Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Corallinales
Family Corallinaceae
Sub-family Corallinoideae
Amphiroa beauvoisii Lamouroux 1816: 299-300
Plants up to 10 cm tall, forming firm often dense tufts, pale pink, grayish or violet, with crustose holdfast bearing several axes. Axes complanate, branching regularly dichotomous to sometimes polychotomous. Genicula purple-black, fairly conspicuous, usually flanked by calcified shoulders of intergenicula above and below. Intergenicula cylindrical proximally to slightly compressed distally, 1-5 mm long and 0.5 to 1 mm in diameter; broadening where branches subtended, sometimes asymmetrical in shape; lateral branching from asymmetric distal portions of intergenicula common, branching every 1-3 intergenicula; terminal segments usually flattened, sometimes forked at ends. Reproductive structures in hemispherical conceptacles (about 300 µm diameter), borne on surfaces of mostly older intergenicula, inconspicuous but visible.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Epilithic in rock pools and from eulittoral fringe to at least 20 m depth. Found from Glencairn, False Bay, to tropical East Africa (17-58). This species is uncommon west of Cape Agulhas but common on the south and east coasts.
World distribution: Widespread in tropical and temperate seas.
Type locality: Portugal (Silva et al. 1996).
Note: A DNA barcoding study of South African articulated corallines (Kogame et al., 2017) showed that more than one species may fit the description of A. beauvoisii, indicating the need for further studies.
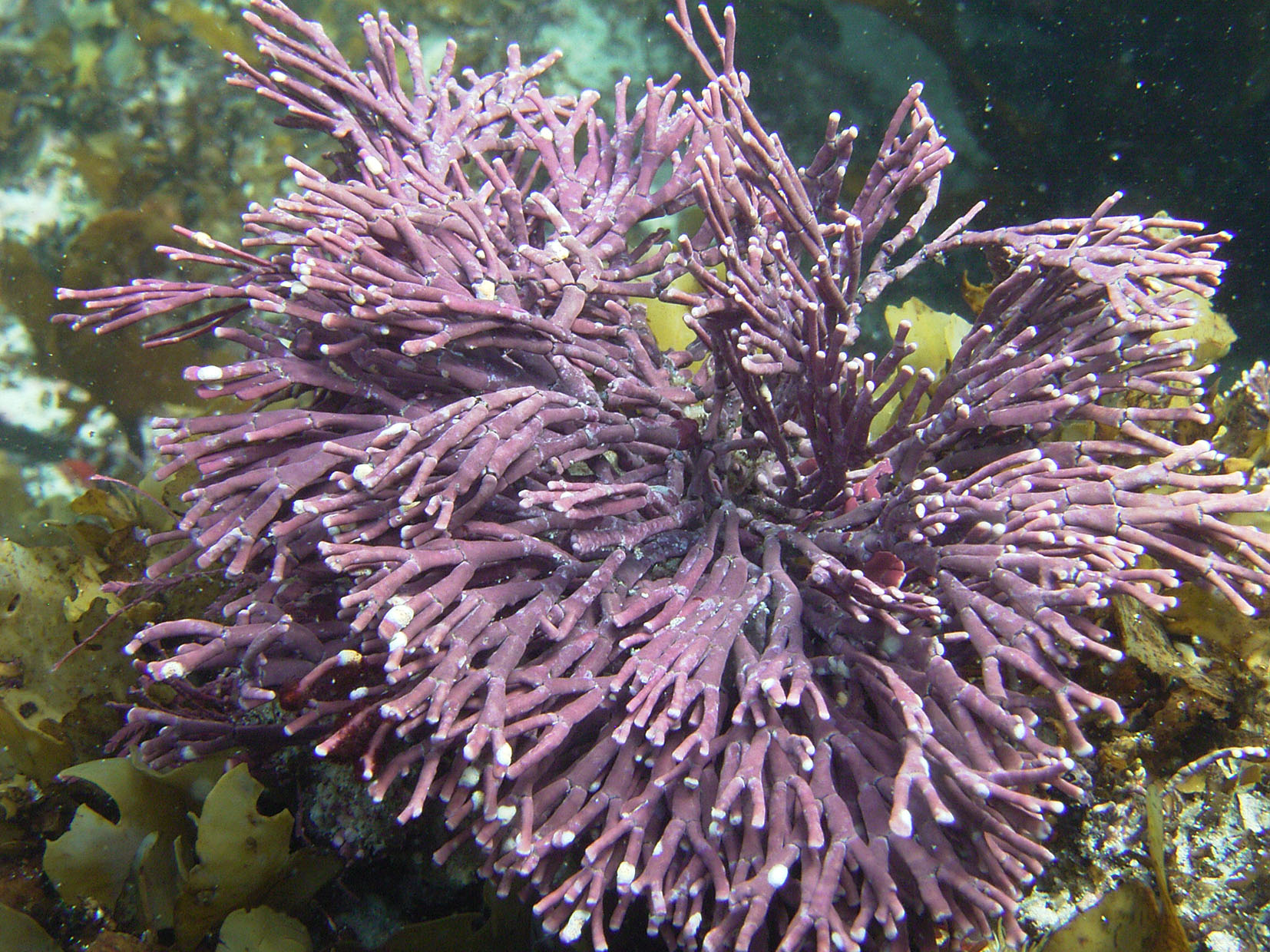

Amphiroa beauvoisii.
