Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Ectocarpales
Family Chordariaceae
Leptonematella fasciculata (Reinke) P.C.Silva 1959: 63
Plants to 2.5 mm long, light brown, comprising dense tufts of erect filaments borne on a disc-like base of branched, radiating filaments; epilithic, epiphytic or epizoic. Erect filaments rather flaccid, uniseriate, simple or branched basally, cells barrel-shaped to square below and 6-8 µm wide, becoming rectangular above, 7-10 (-16) µm wide, 1-3 x as long as broad, each with several discoid plastids; intercalary meristem near base.
Unilocular sporangia not seen in our material. Plurilocular sporangia common, terminal or intercalary, in uniseriate series; extending laterally and becoming broader than vegetative cells, sometimes protruding laterally and to at least 18 µm wide.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Only collected at Tsitsikamma (39). Epiphytic on a Polysiphonia sp.
World distribution: Arctic, cold temperate and temperate localities (Guiry & Guiry 2012).
Note: See Fletcher (1987) for a description of material in the British Isles: Unilocular and plurilocular sporangia reported to occur on the same plants; unilocular sporangia lateral at base of erect filaments, sessile or with 1-several stalk cells, 80-120 µm long.
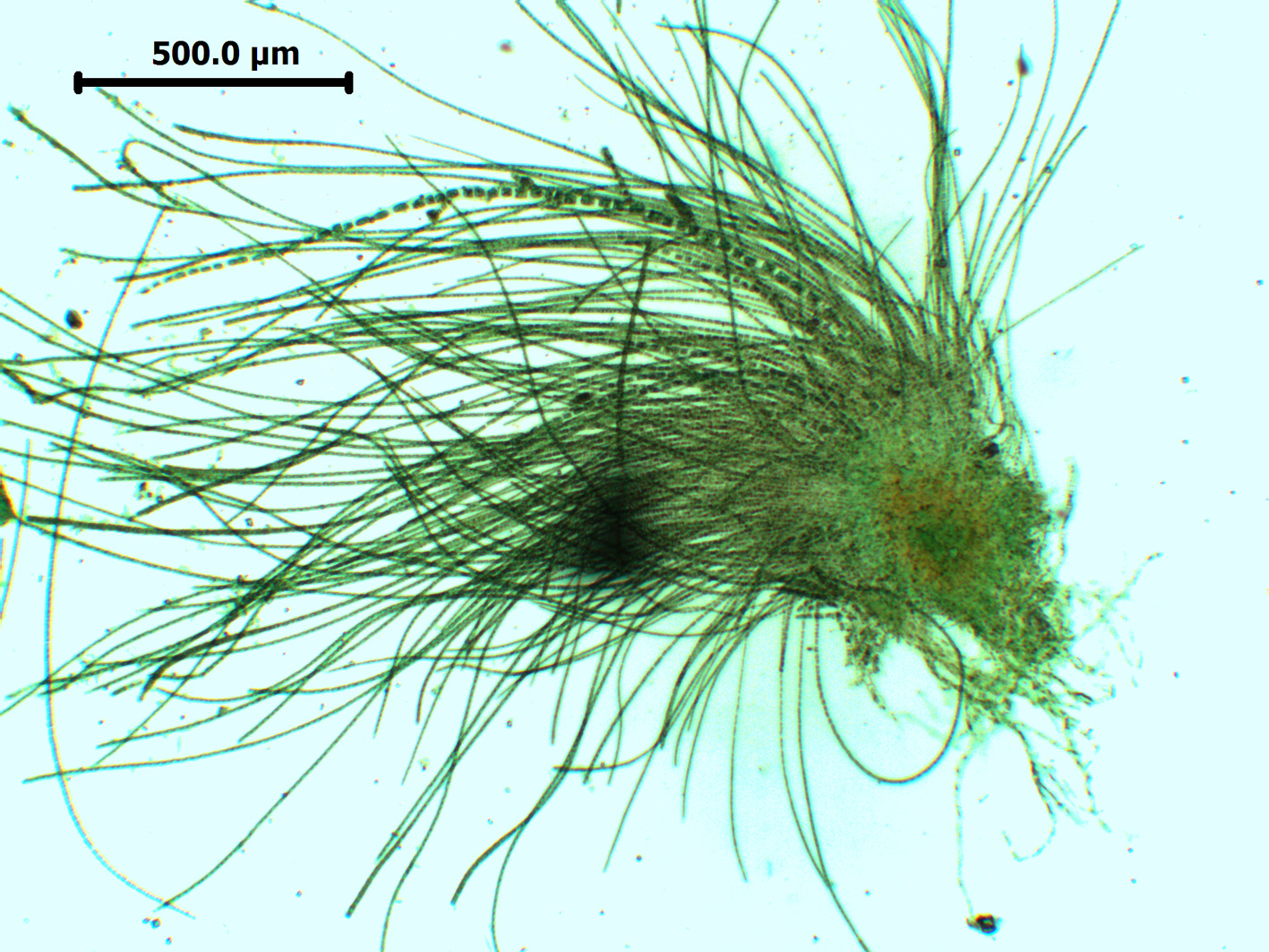

Leptonematella fasciculata, whole thallus, Tsitsikamma (slide specimen).
