Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Sphacelariales
Stypocaulaceae
Phloiocaulon suhrii (J.Agardh) P.C.Silva in P.C.Silva, Basson & Moe 1996: 579
Plants dark brown, up to 30 cm tall, with smooth, sparsely branched main axes ca 1mm in diameter bearing uncorticated, translucent determinate laterals ca 3-4 mm long. Laterals regularly alternately branched in one plane, occasionally with second order of branches; all branches of determinate laterals tapering to appoint, main axis of laterals ca 100 µm in diameter at base, primary branches of laterals ca 80 µm at base. Determinate laterals with (probably seasonal) production and loss from perennial axial system. Deciduous hairs in bundles in axils of young laterals. Main axis in cross section with primary filaments visible as central regular pattern of small squarish cells, secondary cortication visible as a mantle of larger elongate polygonal radiating cells; epidermal cells 3-8 µm in diameter.
Reproductive structures not seen in our material, but see Sauvageau (1914): unilocular sporangia in pairs in each axil, ca.100-120 µm in diameter, on very short pedicels. Plurilocular sporangia on separate plants, 145- 170 µm in diameter, with mixed clusters of micro- and macrogametangia in the same axil, each on a short wide pedicel. Microgametangia orange-brown with locules 4 µm in diameter, macrogametangia dark brown with locules ca. 8 µm in diameter.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Recorded from Betty’s Bay in the Western Cape (Jackelman et al. 1991) to Qolora, just east of the Kei River (19-43). Found from the shallow subtidal to at least 12 m depth.
World distribution: South African endemic.
Type locality: Algoa Bay, Eastern Cape (Silva et al. 1996).
Note: this species was previously misidentified as Phloiocaulon squamulosum (Suhr) Geyler.
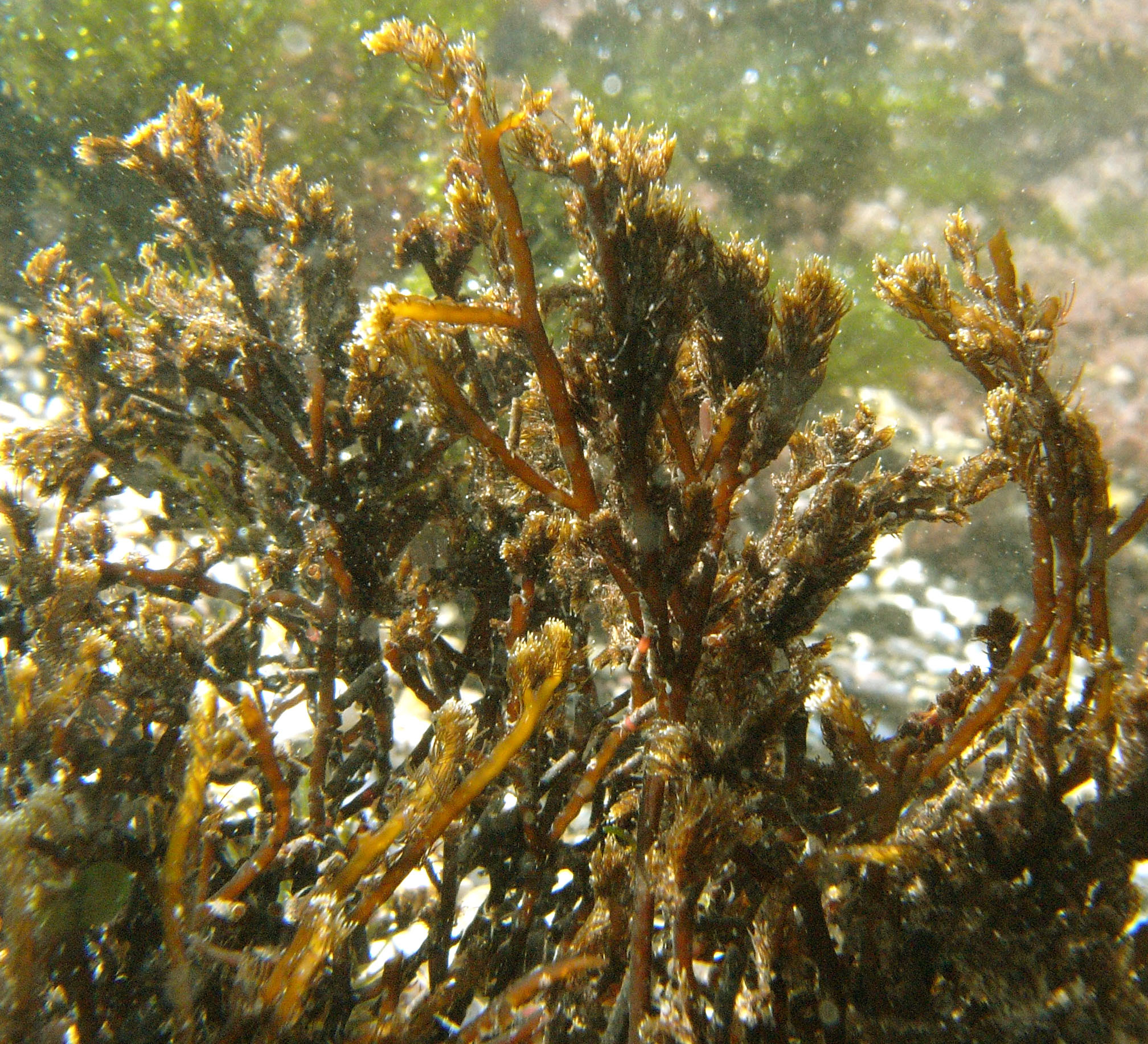

Phloicaulon suhrii, Qolora.