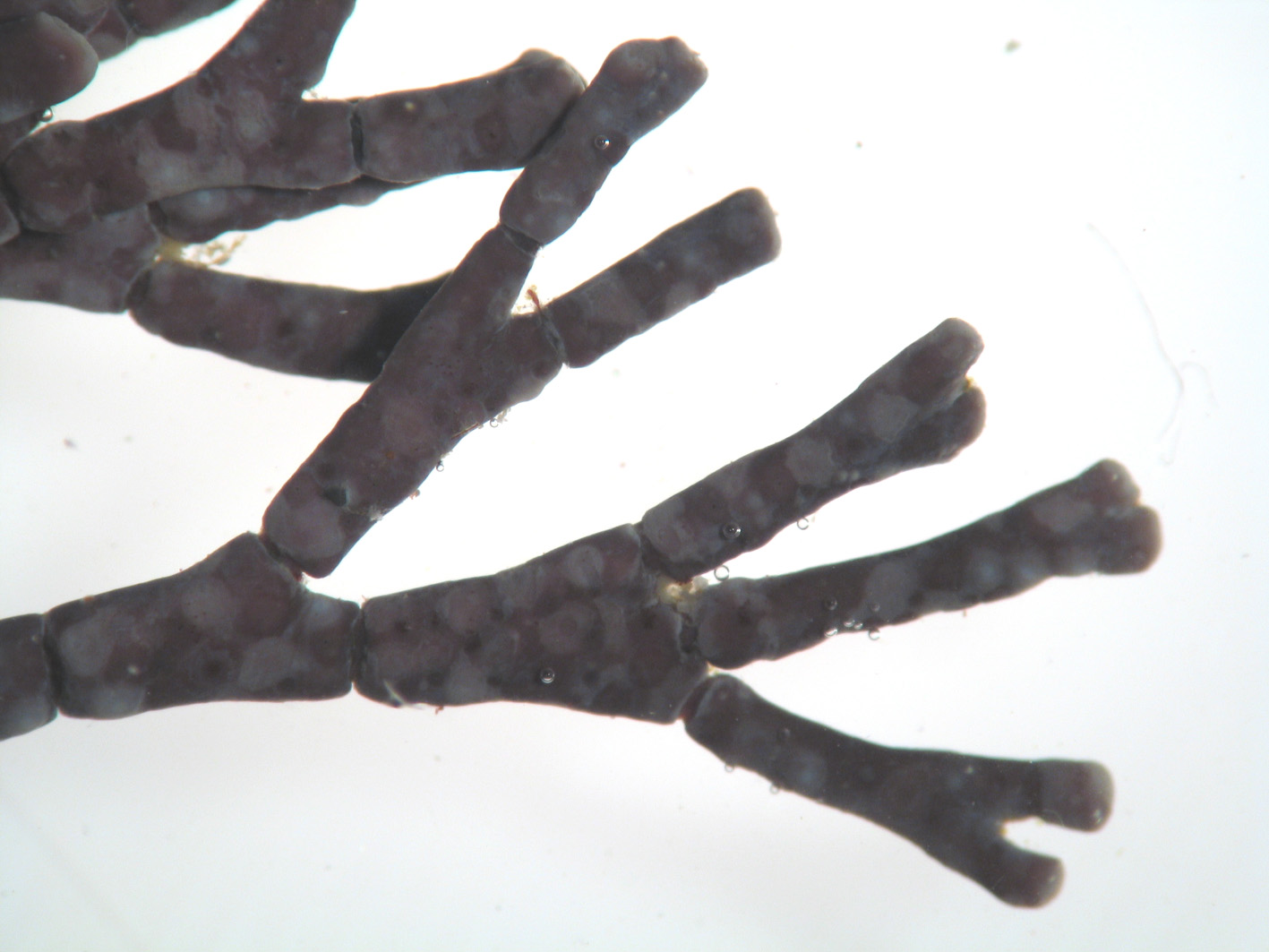
Amphiroa beauvoisii, note genicula.
