Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Gigartinales
Family Cystocloniaceae
Hypnea rosea Papenfuss 1947: 1-2; fig 1; pl. 2; figs 5-8
Plants bright red, up to 17 cm long, comprising irregularly branched axes usually tangled with other algae, main axis only distinguishable in parts of plant. Axes terete, about 1 mm diameter, set with numerous short spinous ramuli imparting spiky appearance. Terminal apices frequent, spinous, may broaden slightly, often hooked or sickle-shaped (falcate). In cross-section composed of inconspicuous central filament, surrounded by large (up to 250 µm diameter) medullary cells with smaller medullary cells towards periphery, encircled by a cortex of small pigmented cells. Tetrasporangial sori on terminal branchlets. Sexual reproductive structures not seen.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Collected from Table Bay eastward, throughout the south and east coasts (15-58).
Common in the lower eulittoral, eulittoral fringe and down to at least several metres depth; entangled in other algae.
World distribution: Also recorded from Mozambique, Kenya and Madagascar (Silva et al. 1996).
Type locality: Mtwalume, KZN, South Africa (Silva et al. 1996).
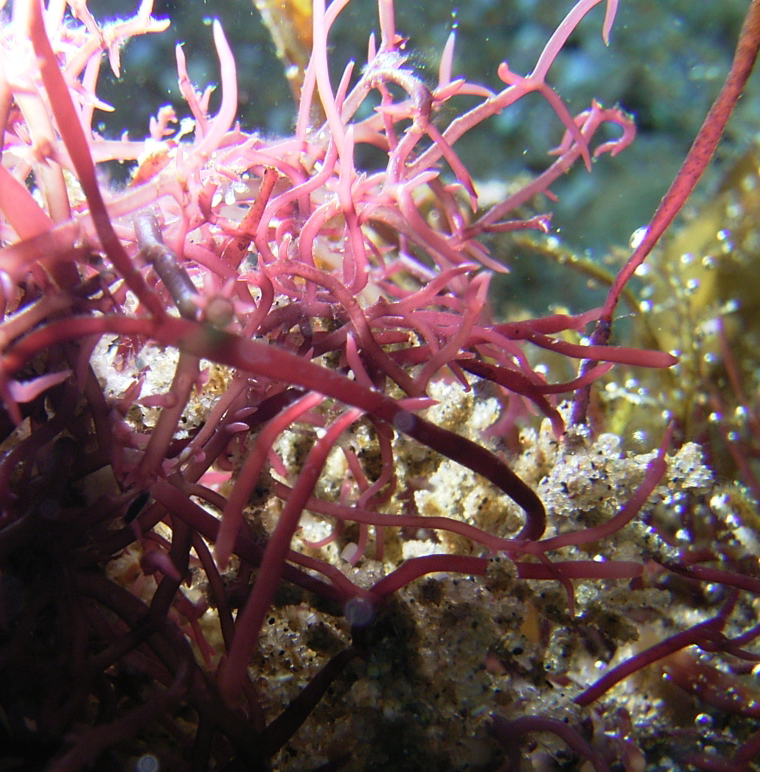

Hypnea rosea, entangled in rock-pool seaweeds.
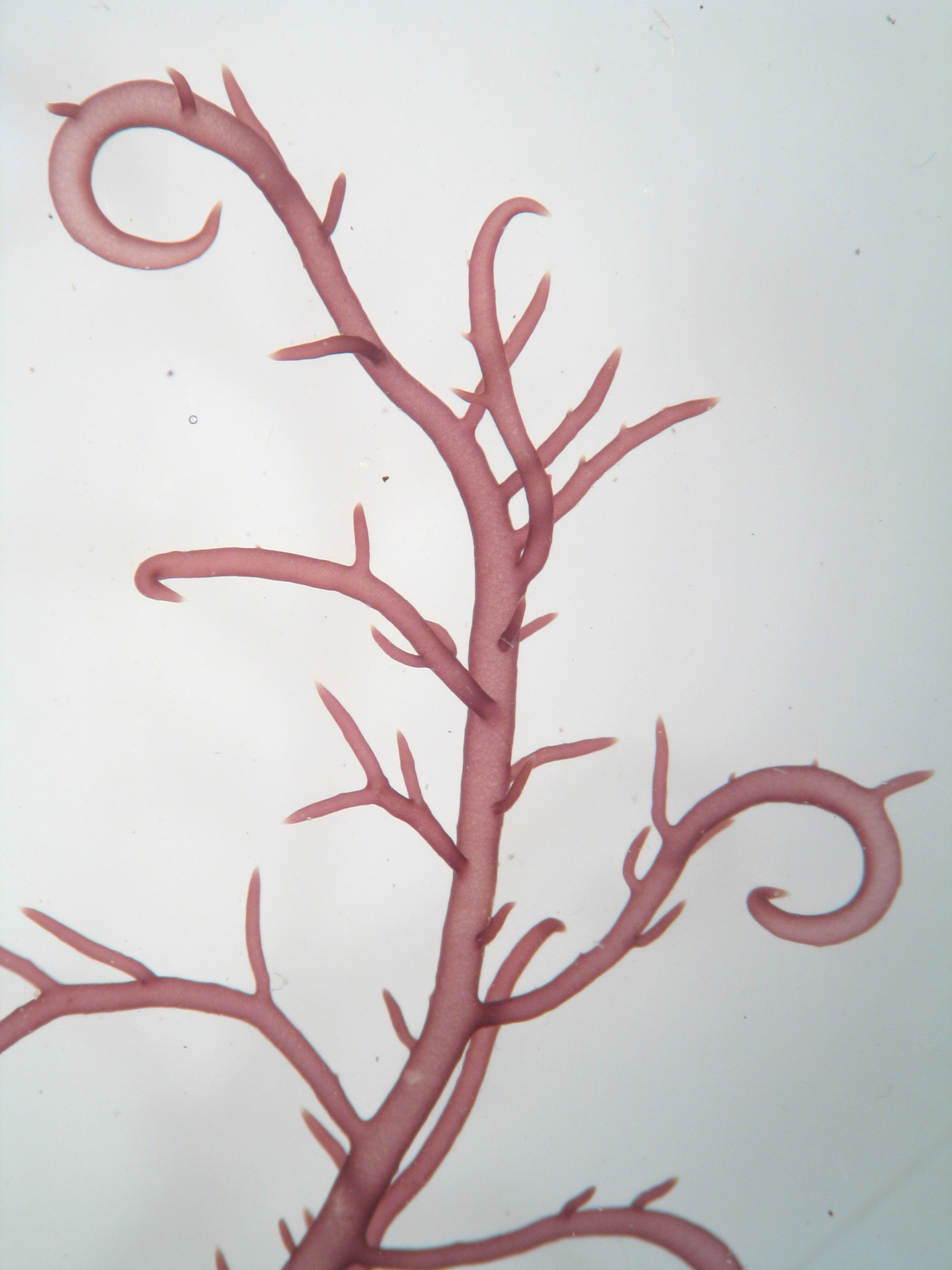
