Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Corallinales
Family Corallinaceae
Subfamily Corallinoideae
Jania verrucosa Lamouroux 1816: 270, pl. 9, fig. 4 nom. rejic
See notes (below) on the application of this name.
Plants erect, up to 6 (-10) cm tall, pale reddish to pink, in sandy turfs or as larger individuals. Basal portions stoloniferous; erect axes regularly dichotomously branched in many planes, branch angle narrow (< 30o), branches often parallel near point of origin. Genicula inconspicuous. Intergenicula calcified, cylindrical to subcylindrical, about 500 µm diameter in proximal part of thallus, narrowing to about 150 µm near apices, 1-3 times longer than broad, those subtending branches somewhat broader and flattened. Tips of branches bleached, acute or bifurcating, sometimes with a median longitudinal depression. Fertile intergenicula triangular, usually forming base of dichotomy but sometimes terminal; conceptacle swollen with pore on upper edge of geniculum.
Collections, ecology and distribution
Common in sand-binding turfs, but may occur as larger, individual plants. Epilithic, occasionally epiphytic, in rock pools, sublittoral fringe and sublittoral zone to at least 8m depth. Typically in sandy, wave-exposed environments. Found from False Bay eastward to northern KwaZulu-Natal (17-58), but see notes 1-3 below.
World distribution: Widespread in warm temperate and tropical regions, but taxonomic and nomeclatural uncertainties mean that distributions cannot be established without further study (Guiry & Guiry 2016).
Type locality: Amérique méridionale (“Central America”) (Silva et al. 1996), but see notes.
Notes: 1. This name is “of uncertain nomenclatural application” (MD Guiry in Guiry & Guiry 2016) and no clear type can be found– see Woelkerling et al. (2015).
2. We use the name to include entities previously recorded as Jania crassa Lamouroux and J. natalensis Harvey.
3. A recent genetic barcoding study of South African articulated corallines (Kogame et al. 2017) showed that even among a limited sample of specimens identified as J. verrucosa, there were two distinct entities.
4. J. verrucosa differs from Jania adhaerens in having larger dimensions and narrower branch angles.
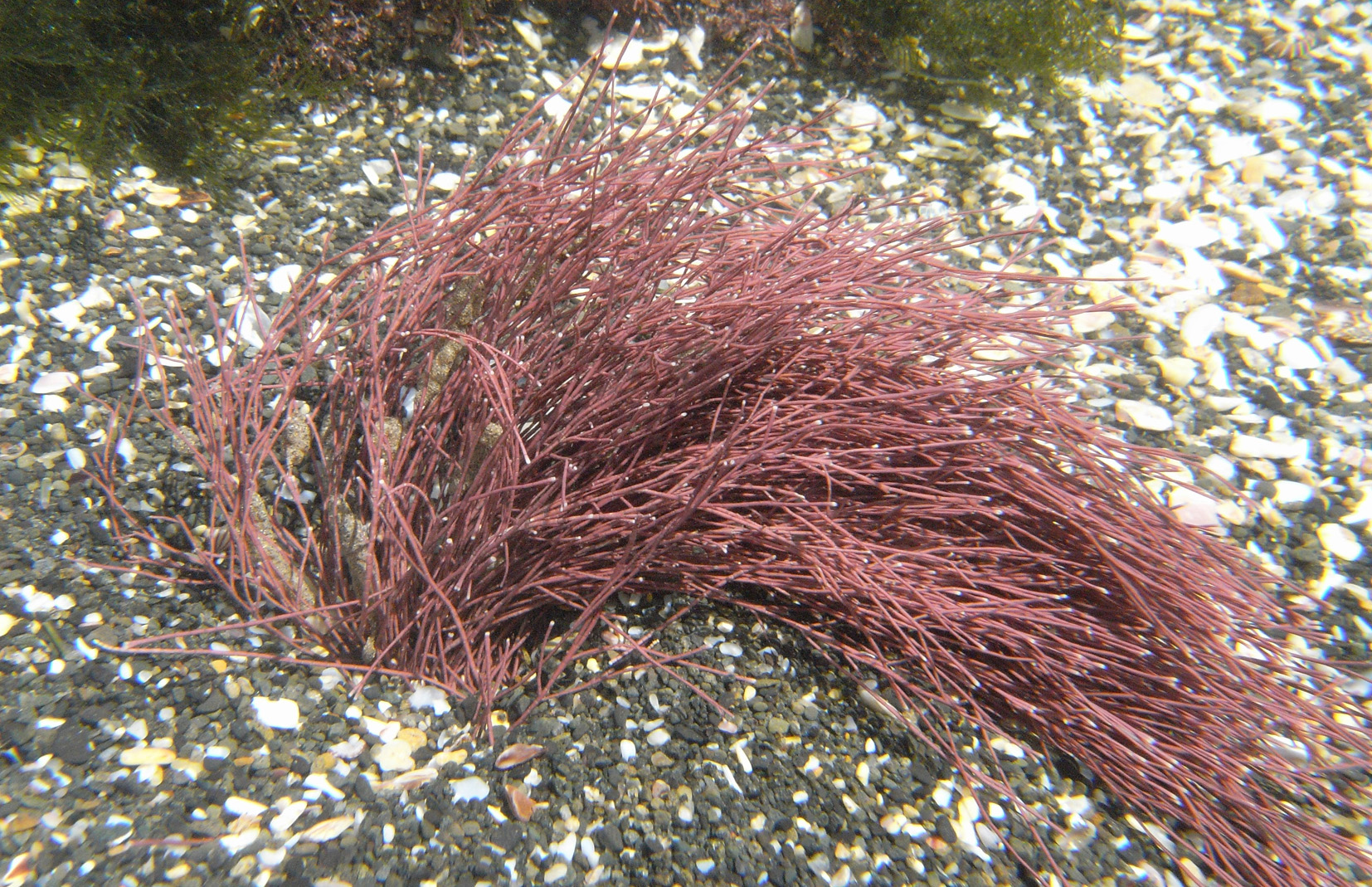

Jania verrucosa, Qologha, east of Kei Mouth.