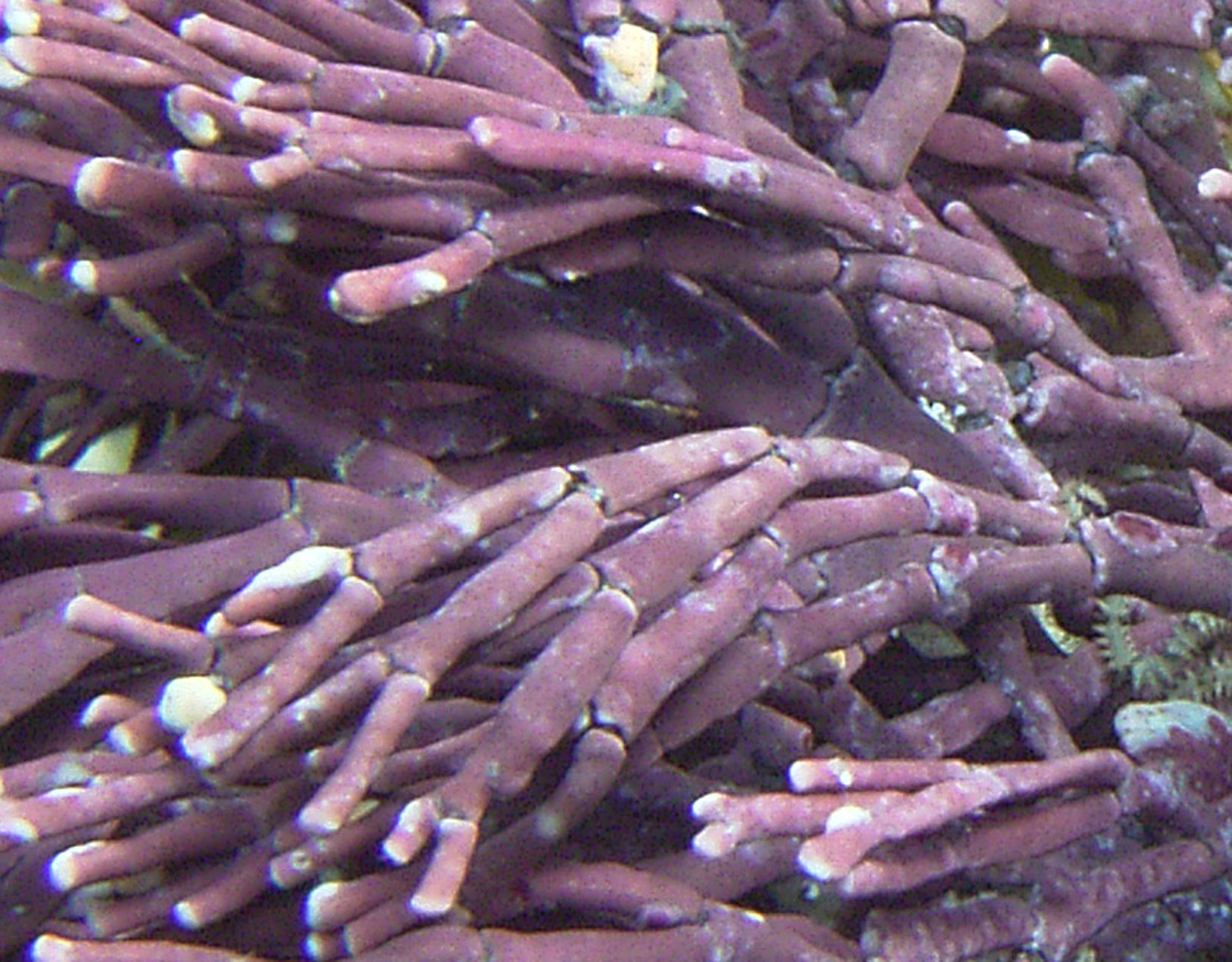
Amphiroa beauvoisii, detail.