Hypnea rosea, detail showing slightly falcate branch-tips (fresh material, Port Alfred).
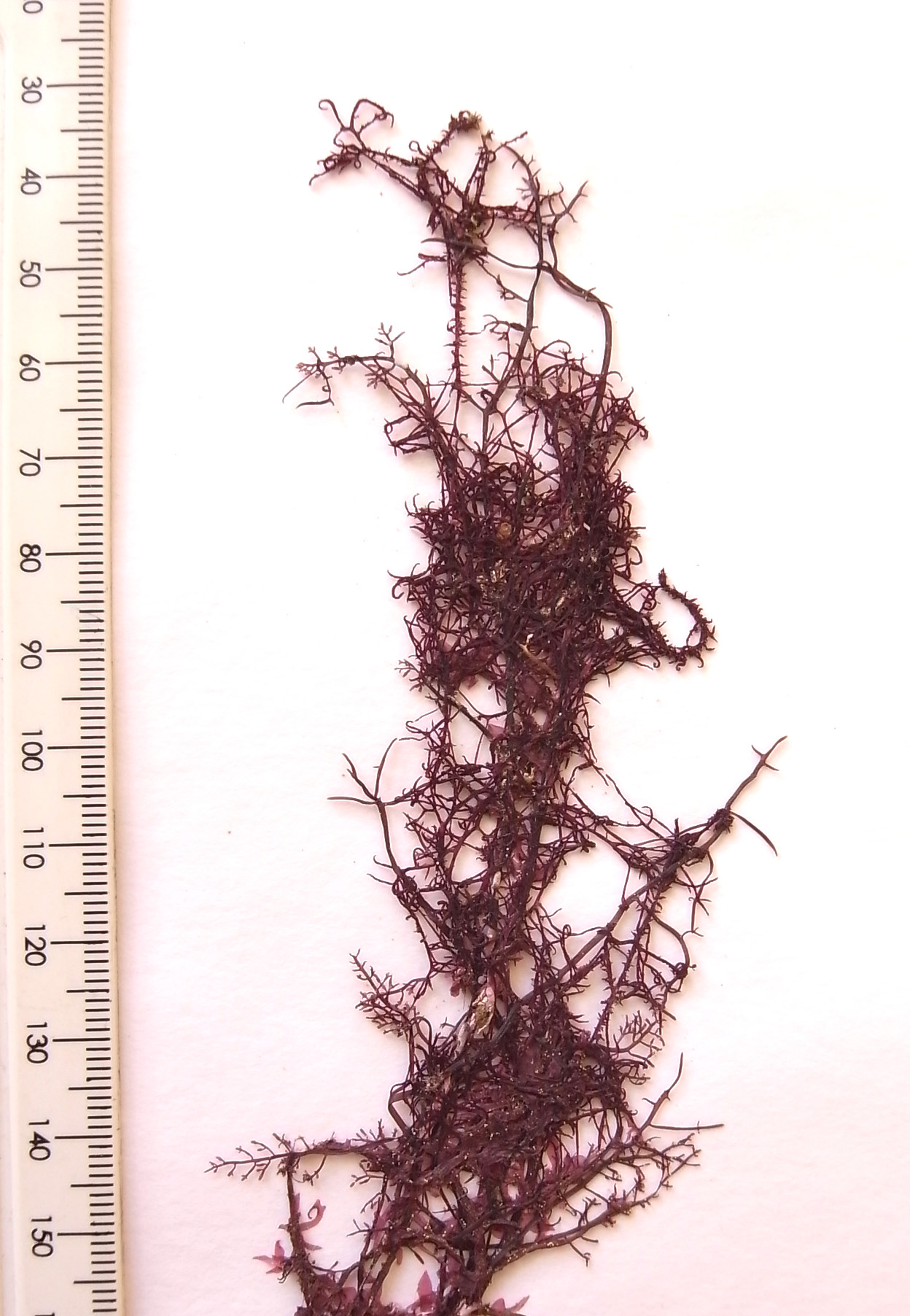

Hypnea rosea, specimen entangled with Gelidium abbottiorum, from Mbotyi (BOL).
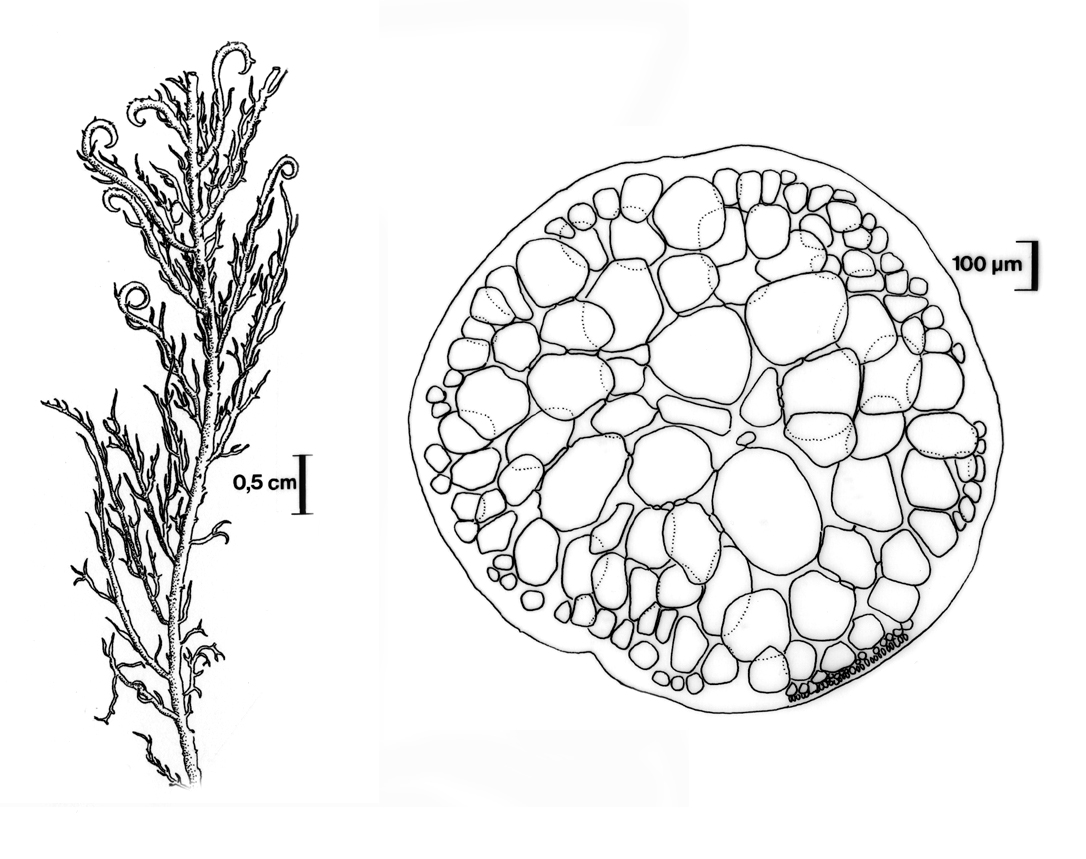
Hypnea rosea. Habit (upper); cross section (below). Reproduced from Stegenga et al. (1997).
References Hypnea rosea
Papenfuss, G.F. 1947. New marine algae from South Africa: I. University of California Publications in Botany 23: 1-15, Plates 1-4.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. 1996. Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. & R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 09 March 2026.