Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Ceramiales
Family Ceramiaceae
Ceramium planum Kützing 1849: 687
Plants on the south coast at the most a few cm tall (on the west coast up to 20 cm: Stegenga et al. 1997). Plants with a percurrent main axis, giving off laterals at intervals of 3 or 4 segments, strictly alternating and in one plane, re-branching several times; adventitious branchlets frequent. Plants without creeping parts. Thallus apices only slightly incurved. Main axis up to 400 µm in diameter (up to 1 mm on the west coast). Segments with on average six periaxial cells, each forming four or five derivatives, developing a full cortication (except for leaving a bare spot on the non-branching sides), about the same in acropetal and in basipetal direction. Central cells at maturity about twice as long as broad, somewhat constricted in the middle. Tetrasporangia completely exerted, mainly developing in the plane of branching of the plant, but at maximum development in a full circle. Tetrasporangia at maturity ca. 50 x 42 µm, tetrahedrally divided. Spermatangia developing on several sub-ultimate branches, mainly in the plane of branching.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
C.planum is primarily a west coast species extending into, but seen only rarely on the south coast Our (rare) records extend as far east as Bird Island (1-38). An epiphyte on larger seaweeds in the subtidal.
World distribution: Also recorded from Namibia (Rull Lluch 2002) and Antarctica (Papenfuss 1964). The alleged occurrence in Mozambique (Silva et al. 1996) is to be regarded with caution.
Type locality: Cape of Good Hope, South Africa (Silva et al. 1996).
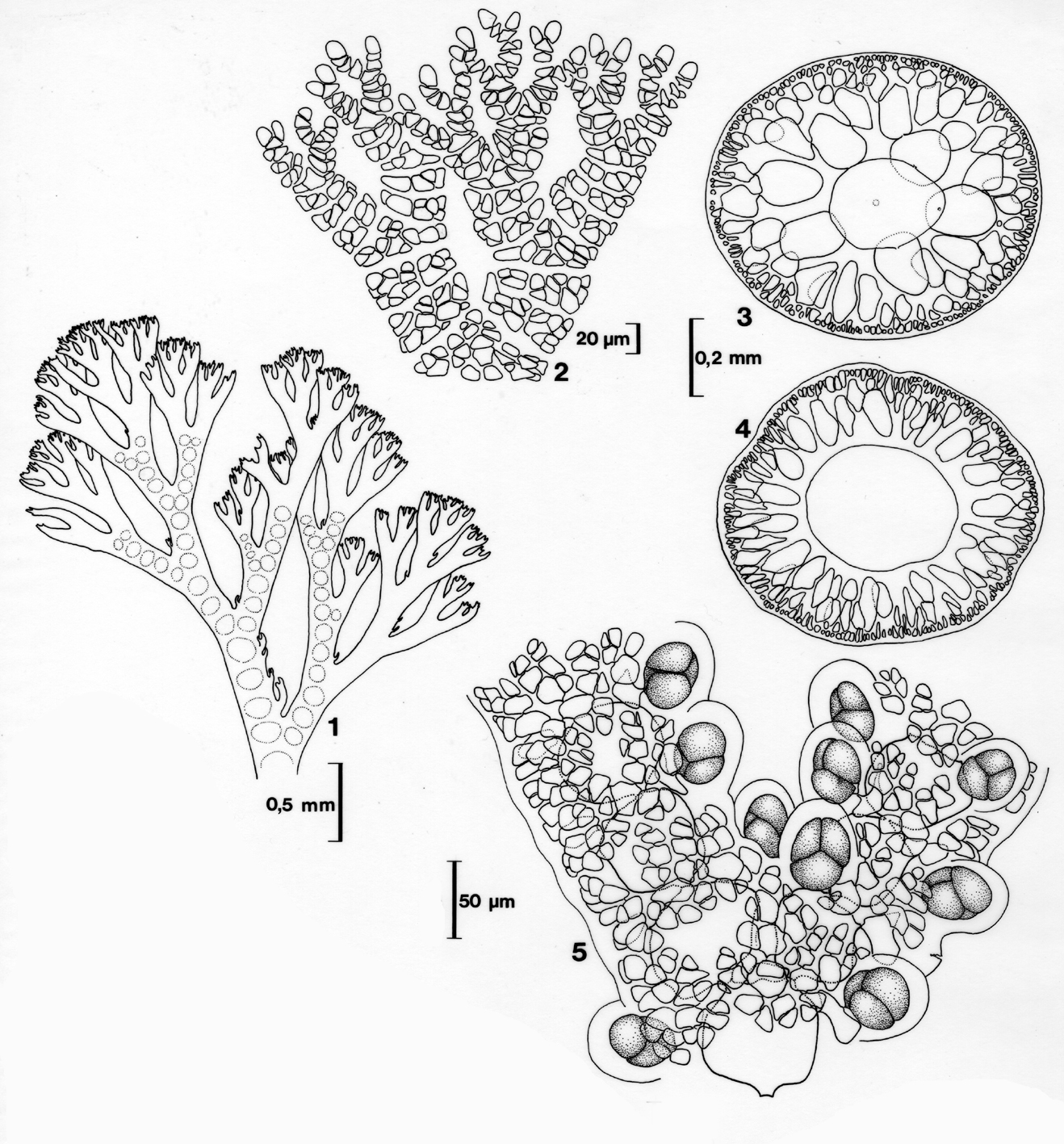
Ceramium planum. 1-2 Thallus apex. 3-4 Cross section of mature segments (in 3 showing periaxial cells). 5 Tetrasporangia. Reproduced from Stegenga et al. (1997).
References Ceramium planum
Kützing, F.T. 1849. Species algarum. pp. [i]-vi, [1]-922. Lipsiae [Leipzig]: F.A. Brockhaus.
Papenfuss, G.F. 1964. Catalogue and bibliography of Antarctic and Sub-Antarctic benthic marine algae. In: Bibliography of the Antarctic Seas. (Lee, M.O. Eds) Vol.1, pp. 1-76. Washington D.C.: American Geophysical Union.
Rull Lluch, J. 2002. Marine benthic algae of Namibia. Scientia Marina 66 (Supplement 3): 258 pp.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. 1996. Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. & R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 16 February 2026.