Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Ceramiales
Family Wrangeliaceae
Griffithsia confervoides Suhr 1840: 281
Plants partly creeping, the erect parts rarely over 3 cm high. Axes subdichotomously branched at intervals of one to five segments, basal ramifications often trichotomous. Cells very large, up to 0.5 (-1) mm in diameter and up to 2 mm long, uncorticated, elongate and slightly swollen, somewhat broader at the top than at the base. Apical cells about 100 µm across when cut off. Plants attached by rhizoids from the acropetal end of the cells of the basal (creeping) part.
Tetrasporangial clusters in several verticils on (swollen) subapical cells, surrounded by up to 10 involucral cells, the latter originating from the subapical cell. Sporangia of different ages sitting on a small stalk cell, measuring up to 100 X 75 µm, tetrahedrally divided. Male stands in similar arrangement as tetrasporangia, also surrounded by several involucral cells. Male stands profusely branched and reaching a size of ca. 250 µm. Female stands developing on a subterminal cell, as a rule when three sterile cells are present on it. Female fertile axis three-celled, the subapical cell with a supporting cell and a sterile pericentral cell; supporting cell with a sterile cell and a four-celled carpogonial filament. As the carpogonium is fertilized the number of involucrals gradually increases to about ten. At the same time a number of (small) single cells or short filaments are cut off from the basal cell of the fertile filament. Carposporophytes with as many as four (-five) roundish gonimoblasts of different age, carpospores up to ca. 50 µm in diameter.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Recorded along the whole South African coast (1-58). Rather common along the south coast, in the low eulittoral and sublittoral zones. Although sometimes epiphytic, there is no close relationship with certain substrata and the species grows on inanimate substrata as well.
World distribution: Southern African endemic, also recorded from Namibia and Mozambique.
Type locality: "Falsa-Bai"; "Kaffernküste", South Africa (False Bay?) (Silva et al. 1996).
Note: Griffithsia cymosa Simons, described from Namibia, is regarded as a synonym of G. confervoides.
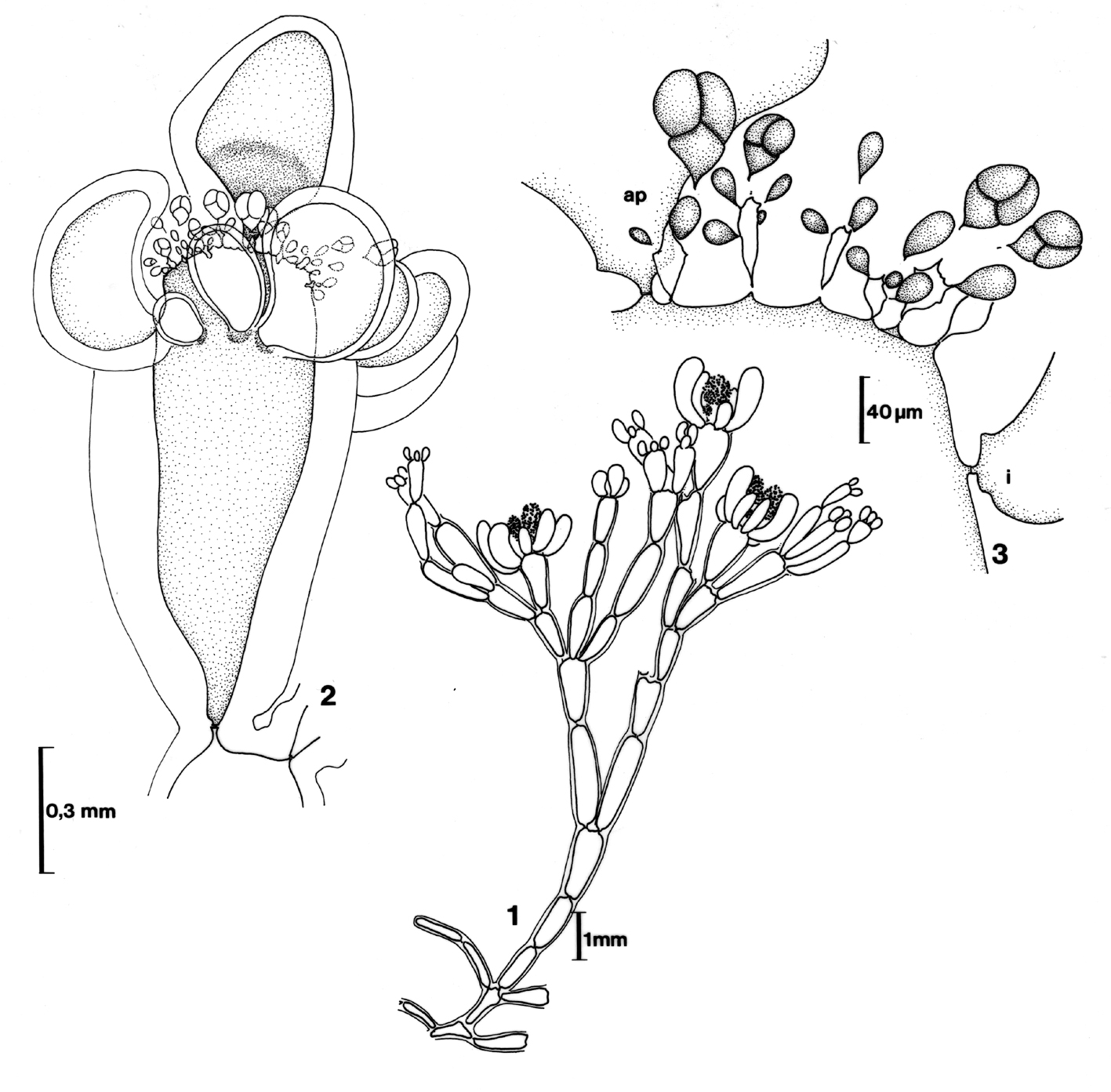
Griffithsia confervoides. 1 Habit (female). 2 tetrasporangial stand. 3 Detail of tetrasporangial stand. Reproduced from Stegenga et al. (1997).
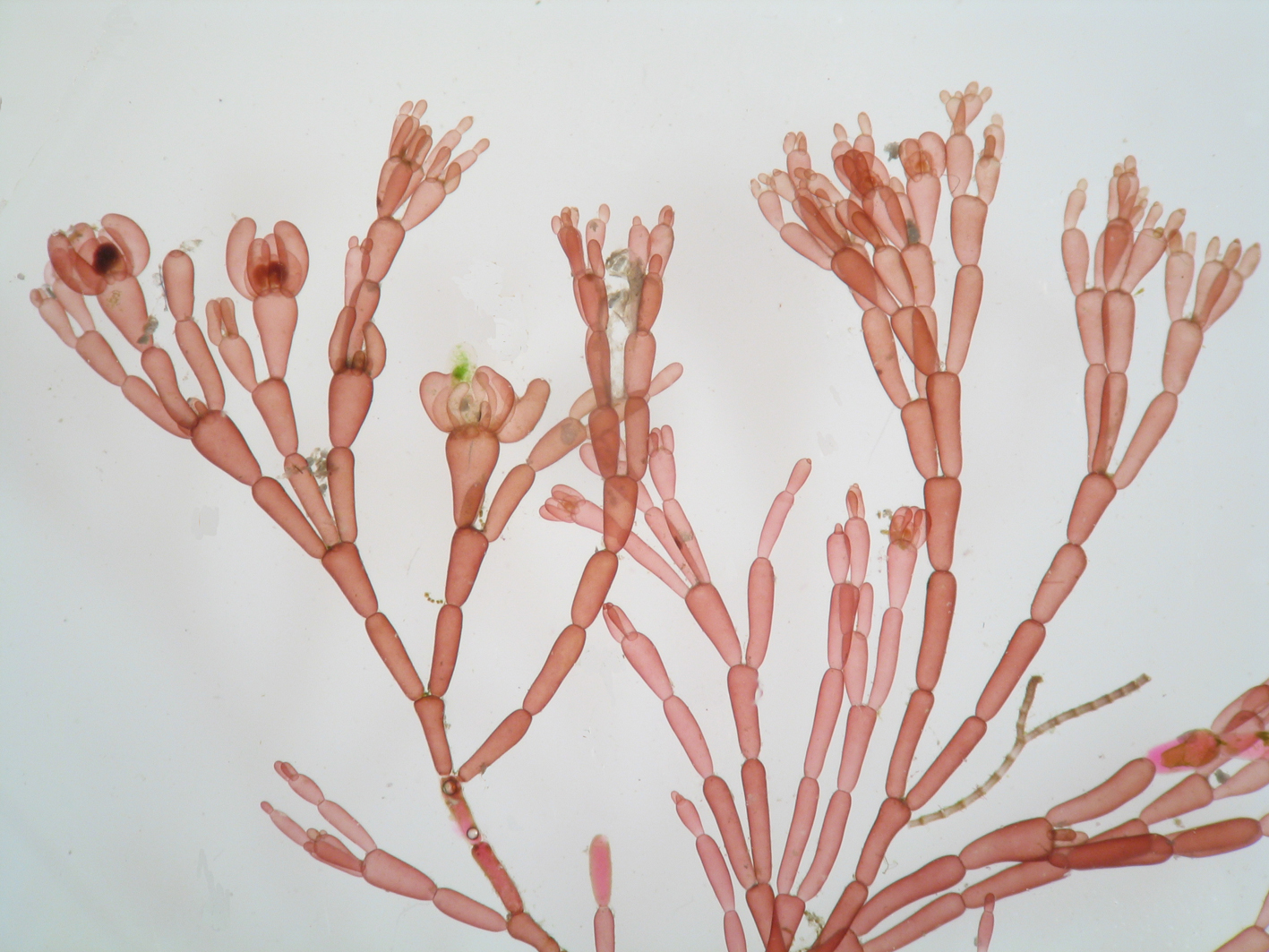

Griffithsia confervoides. Fresh specimen, De Hoop.
