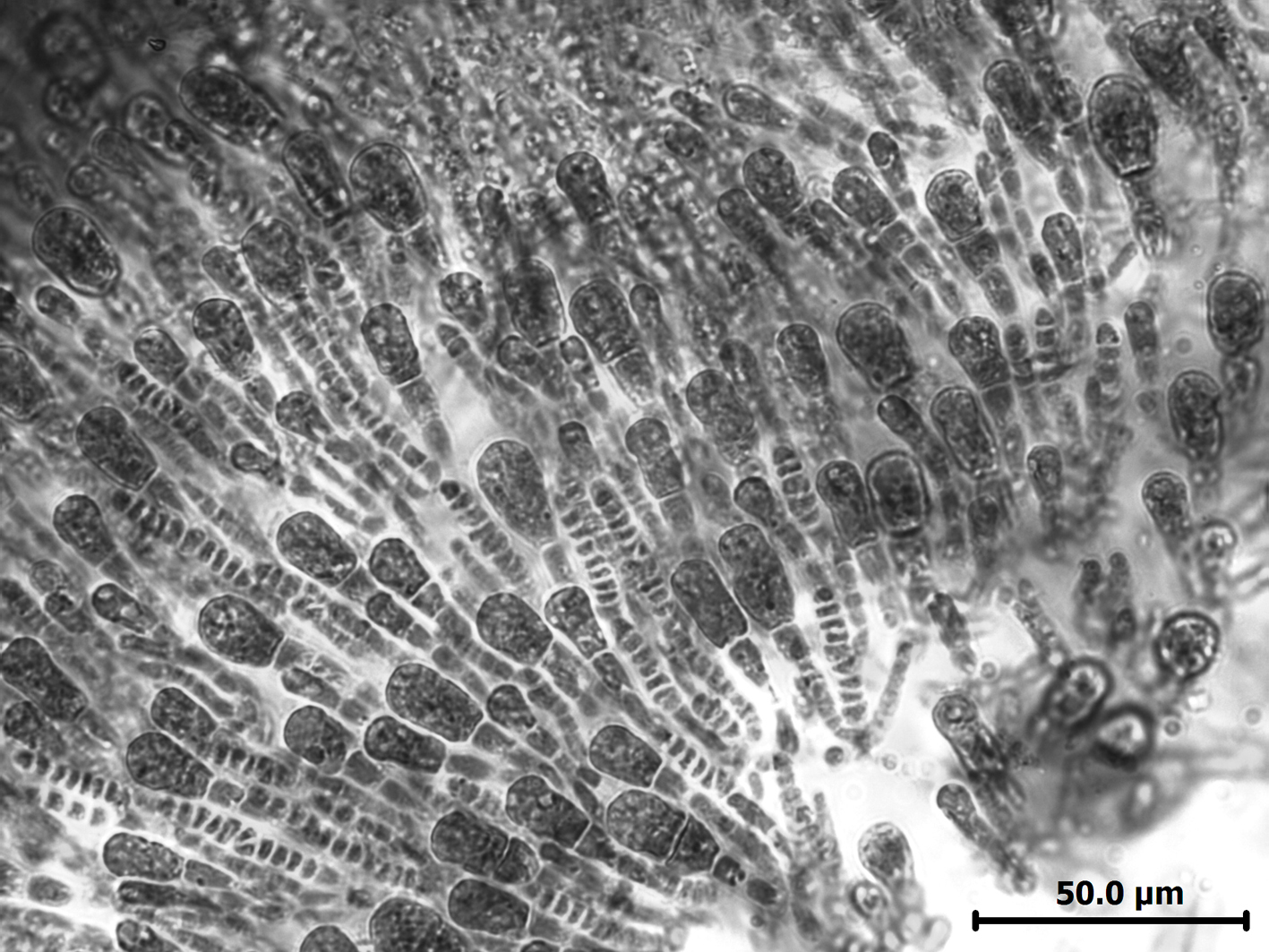
Leathesia marina, squash preparation of cortical filaments.
