Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Fucales
Family Sargassaceae
Sargassum elegans Suhr 1840: 257
Plants dark brown to yellowish-brown, up to 50-60 cm high, attached to the substrate by a small conical to rather flattened holdfast to 1.5 cm wide that bears one to several terete perennial main axes up to 2 cm long and 0.6 cm in diameter. Main axes giving rise to several primary axes, terete and smooth, sometimes with a few spines. Secondary axes shorter, alternately and spirally attached, bearing leaves, vesicles and receptacles. Leaves linear-lanceolate, 1.1 to 4 cm long and 0.3 to 0.7 cm wide, crypstostomata inconspicuous or few and scattered when visible, midrib percurrent and slightly raised, pedicel mostly non-existent, basis asymmetrical and cuneate, margins smooth, seldom slightly dentate, apex rounded to slightly acute. Vesicles spherical to oblong and smooth, up to 5 mm in diameter, pedicel flattened to leaf-like and longer than the vesicle. Receptacles compound, terete, attached in tight clusters, surface warty.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Found from Saldanha Bay on the west coast then south and eastwards along the entire coast up to Sodwana Bay (12-57). A subtidal species that can be abundant in rock pools.
World distribution: Also recorded from Mozambique (Silva et al. 1996).
Type locality: South Africa (Suhr 1840), “Am Cap der guten Hoffnung” [between Omsamculo (Umzimkulu) and Omcomas (Umkomaas) rivers, Natal, South Africa fide Drège, 1843: 157] (Silva et al. 1996).
Note: see Mattio et al. (2015) for a recent taxonomic treatment of South African Sargassum species.
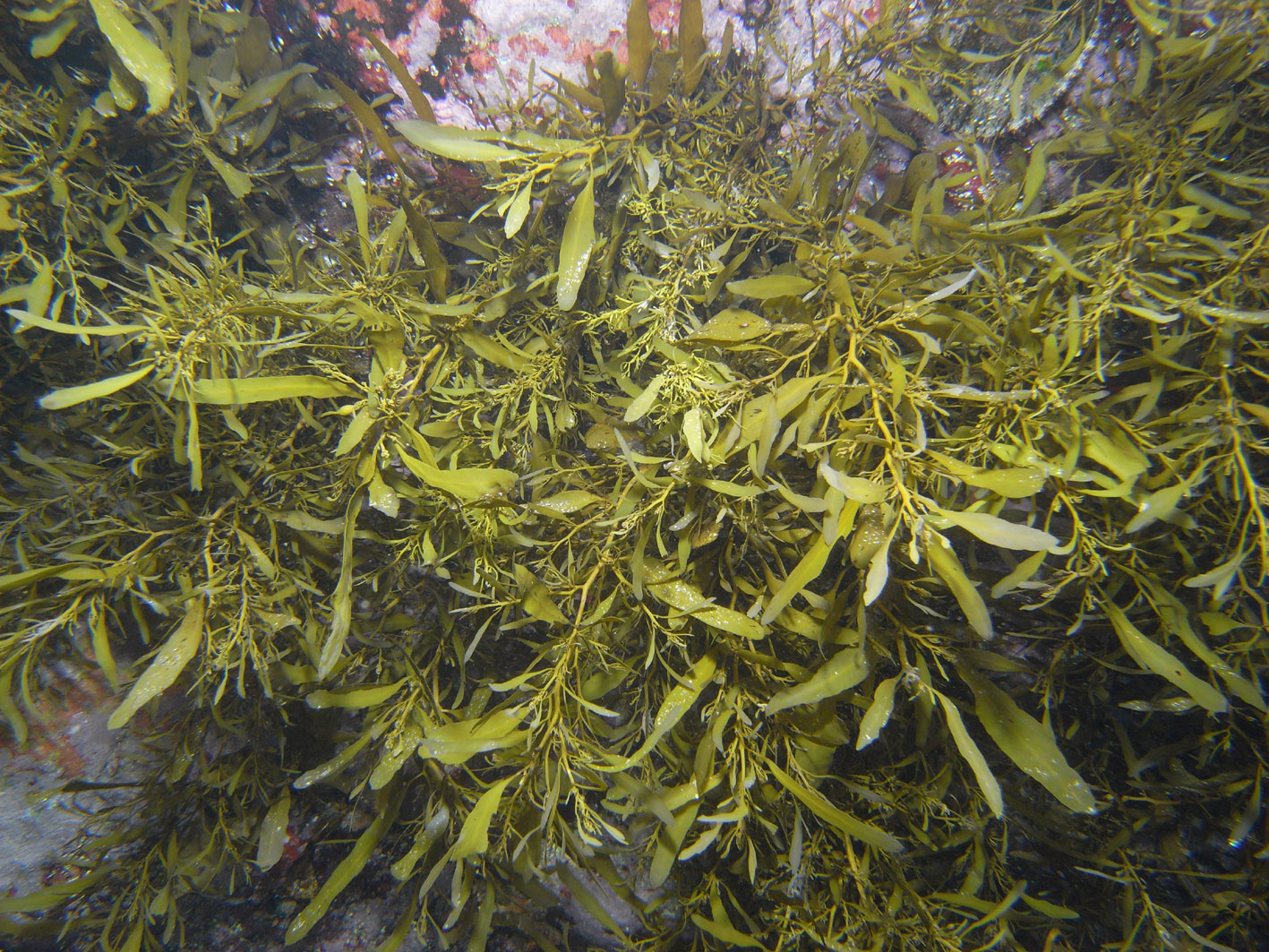

Sargassum elegans, Tsitsikamma rock pool.