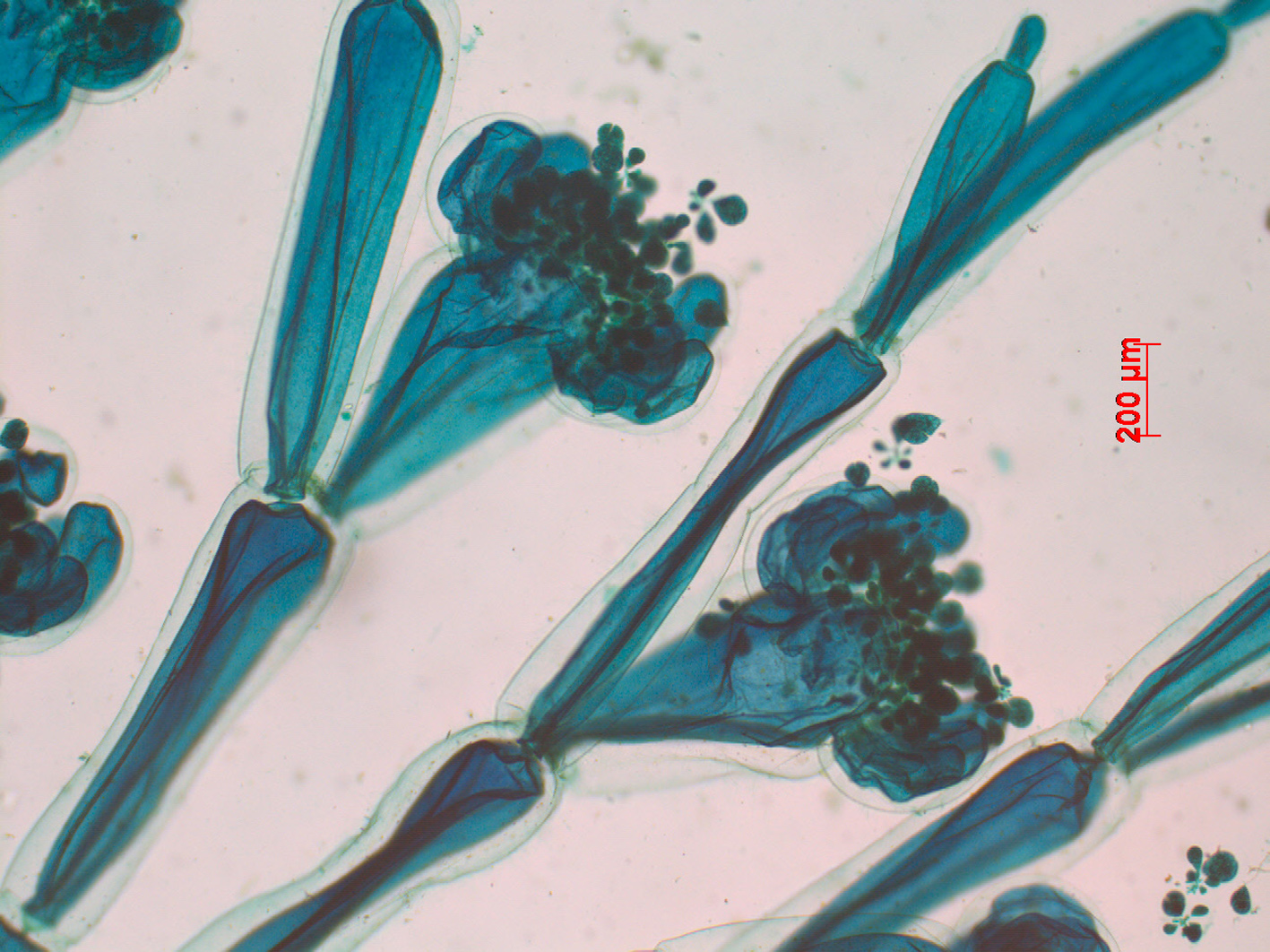
Griffithsia confervoides. Tetrasporangial stands, stained slide, Goukamma.
