Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Ceramiales
Family Rhodomelaceae
Aphanocladia ecorticata Stegenga, R.J.Anderson & Bolton 2004: 167-170, figs 1-5
Plants small, filamentous, uncorticated. Main axes prostrate and probably of indefinite growth, attached by rhizoids cut off from ventral pericentral cells and with two opposite lateral rows of pinnate branchlets. Main axes up to 60 µm in diameter, segments up to 1.5 times longer than broad; branchlets ca. 35-50 µm in diameter, segments about as long as broad, and up to about 1.5 mm long but to 2.5 mm long when bearing tetrasporangia. Segments with 4 pericentral cells; branch initials arranged in a quarter spiral (either left- or right-handed) in successive segments. Trichoblasts absent. Tetrasporiferous segments with 5 pericentral cells; tetrasporangia developing in spiral series in ultimate branchlets, one per segment, globose and to ca 60 µm diameter, tetrahedrally divided, each with two long and one short cover cell. Other reproductive structures not seen.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Known from a single collection off Leven Point, near Stilbaai (26), from 5-6 m depth. Epiphytic on crustose corallines.
World distribution: South African endemic (and the only record of Aphanocladia from the Indian Ocean).
Type locality: near Leven Point, Western Cape Province, South Africa (Stegenga et al. 2004).
Note: The first (and only other) entity in this genus reported from South Africa (from west of Cape Agulhas) is Aphanocladia cf skottsbergii (Stegenga et al. 1997). However, that entity is larger, slightly corticated, and has a somewhat different branching pattern (Stegenga et al. 2004).
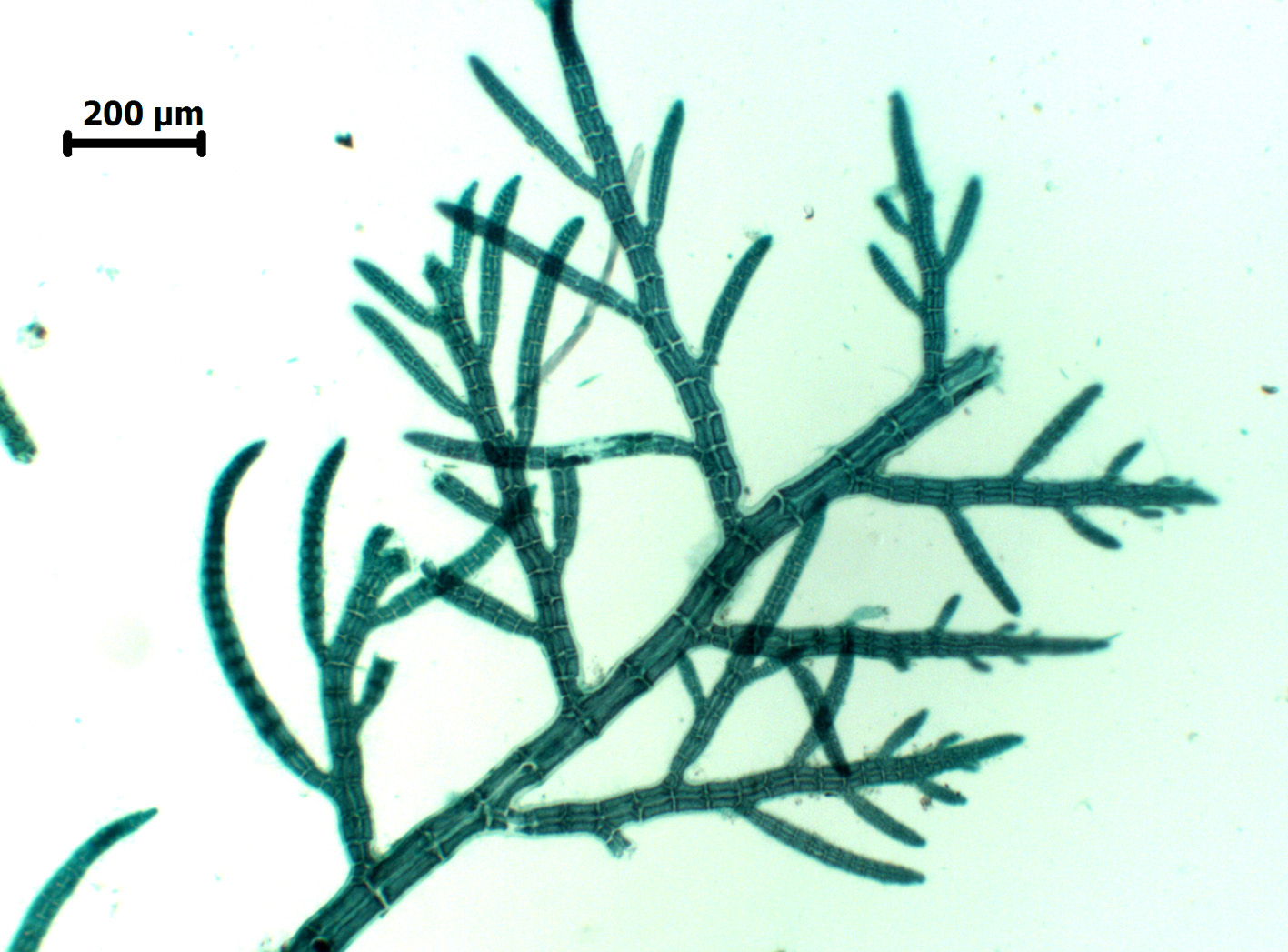

Aphanocladia ecorticata, dorsal view (stained slide).