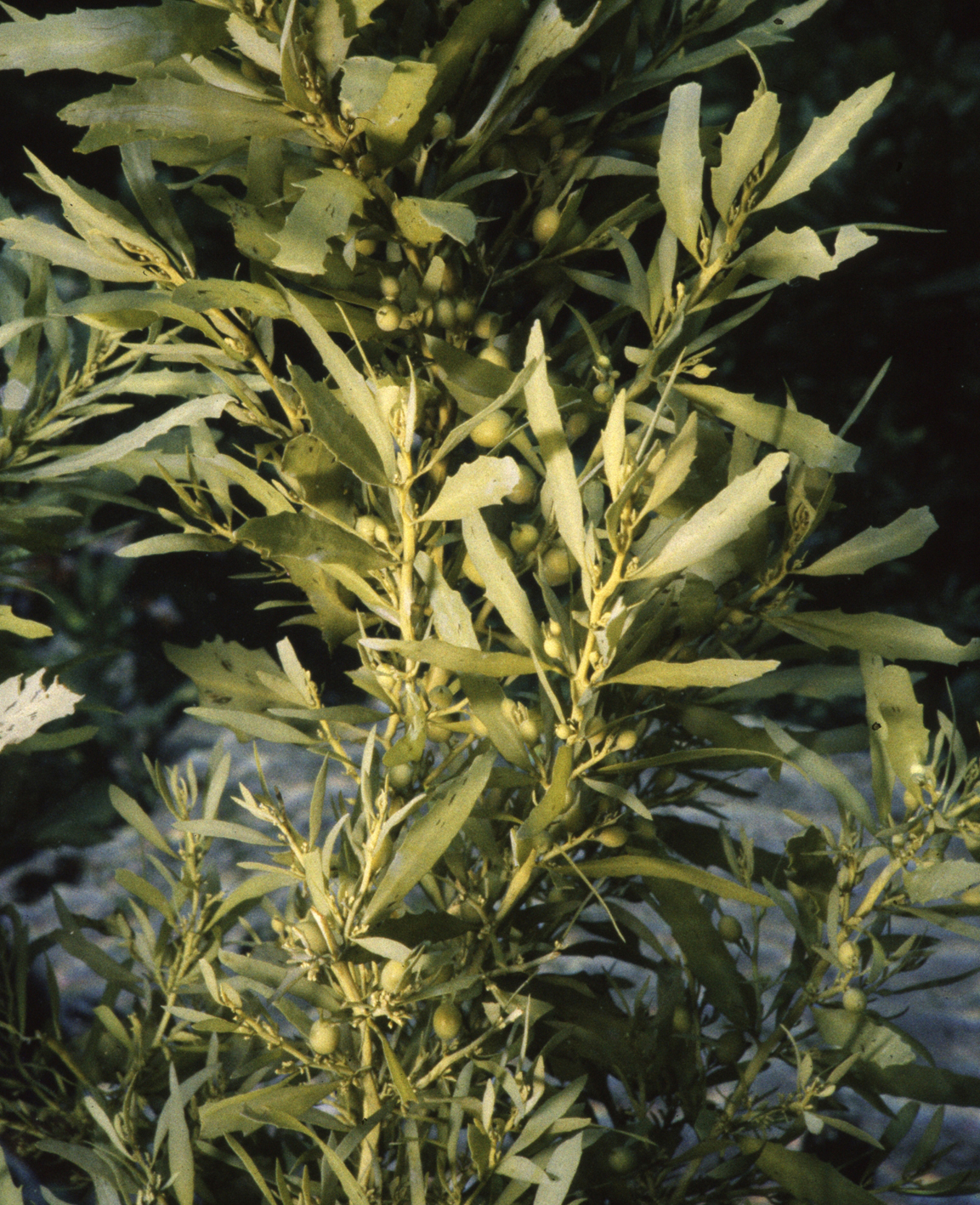

Sargassum elegans, Tsitsikamma.