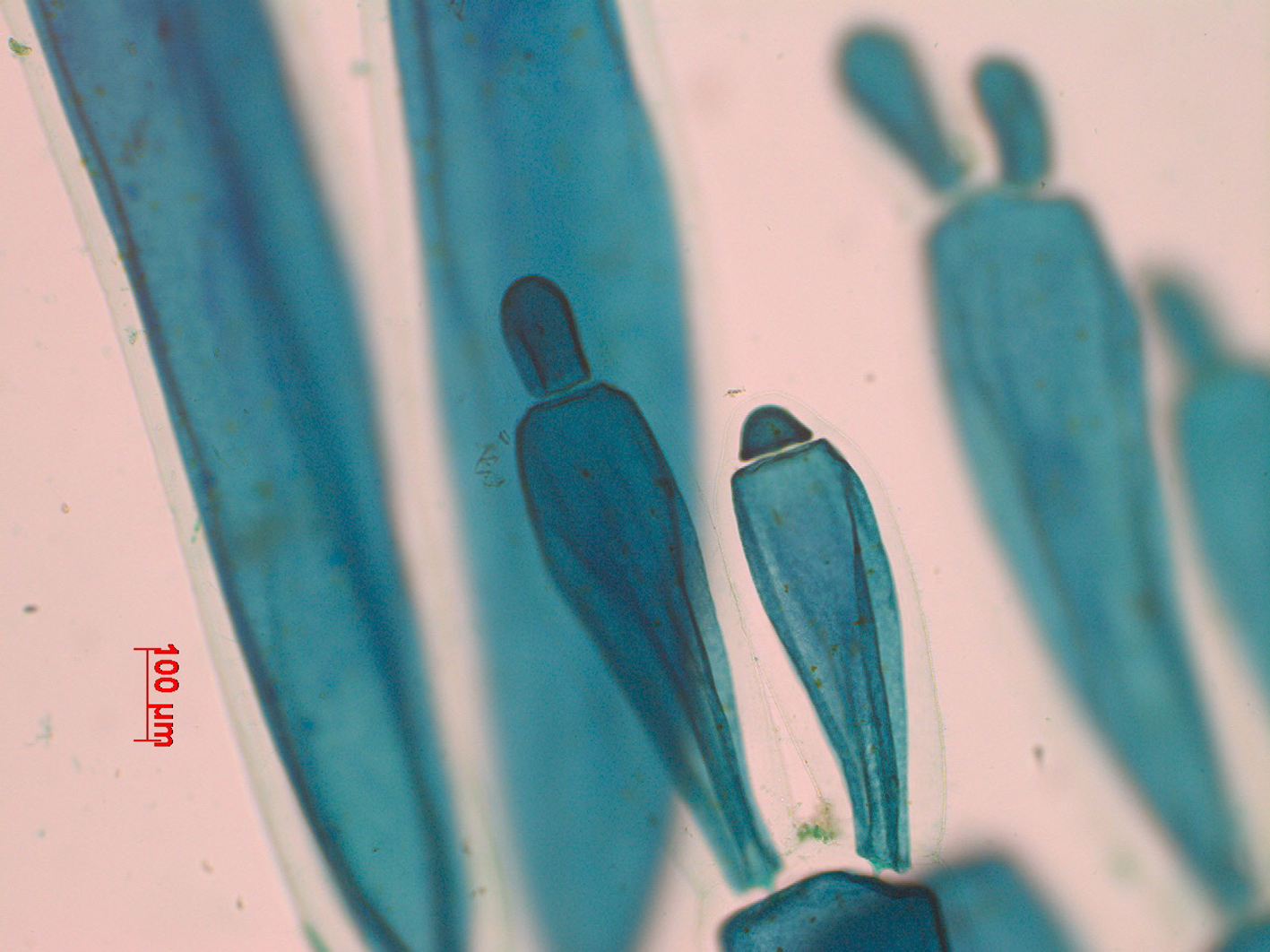

Griffithsia confervoides. Apical cells, stained slide, Goukamma.
References Griffithsia confervoides
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. 1996. Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. & R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Suhr, J.N. von 1840. Beiträge zur Algenkunde. Flora 23: 257-265, 273-282, 289-298.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 11 March 2026.