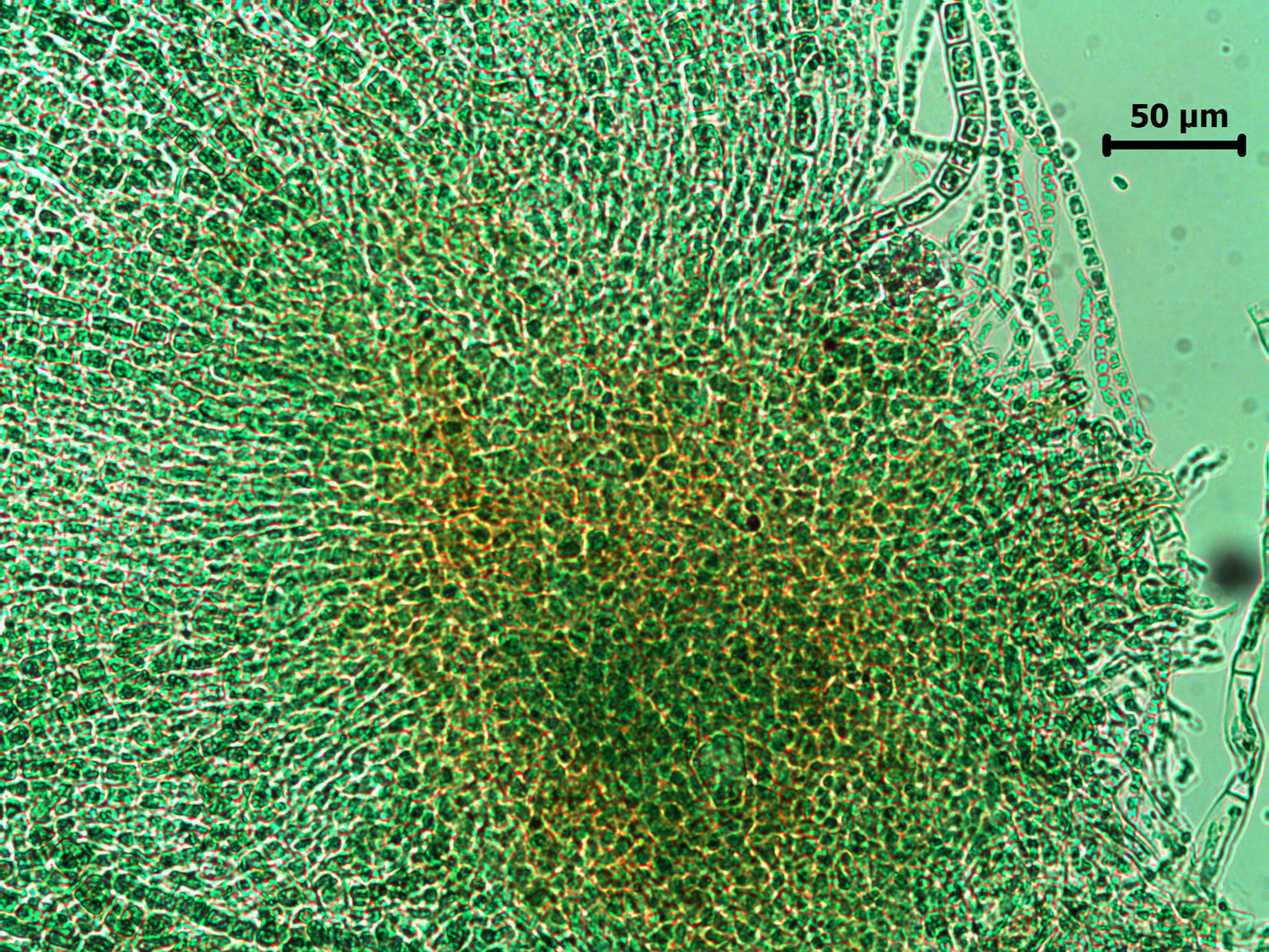
Leptonematella fasciculata, base of thallus, Tsitsikamma (slide specimen).
