Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Cladophorales
Family Cladophoraceae
Cladophora flagelliformis (Suhr) Kützing 1849: 388
Plants dark green, erect, up to about 10 (-20) cm tall, forming dense tufts, attached by matted rhizoids developing from basal cells of erect filaments. Percurrent main axis obvious in erect filaments, although not different in size from many primary laterals. Growth in main filaments intercalary, in young laterals also by apical cell division. Branching irregular, up to four laterals per cell in west coast plants but fewer (usually only one per cell) in east coast plants. Laterals cut off via an oblique wall that moves into a transverse position in older branches. Laterals rebranched, often with short ramuli on proximal parts, but in distal parts unbranched and flagelliform. Apical cells of growing branches cylindrical or slightly tapering, 50-80 µm in diameter, up to 400 µm long; main axis and primary laterals ca. 100-150 µm in diameter, increasing to ca. 400 µm in the fertile tips; cells 1-3 times longer than broad (up to 5 times proximally).
Note: The cell dimensions of west coast material (Stegenga et al. 1997) differ somewhat from east coast material, but the dimensions of the latter fall within the limits of the former (Leliaert & Coppejans 2003). Our south coast specimens are in general smaller than those from the west coast.
Collections ecology and regional distribution
Recorded along the west coast and as far east as Durban; in the lower eulitoral zone and rock pools (1-52).
World distribution: Also recorded from Auckland Islands, Namibia, Tristan Da Cunha and Tanzania (Guiry & Guiry 2012).