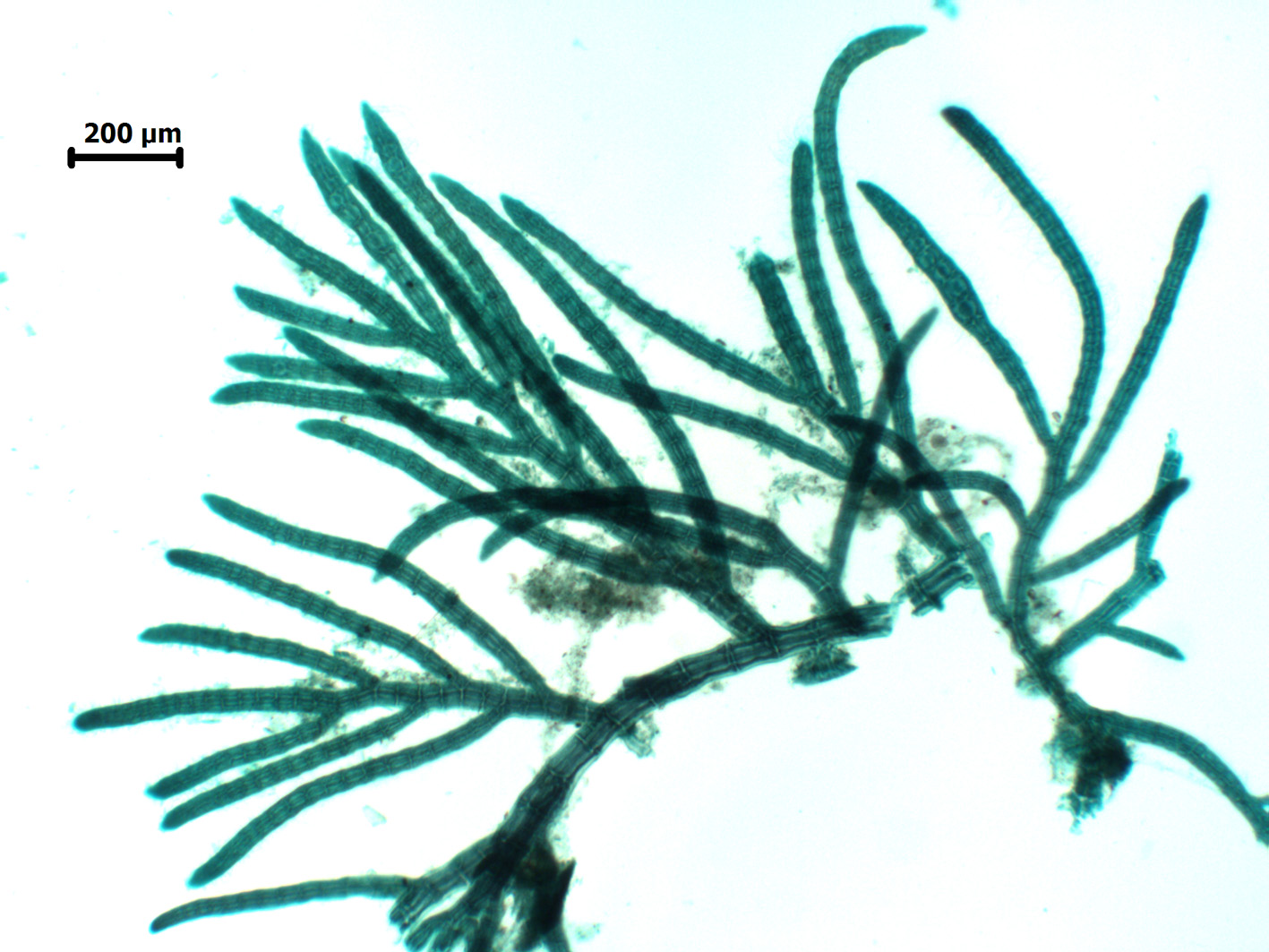

Aphanocladia ecorticata, side view (stained slide).