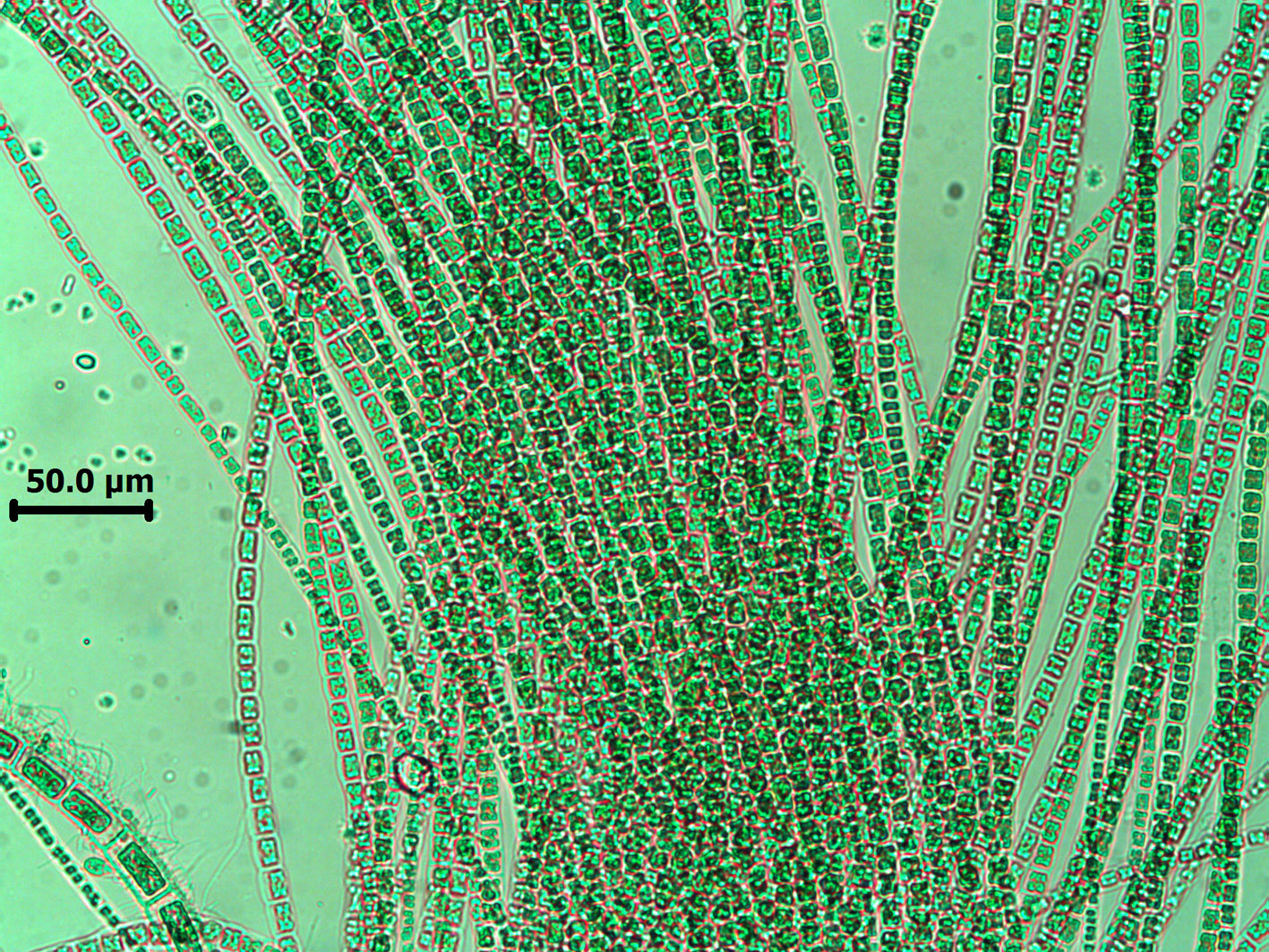
Leptonematella fasciculata, upright filaments, Tsitsikamma (slide specimen).