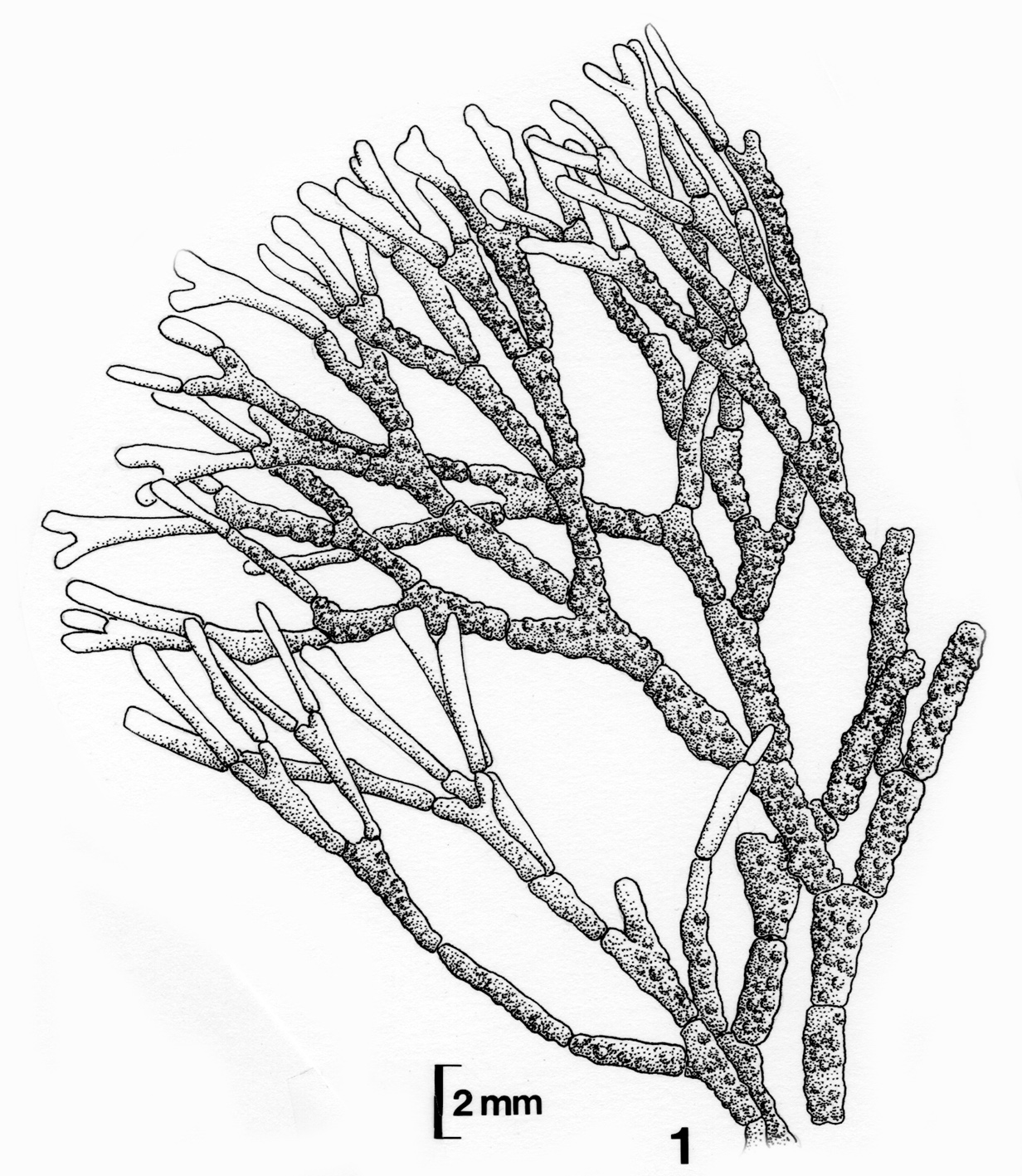
Amphiroa beauvoisii. Fertile thallus. Reproduced from Stegenga et al. (1997).
References Amphiroa beauvoisii
Kogame, K., Uwai, S., Anderson, R.J., Choi, H-G. & J.J. Bolton. (2017). DNA barcoding of South African geniculate coralline red algae (Corallinales, Rhodophyta). South African Journal of Botany 108: 337-341.
Lamouroux, J.V.F. (1816). Histoire des polypiers coralligènes flexibles, vulgairement nommés zoophytes. pp. [i]-lxxxiv, chart, [1]-560, [560, err], pls I-XIX, uncol. by author. Caen: De l'imprimerie de F. Poisson.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. (1996). Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. and R. J. Anderson. (1997). Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 09 March 2026.