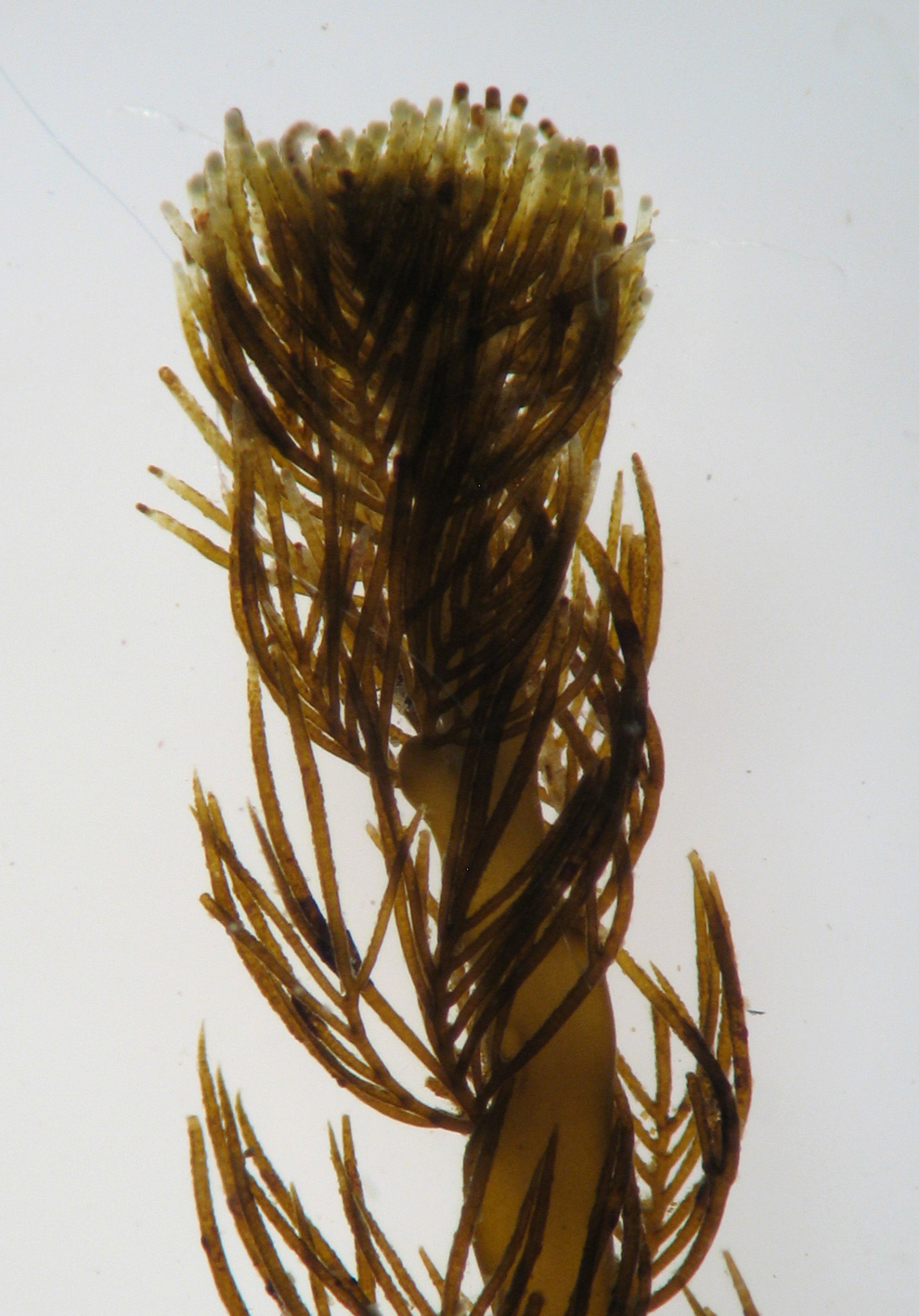

Phloicaulon suhrii, tip of axis with determinate laterals, fresh material.
