Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Fucales
Family Sargassaceae
Sargassum incisifolium (Turner) C. Agardh 1820: 14-15
Plants dark brown to yellowish-brown, up to 50-60 cm high, attached to the substrate by a large conical holdfast to 4 cm wide that bears one or several strong perennial main axes up to 6 cm long and 2 cm in diameter. Main axis giving rise to several primary axes, thick, smooth and triangular in cross-section, somewhat flattened and up to 0.8 cm large. Secondary axes shorter, alternately and spirally attached, bearing leaves, vesicles and receptacles. Leaves oblong-lanceolate, 3 to 7 cm long and 0.6 to 2.1 cm broad, patterns of darker brown colour visible on most of the blades, crypstostomata inconspicuous, midrib percurrent and raised, pedicel short sometimes bearing a few teeth, leaf base asymmetrical rounded or cuneate, leaf margins mostly smooth, partially incised, occasionally dentate, apex rounded to acute. Vesicles oblong often pointed at the apex or with a spine like mucro, up to 10 mm long and 9 mm large, pedicel terete and shorter than the vesicle. Receptacles simple, lanceolate, flattened, surface warty, edges deeply dentate, attached in open clusters by a very short pedicel.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Recorded from Platboombaai, just west of Cape Point, eastwards along the entire coast and into Mozambique (17-58). A subtidal species that can form large beds at depths from a few to at least 10 m, sometimes found in rock pools and the lower eulittoral.
World distribution: Also occurring in the south-east of Madagascar (L. Mattio pers. com.). Doubtful records from Mauritius as S. heterophyllum (Turner) C. Agardh (Dickie 1874, Jadin 1934, Børgesen 1941), Mozambique (Silva et al. 1996, Critchley et al. 1997) and India (Silva et al. 1996, Sahoo et al. 2001).
Type locality: Cape of Good Hope, South Africa (Turner 1811).
Note: Sargasum heterophyllm C. Agardh and Fucus heterophyllus Turner are recorded as heterotypic synonyms of S. incisifolium. See Mattio et al. (2015) for a recent taxonomic treatment of South African Sargassum.