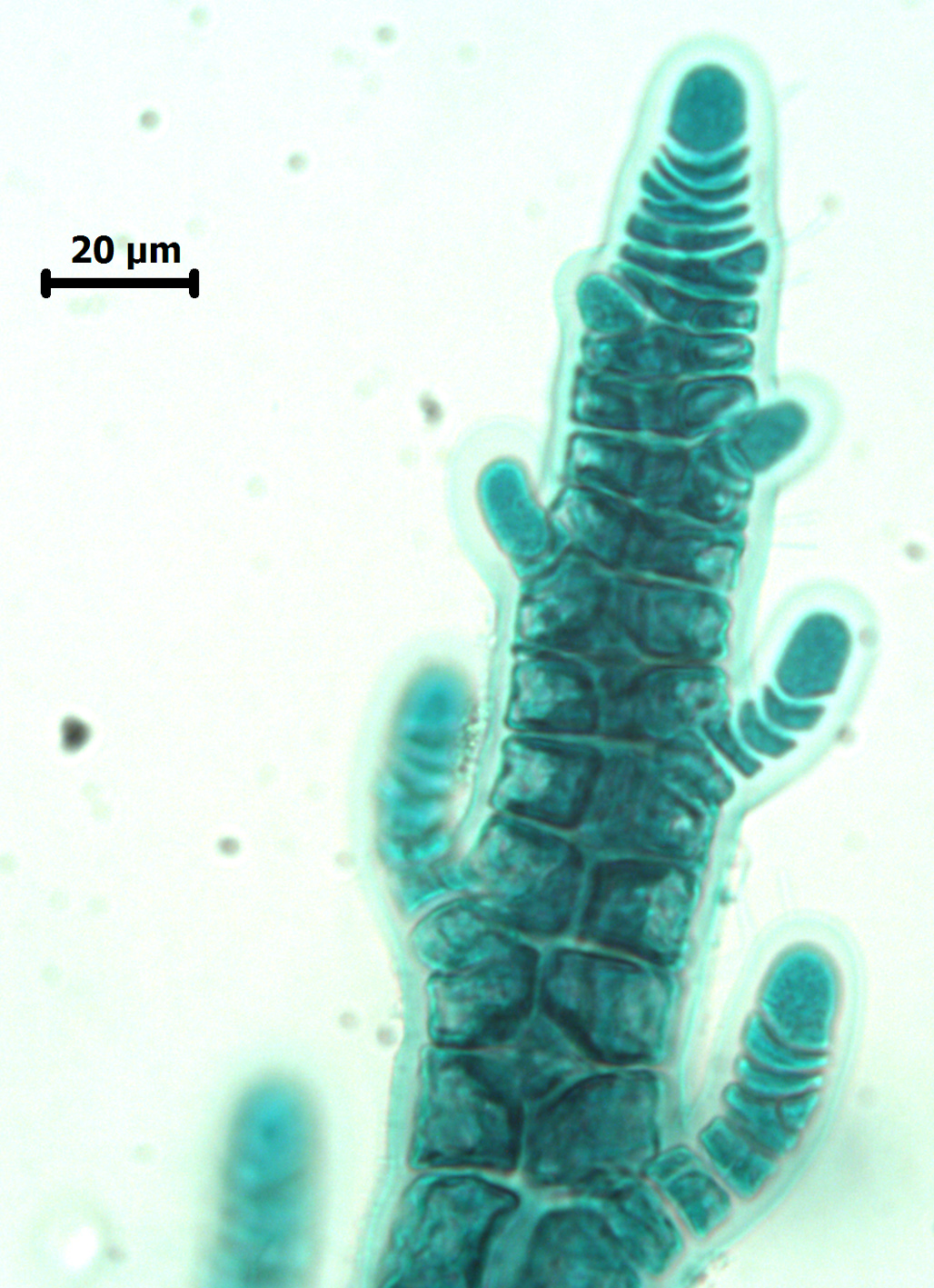
Aphanocladia ecorticata, branch apex (stained slide).