Type locality: Cape of Good Hope (Silva et al. 1996).
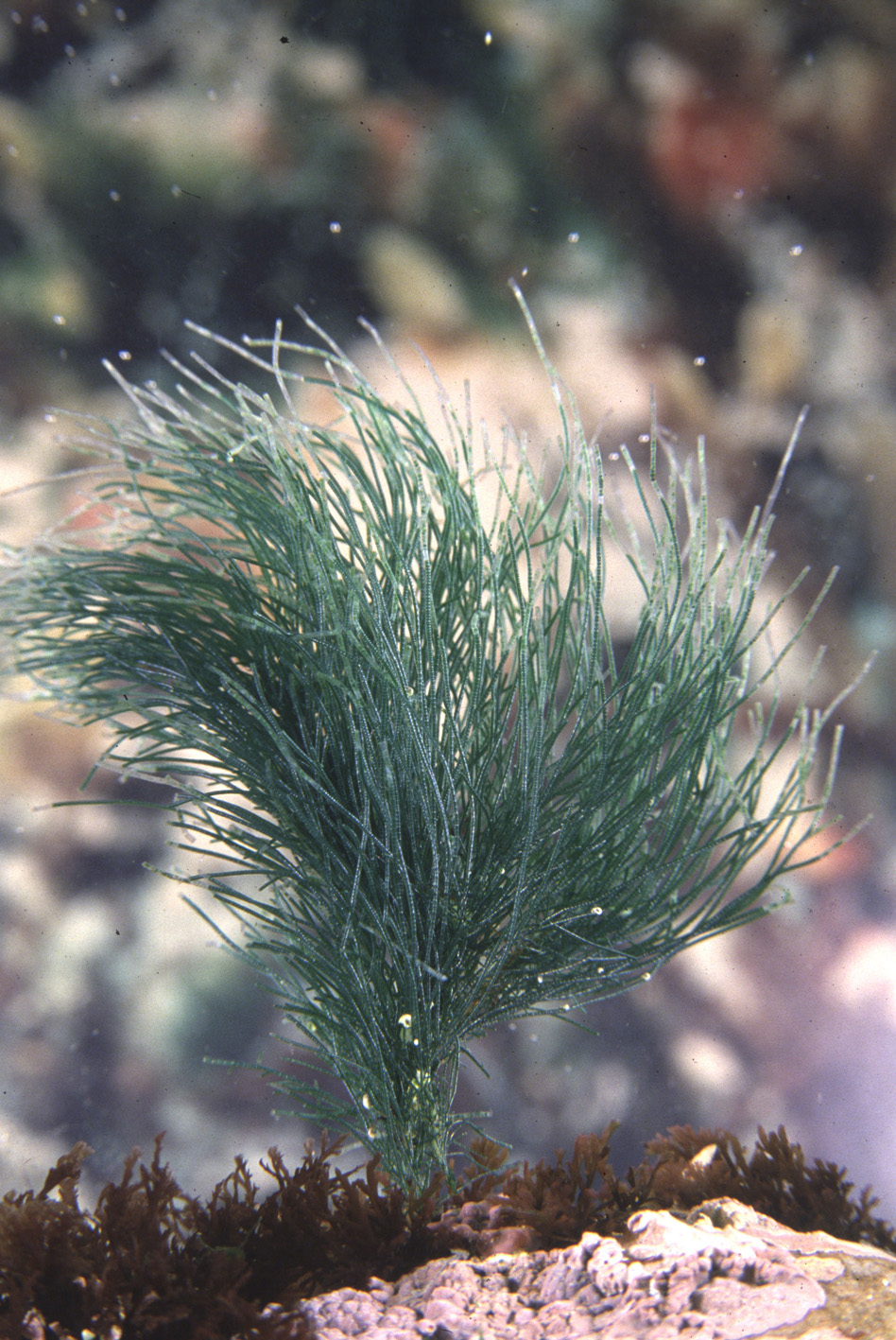

Cladophora flagelliformis (habit)
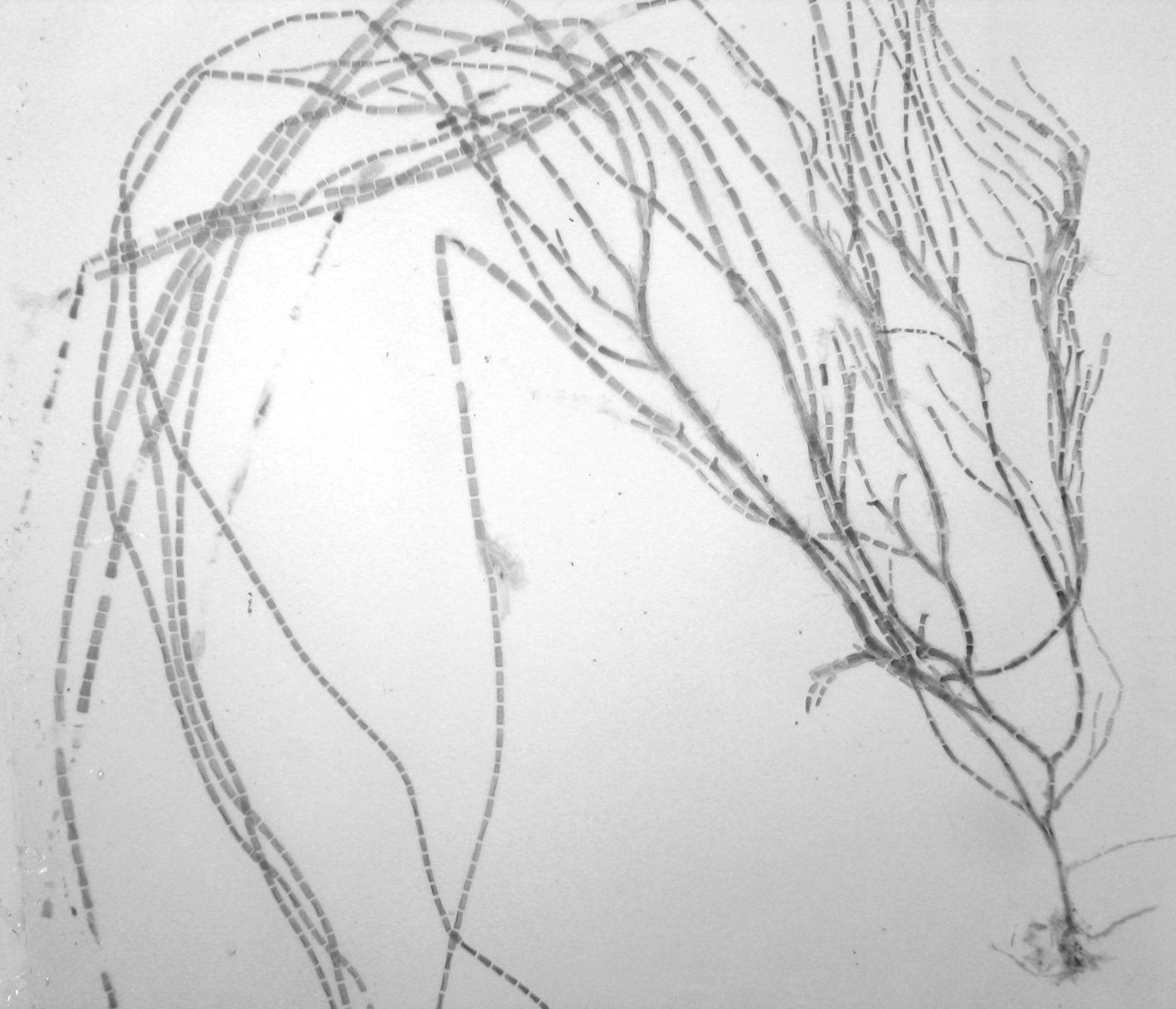

Cladophora flagelliformis, individual thallus, ca. 3 cm long
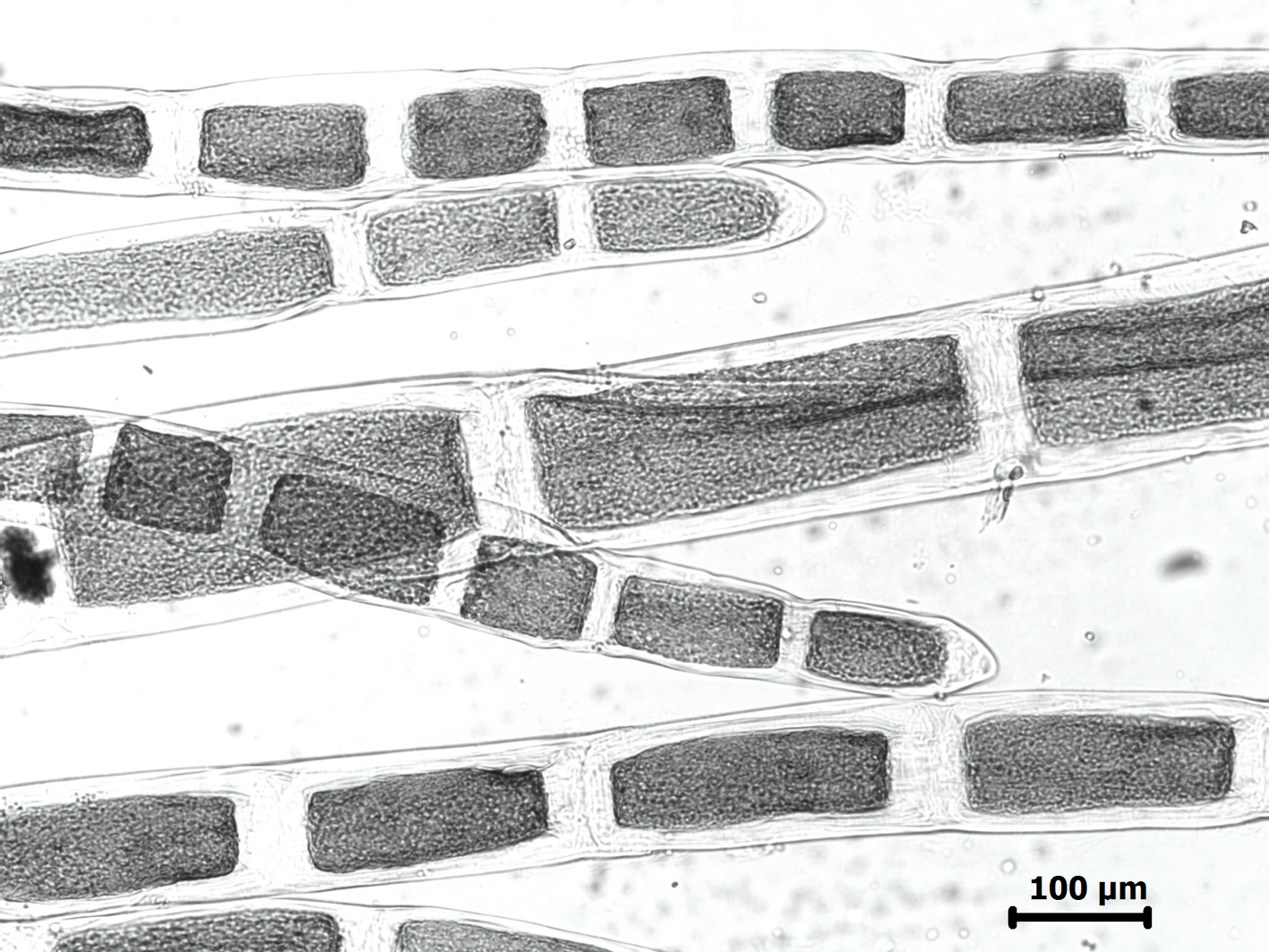
Cladophora flagelliformis, apical cells
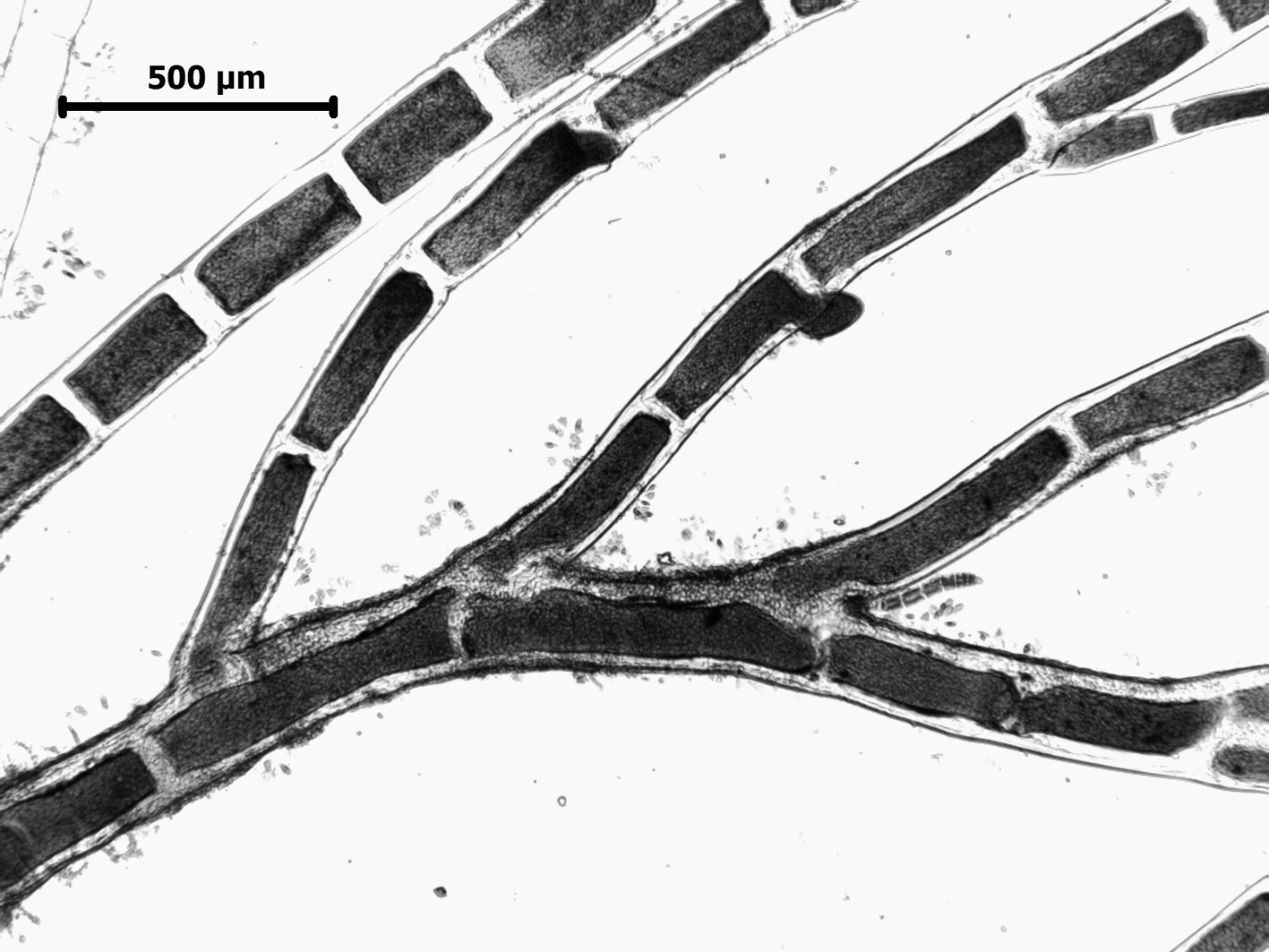
Cladophora flagelliformis, branching
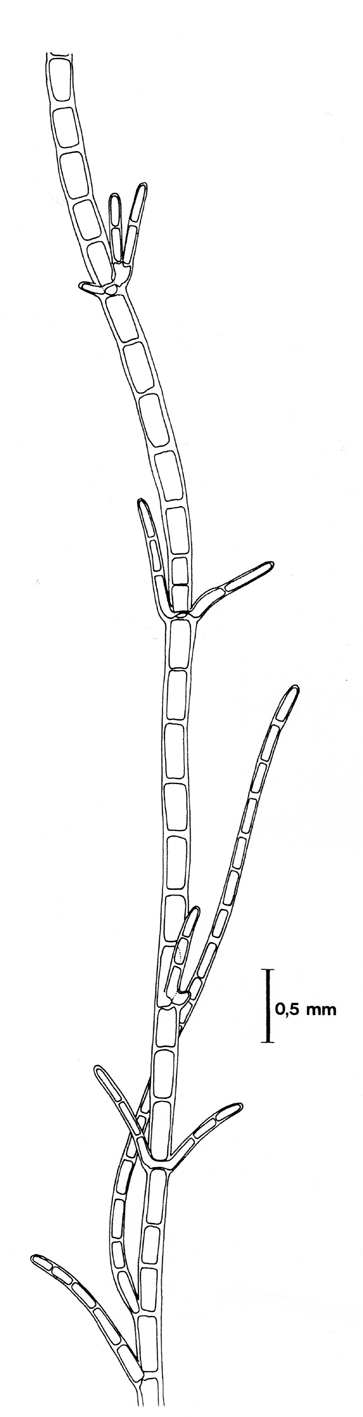
Cladophora flagelliformis, drawing reproduced from Stegenga et al. (1997).
References Cladophora flagelliformis:
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. 2012. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched July 2012.
Kützing, F.T. (1849). Species algarum. pp. [i]-vi, [1]-922. Lipsiae [Leipzig]: F.A. Brockhaus.
Leliaert, F. and E.Coppejans. 2003. The marine species of Cladophora (Chlorophyta) from the South African east coast. Nova Hedwigia 76: 48-52.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. (1996). Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. and R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 09 March 2026.