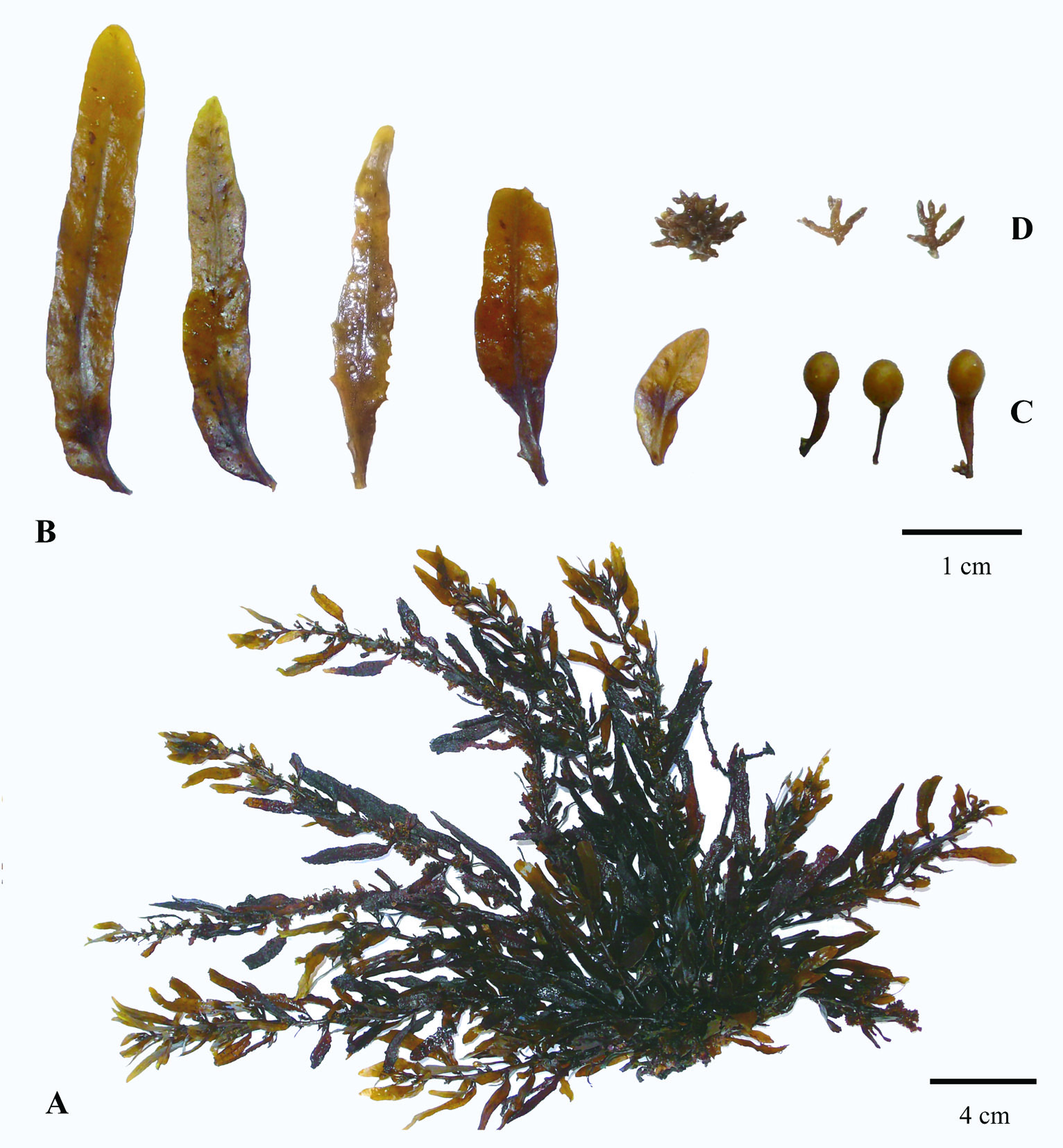

Sargassum elegans. A- habit. B – leaves. C – vesicles. D – receptacles.