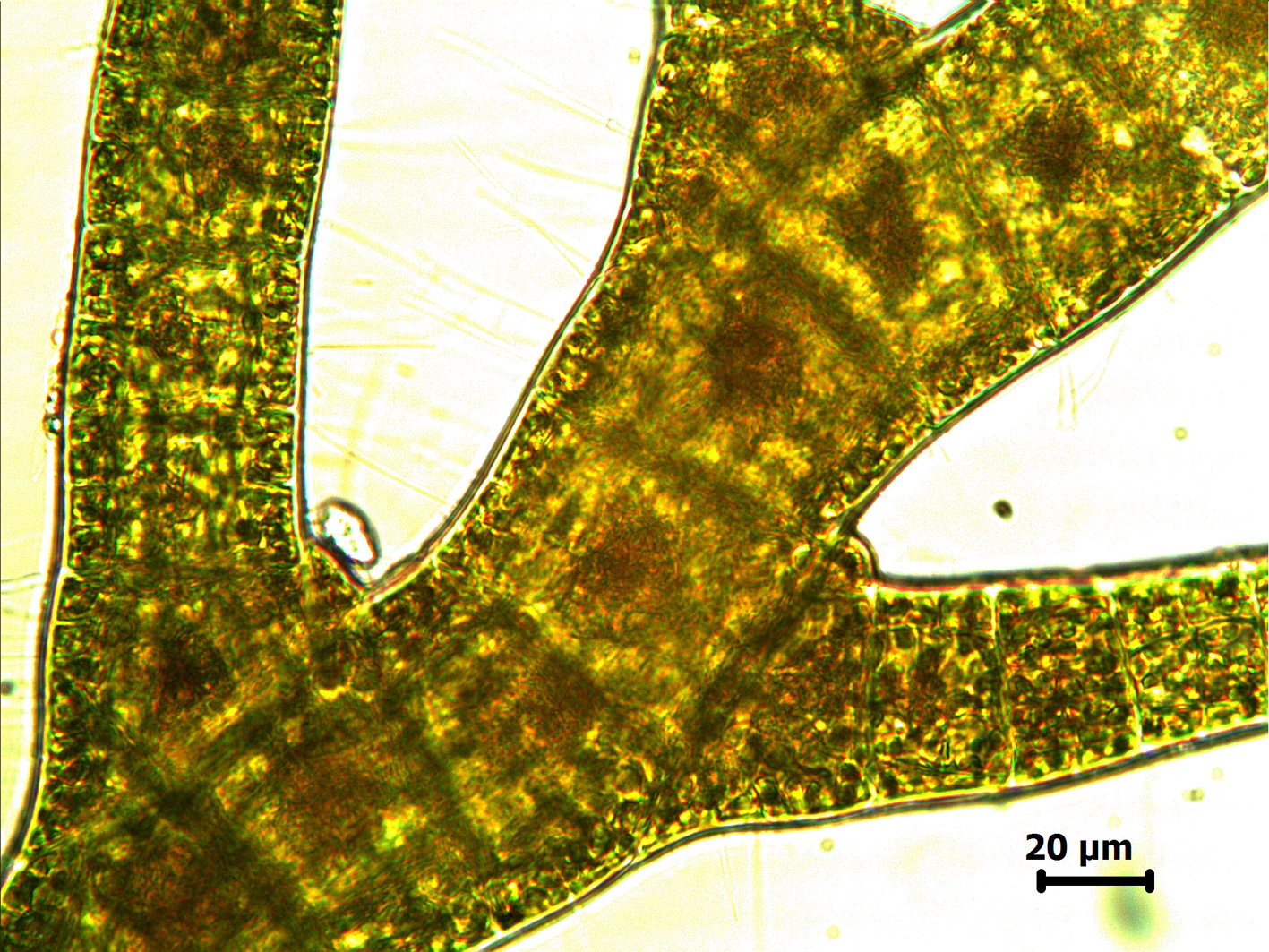

Phloicaulon suhrii, branching of determinate laterals.