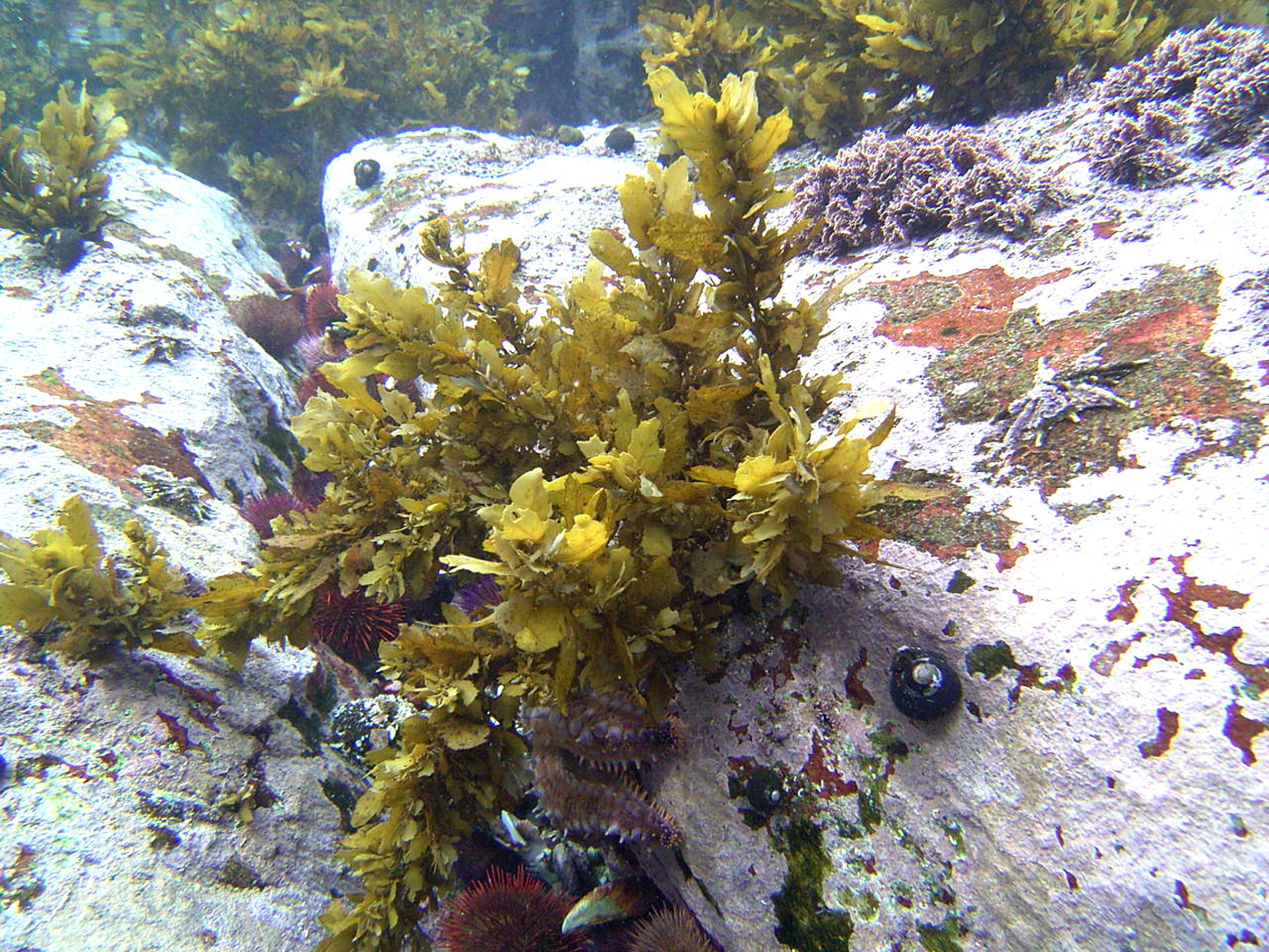

Sargassum incisifolium, Arniston.
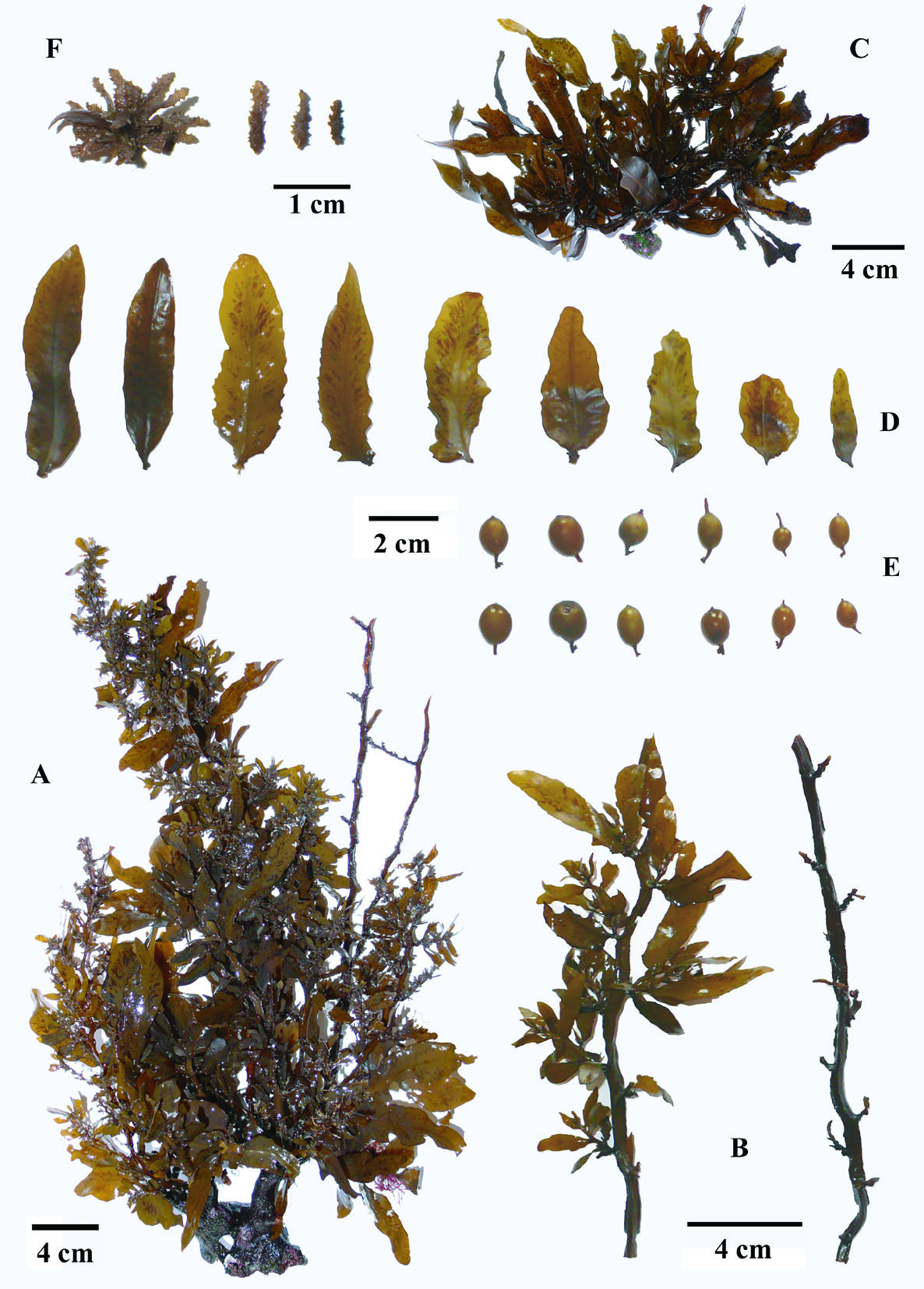

Sargassum incisifolium, A- habit. B – main axes. C – leaf arrangement. D – leaves. E – vesicles. F – receptacles.
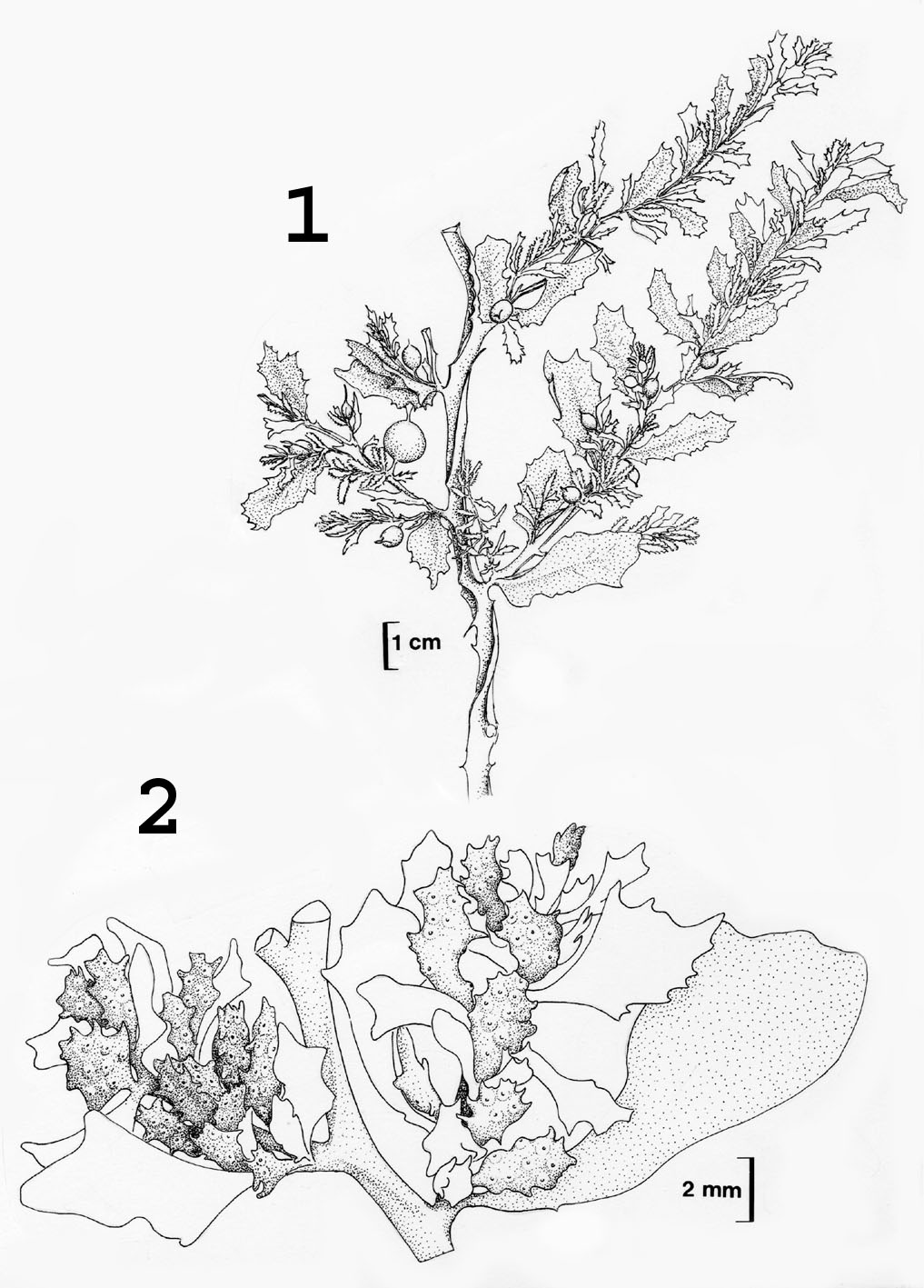
Sargassum incisifolium, details of fertile thalli. Reproduced from Stegenga et al. (1997).
References Sargassum
Agardh, C.A. (1820 '1821'). Species algarum rite cognitae, cum synonymis, differentiis specificis et descriptionibus succinctis. Volumen primum. Pars prima. pp. [i-iv], [1]-168. Lundae [Lund]: ex officina Berlingiana.
Børgesen, F. (1941). Some marine algae from Mauritius. II. Phaeophyceae. Kongelige Danske Videnskabernes Selskab, Biologiske Meddelelser 16(3): 81, 24 figs, 8 plates.
Critchley, A.T., Aken, M.E., Bandeira, S.O. & Kalk, M. (1997). A revised checklist for the seaweeds of Inhaca Island, Mozambique. South African Journal of Botany 63: 426-436.
Dickie, G. (1874). On the algae of Mauritius. Journal of the Linnean Society of London, Botany 14: 190-202.
Jadin, F. (1934). Algues des îles de la Réunion et de Maurice. Annales de Cryptogamie Exotique 7: 147-172.
Mattio L, Anderson RJ, Bolton JJ. 2015. A revision of the genus Sargassum (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) in South Africa. South African Journal of Botany 98: 95-107.
Sahoo, D., Nivedita & Debasish (2001). Seaweeds of Indian coast. pp. xxi + 283. New Delhi: A.P.H. Publishing.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. (1996). Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. and R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Turner, D. (1809-1811). Fuci sive plantarum fucorum generi a botanicis ascriptarum icones descriptiones et historia. Fuci, or colored figures and descriptions of the plants referrred by botanists to the genus Fucus. Vol. 3 pp. [i], [1]-148 , [1-2], pl. 135-196 (col. copp. by W.J. Hooker). Londini [London]: typis J. M'Creery, impensis J. et A. Arch.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 09 March 2026.