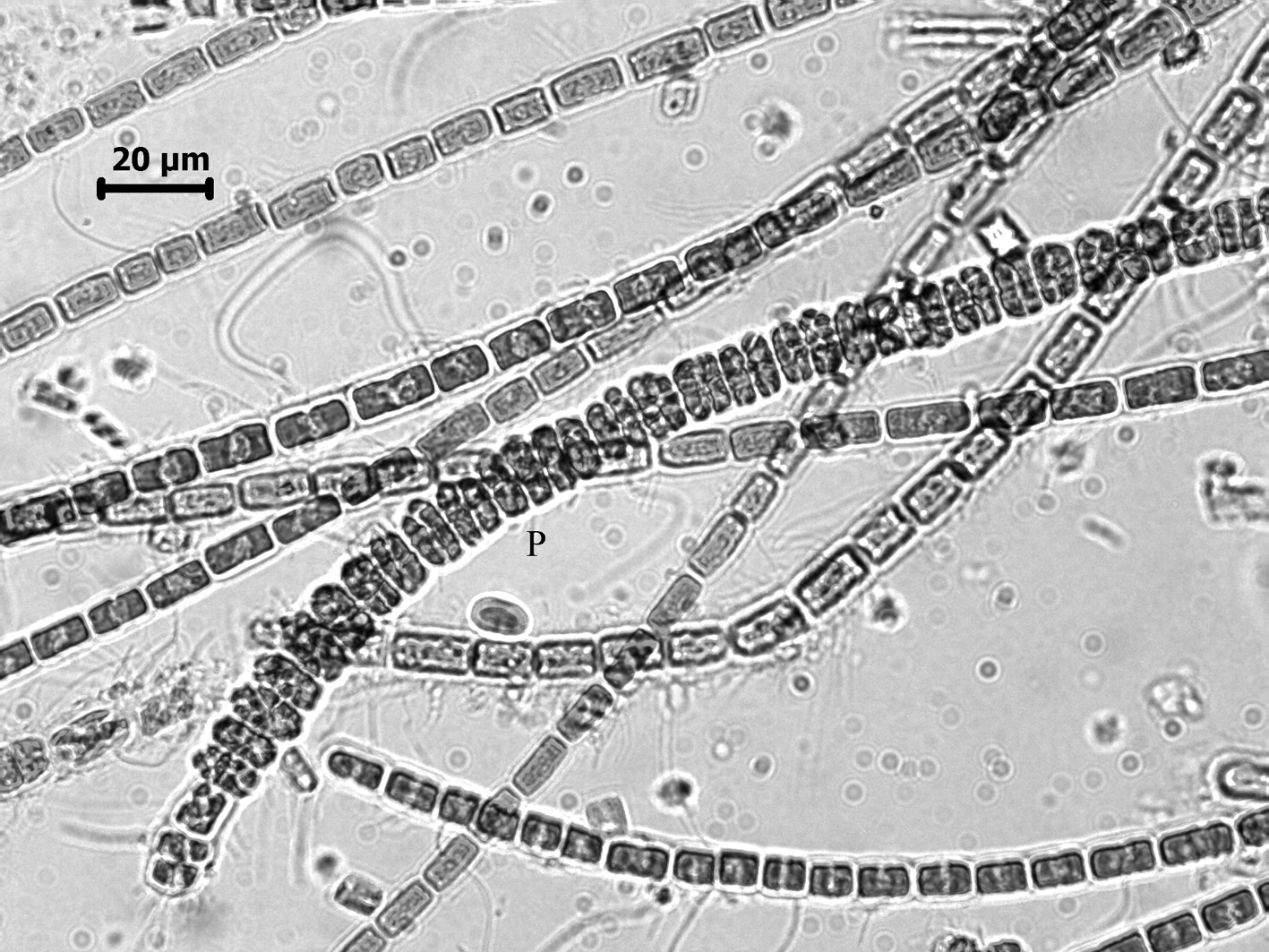
Leptonematella fasciculata, vegetative filaments and plurilocular sporangia.
References Leptonematella
Fletcher, R. L. 1987. Seaweeds of the British Isles. Volume 3. Fucophyceae (Phaeophyceae) Part 1. British Museum (Natural History), London. 359 pp.
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. 2012. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched January 2012.
Silva, P.C. (1959). Remarks on algal nomenclature II. Taxon 8: 60-64.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 09 March 2026.