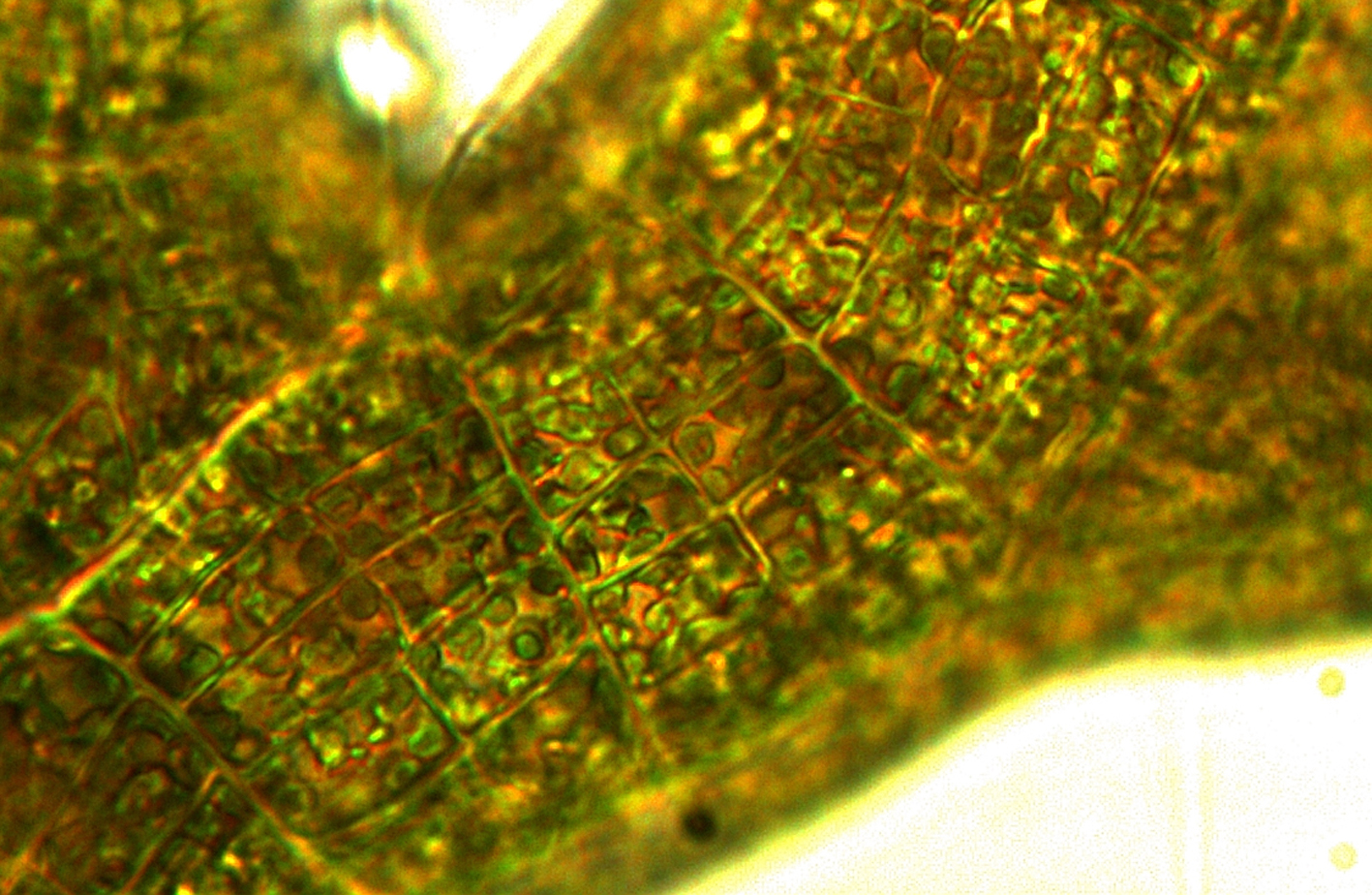
Phloicaulon suhrii, cell detail.
