Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Acrochaetiales
Family Acrochaetiaceae
Acrochaetium moniliforme (Rosenvinge) Børgesen 1915: 22
Plants rarely over a few hundred µm tall. Gametophytes with a unicellular base and 1-3 erect axes. Tetrasporophytes with a multicellular filamentous base originating from a septately germinated spore; septation pattern typically two-celled. Erect axes in both generations arcuate, with a secund series of laterals, 8-10 (-12) µm in diameter, tapering towards the apex. Cells barrel-shaped, slightly shorter to slightly longer than broad. Monosporangia terminal or lateral on main axis and main branches, single, ovate, 8-10 x 5-7 µm.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Recorded from False Bay to Hluleka (17 – 45), epiphytic on various algae (Stegenga et al. 1997).
World distribution: various tropical and warm temperate localities worldwide (Guiry & Guiry 2014).
Type locality: “various in Denmark” (Silva et al. 1996).
Note: tetrasporophytic phase not recorded from South Africa (Stegenga et al. 1997). See also Stegenga (1985) for further details.
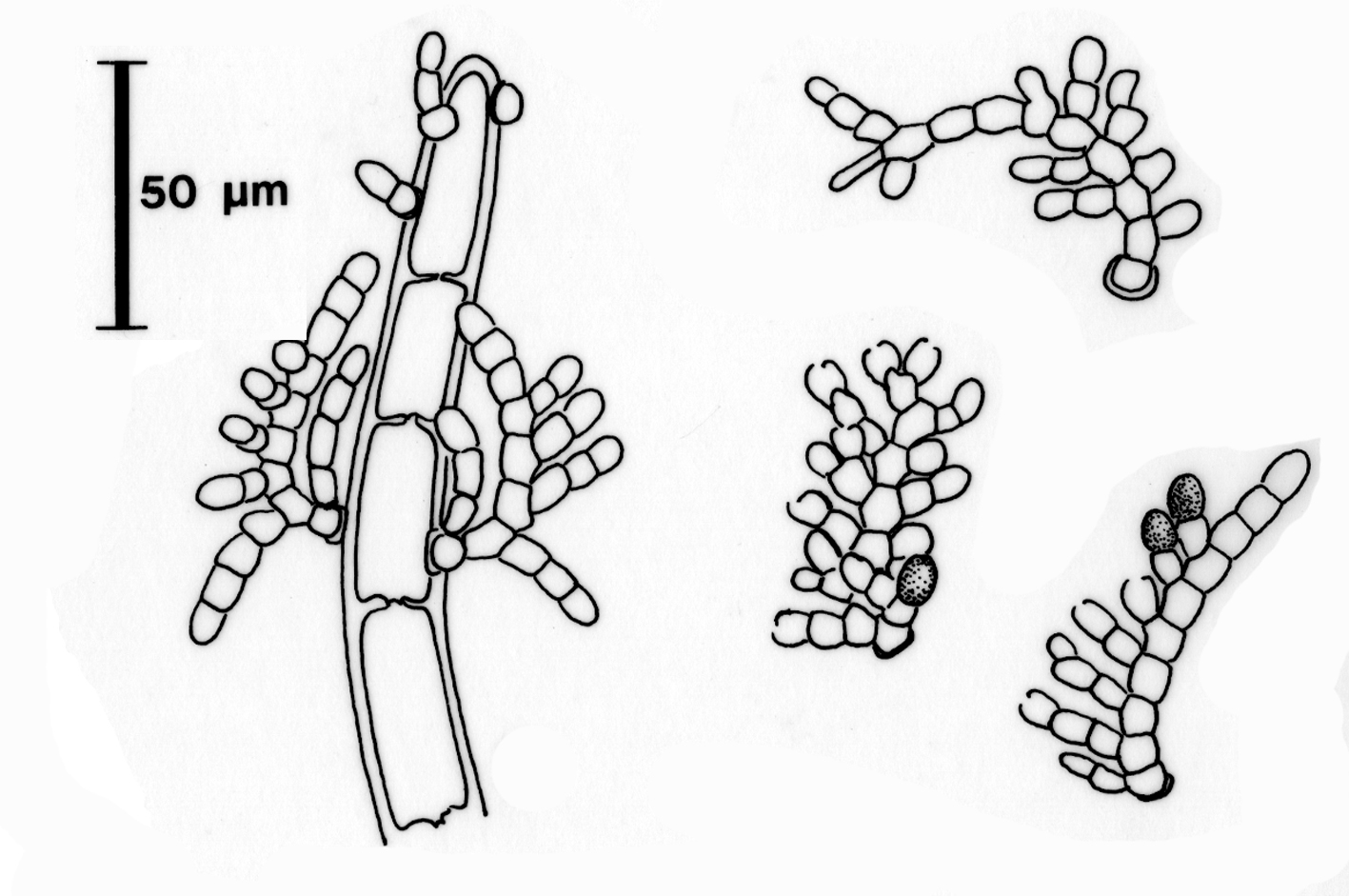
Acrochaetium moniliforme, gametophytes (Illustrations reproduced from Stegenga et al. 1997).
References Acrochaetium moniliforme
Børgesen, F. (1915). The marine algae of the Danish West Indies. Part 3. Rhodophyceae (1). Dansk Botanisk Arkiv 3: 1-80, Figs 1-86.
Guiry W. in Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. 2014. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched on 21 October 2014.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. (1996). Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Stegenga, H. (1985). The marine Acrochaetiaceae (Rhodophyta) of southern Africa. South African Journal of Botany 51: 291-330, 25 figs, 1 table.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. and R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 16 February 2026.