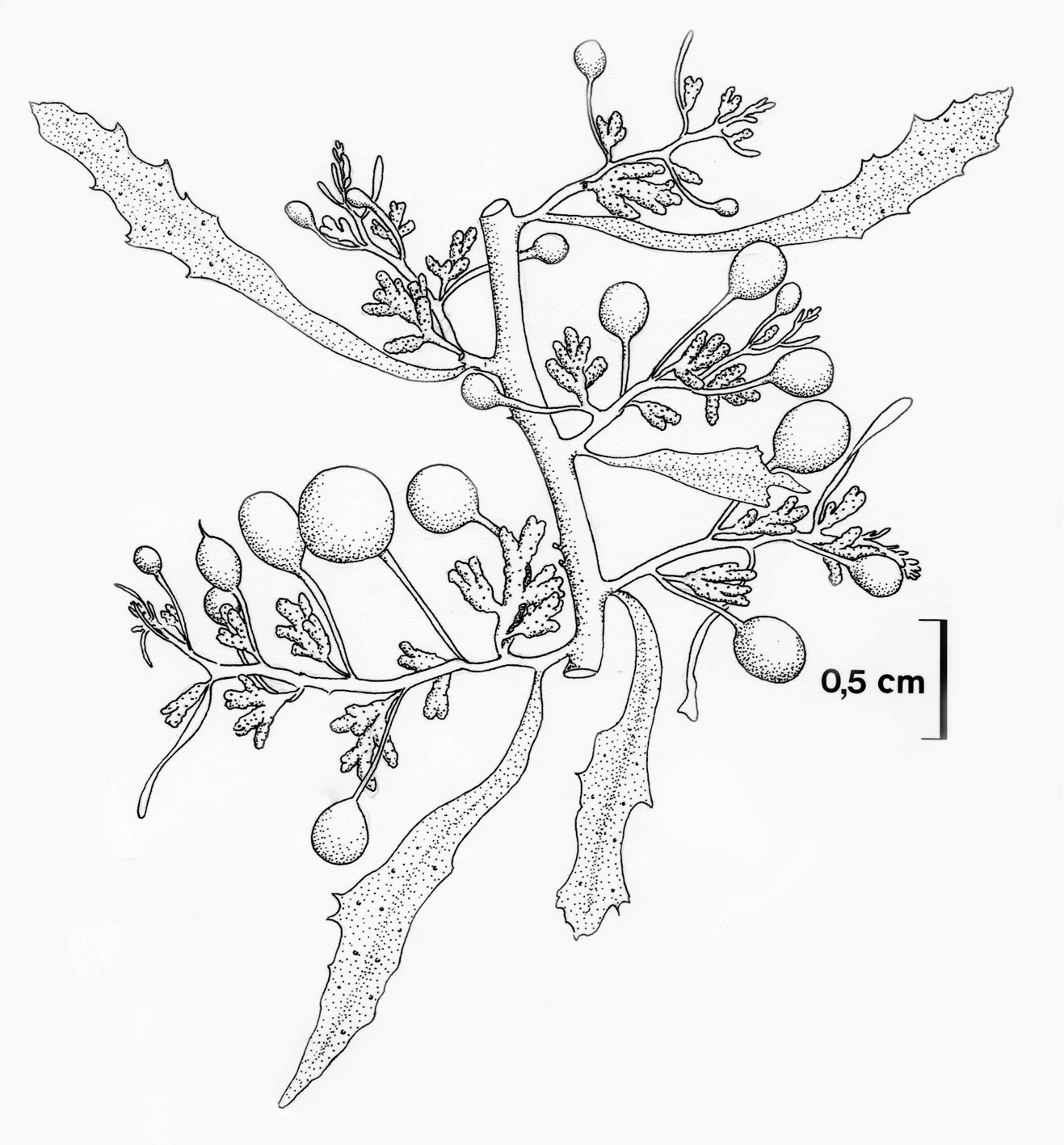
Sargassum elegans, detail of thallus. From Stegenga et al. (1997).
References Sargassum elegans
Mattio L, Anderson RJ, Bolton JJ. 2015. A revision of the genus Sargassum (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) in South Africa. South African Journal of Botany 98: 95-107.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. (1996). Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. and R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Suhr, J.N. von (1840). Beiträge zur Algenkunde. Flora 23: 257-265.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 16 February 2026.