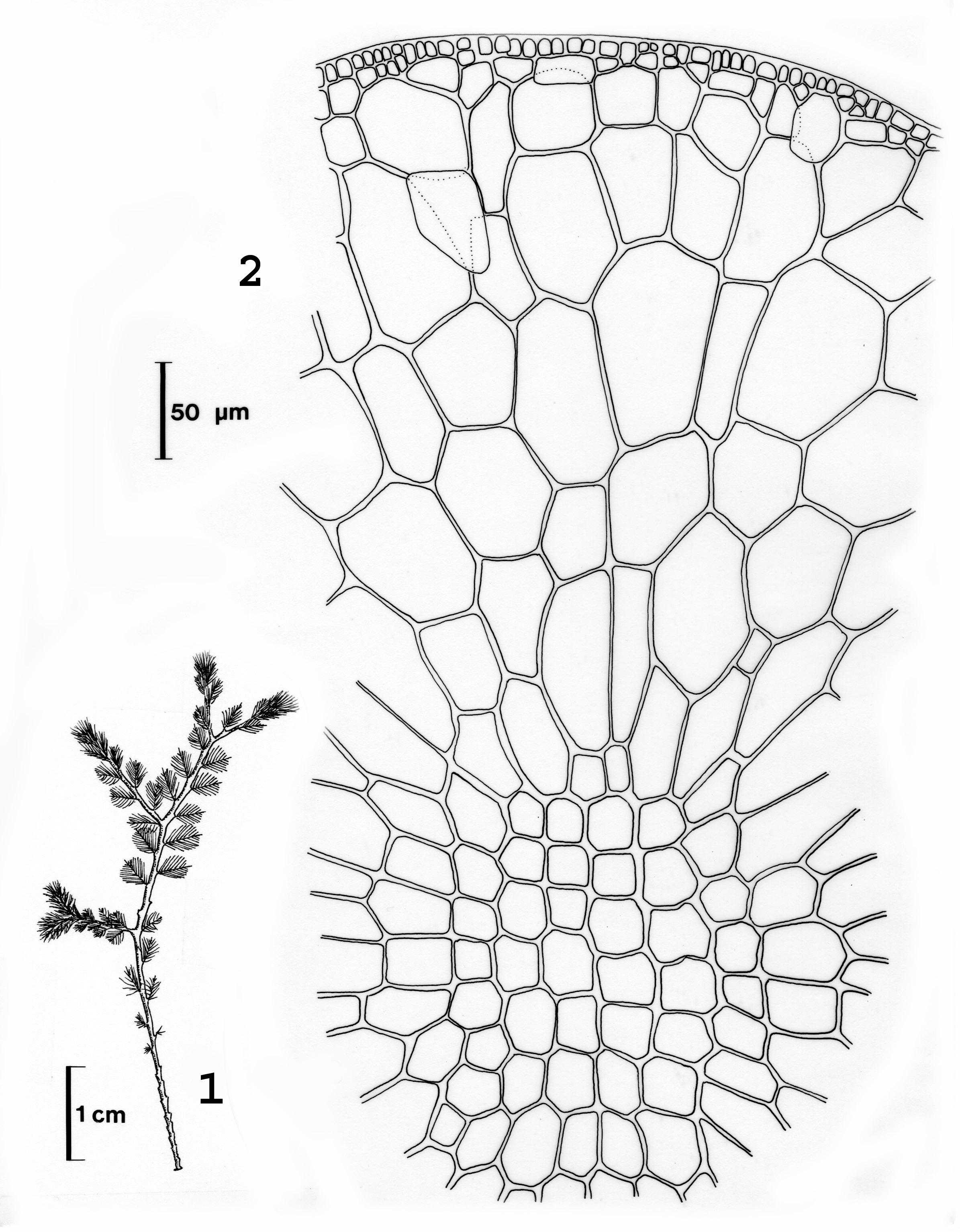
Phloicaulon suhrii. 1. Habit. 2. Cross section of main axis. Reproduced from Stegenga et al. (1997).
References Phloicaulon
Jackelman, J.J., Stegenga, H. and JJ Bolton. 1991. The marine benthic flora of the Cape Hangklip area and its phytogeographical affinities. South African Journal of Botany 57: 295-304.
Sauvageau, C. (1914). Remarques sur les Sphacélariacées. Vol. 3 pp. iii-xii, 481-634, 128 figs. Bordeaux.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. (1996). Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. and R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 11 March 2026.