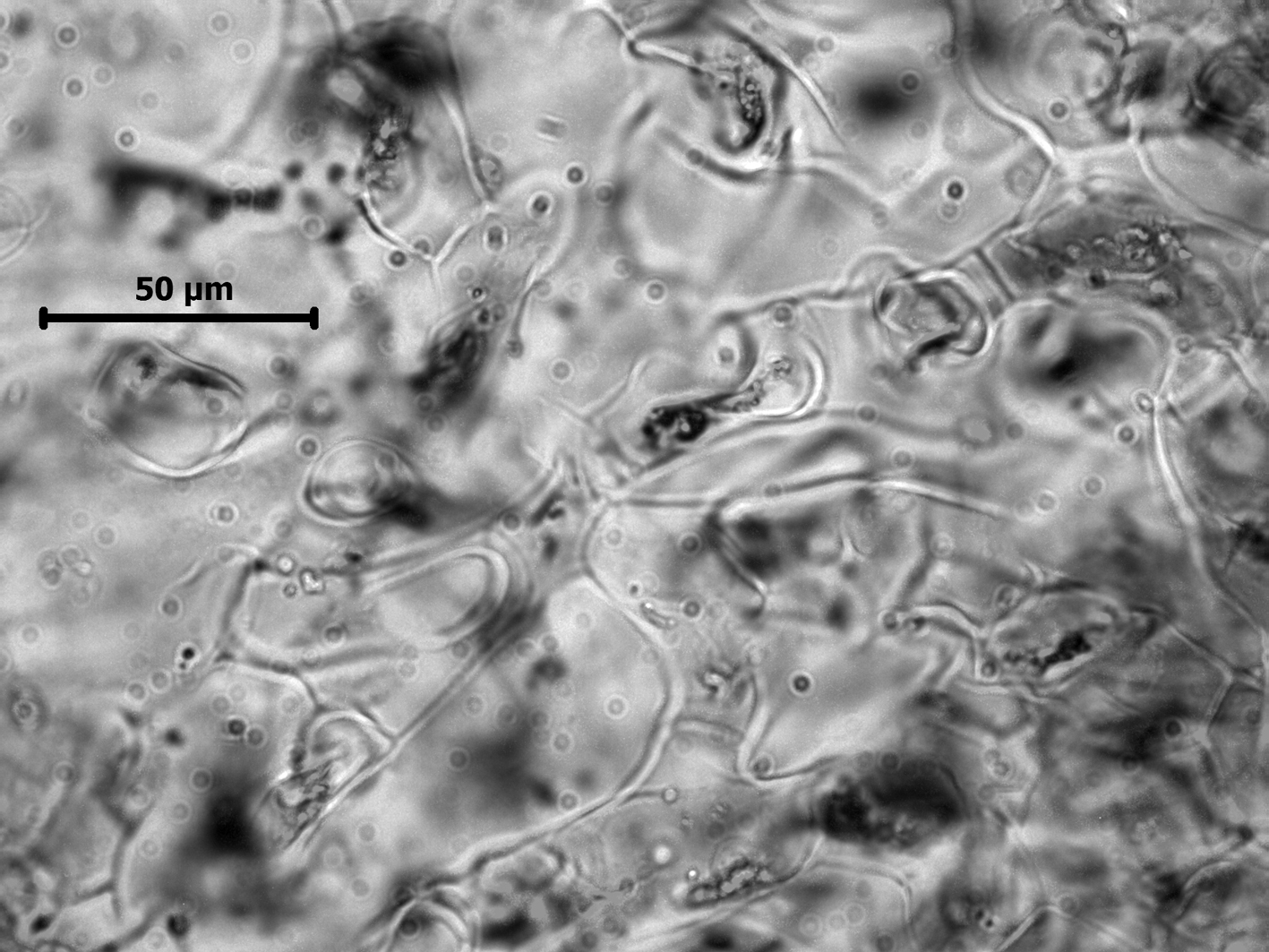
Leathesia marina, branched network of medullary cells
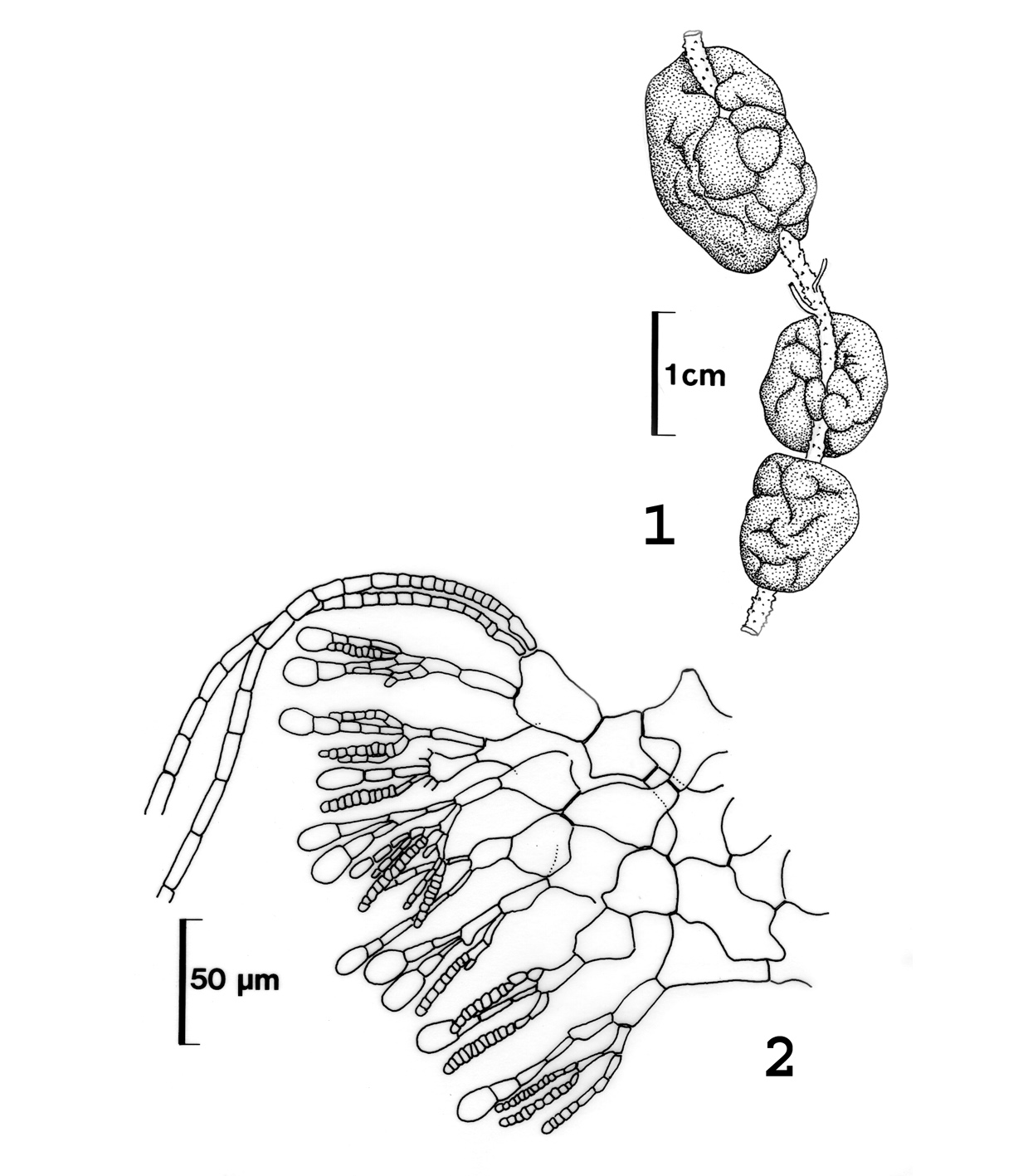
Leathesia marina. 1. Habit, on Chordariopsis capensis. 2. Section, with plurilocular sporangia (reproduced from Stegenga et al. 1997).
References Leathesia
Decaisne, J. (1842). Essais sur une classification des algues et des polypiers calcifères de Lamouroux. Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Botanique, Seconde série 17: 297-380, pls 14-17.
M.D. Guiry in Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. 2014. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched on 09 September 2014.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. (1996). Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. and R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 09 March 2026.