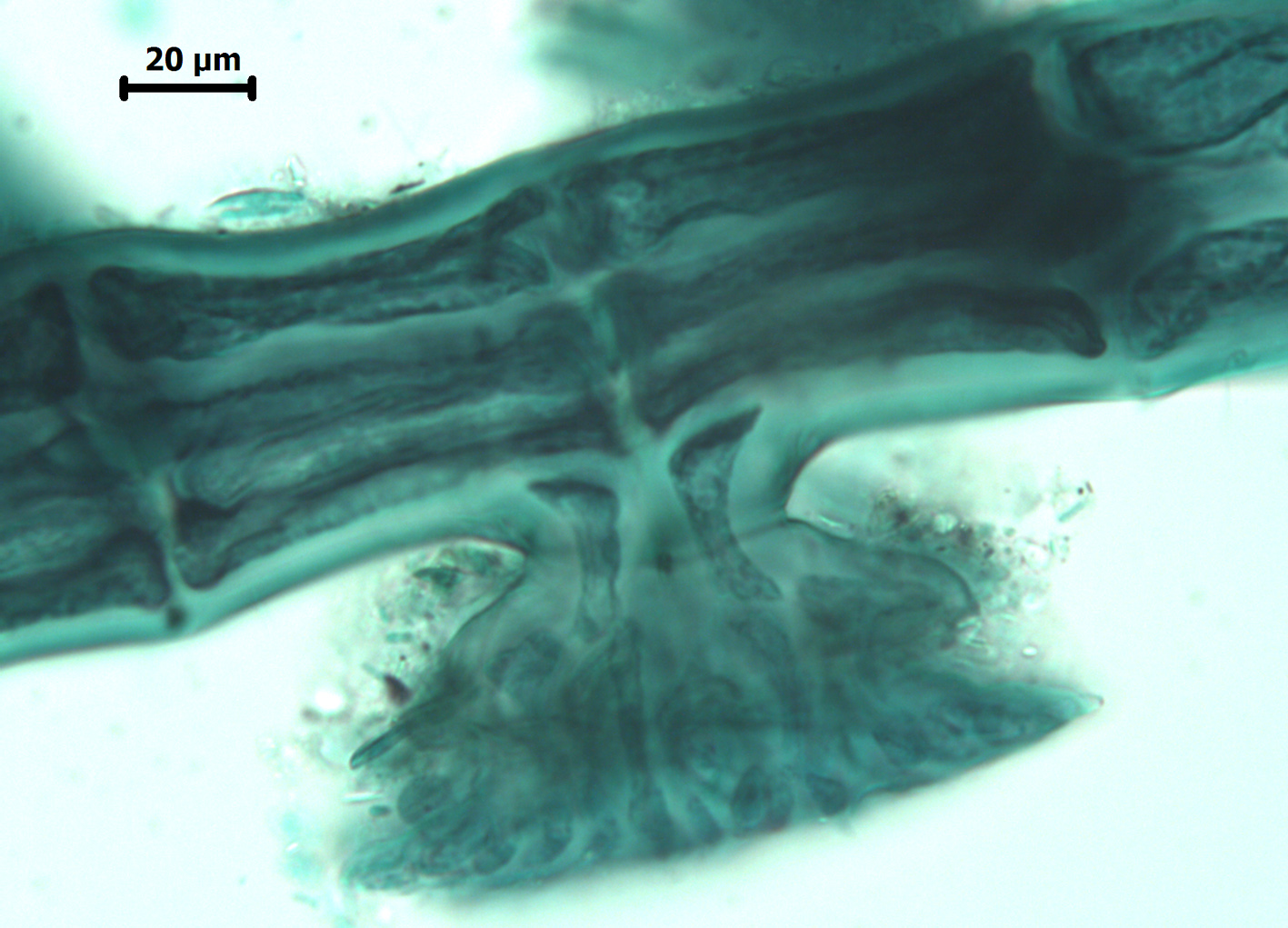
Aphanocladia ecorticata, attachment disc (stained slide).

Aphanocladia ecorticata, tetrasporangia (stained slide).
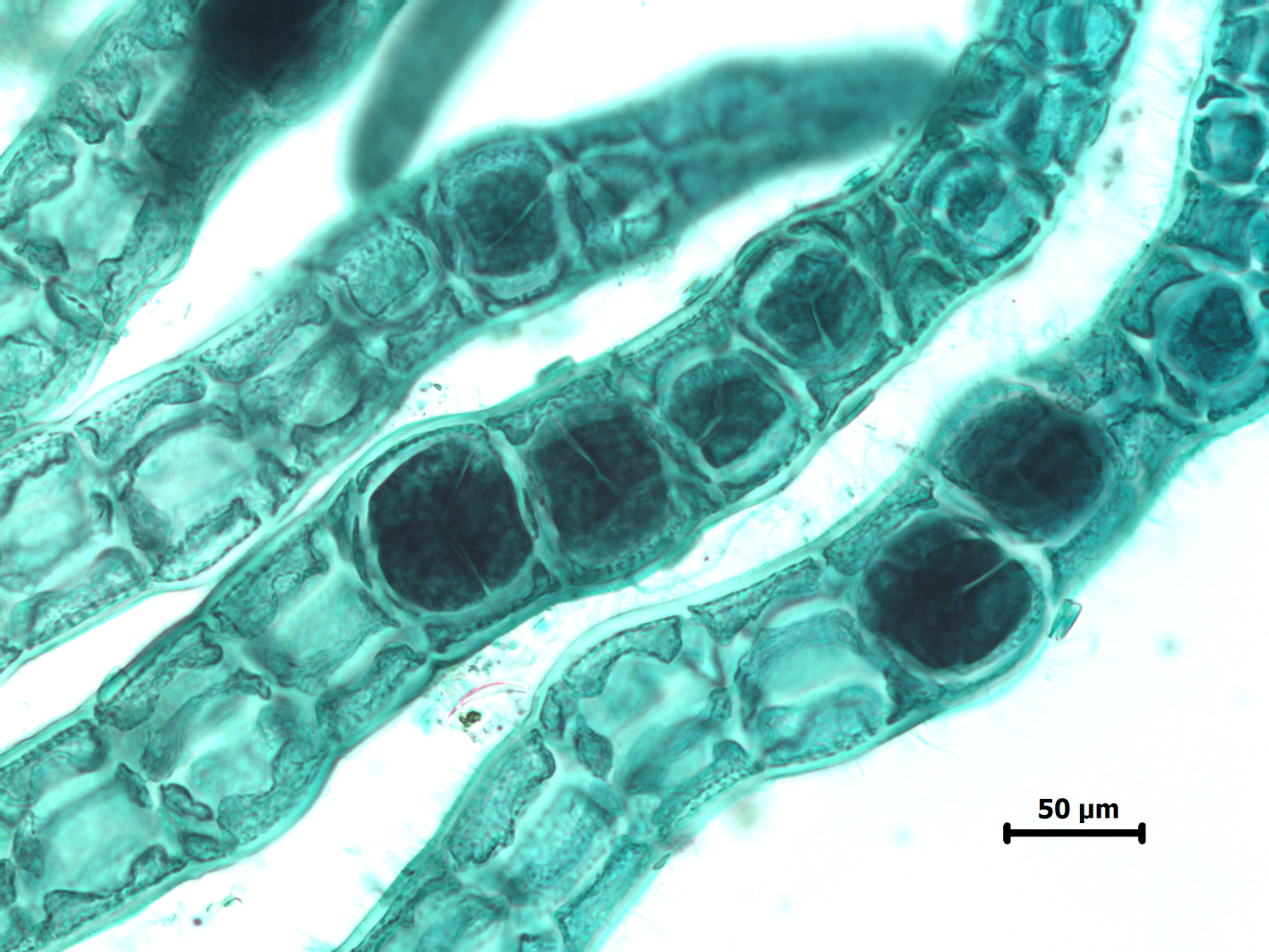
Aphanocladia ecorticata, detail of tetrasporangia (stained slide).
References Aphanocladia corticata
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. & R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Stegenga, H., Anderson, R.J. & Bolton, J.J. 2004. Aphanocladia ecorticata nov. sp. (Rhodophyta, Rhodomelaceae) from the South African south coast. Botanica Marina 47: 167-170.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 09 March 2026.