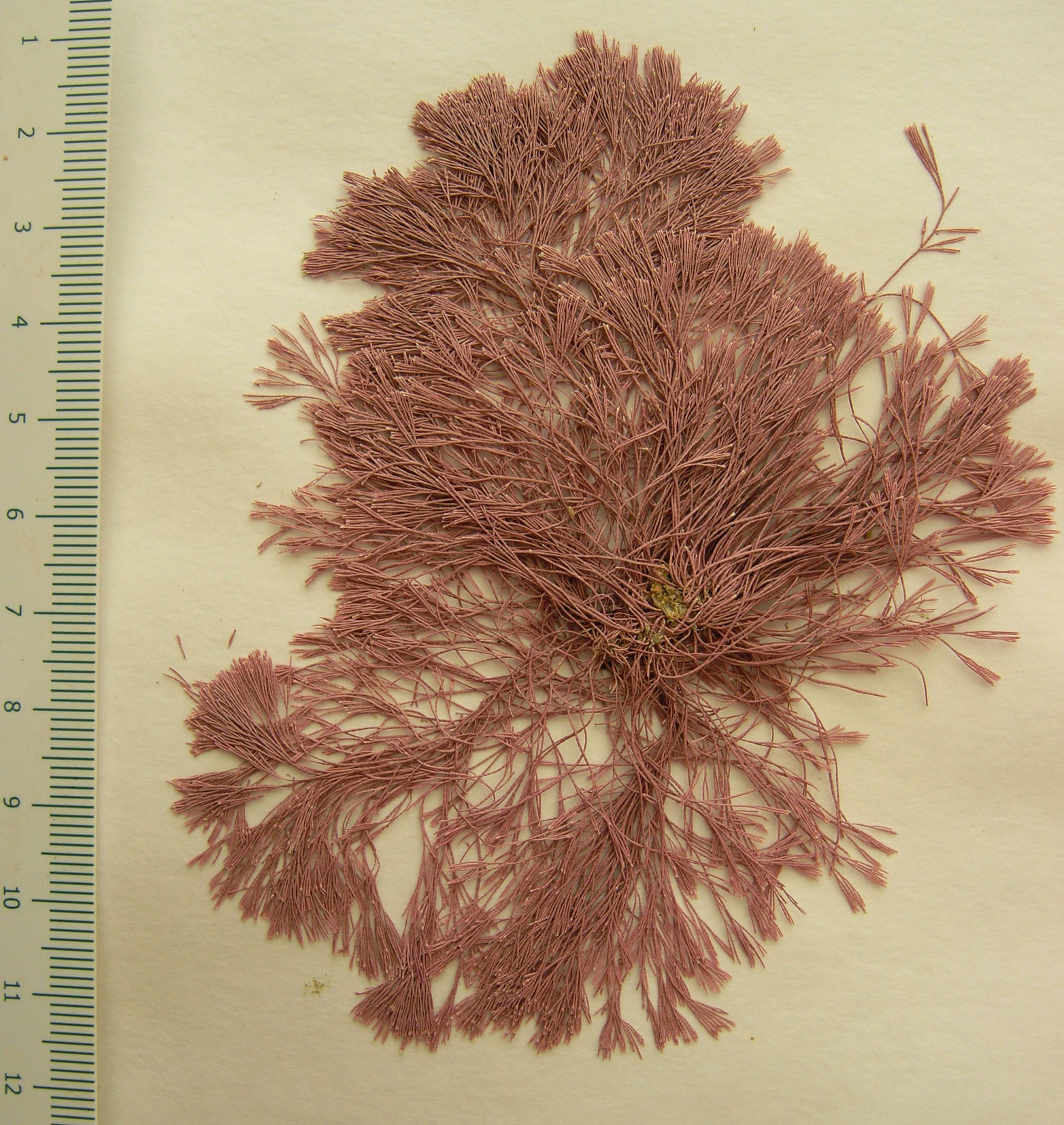

Jania verrucosa, herbarium specimen.
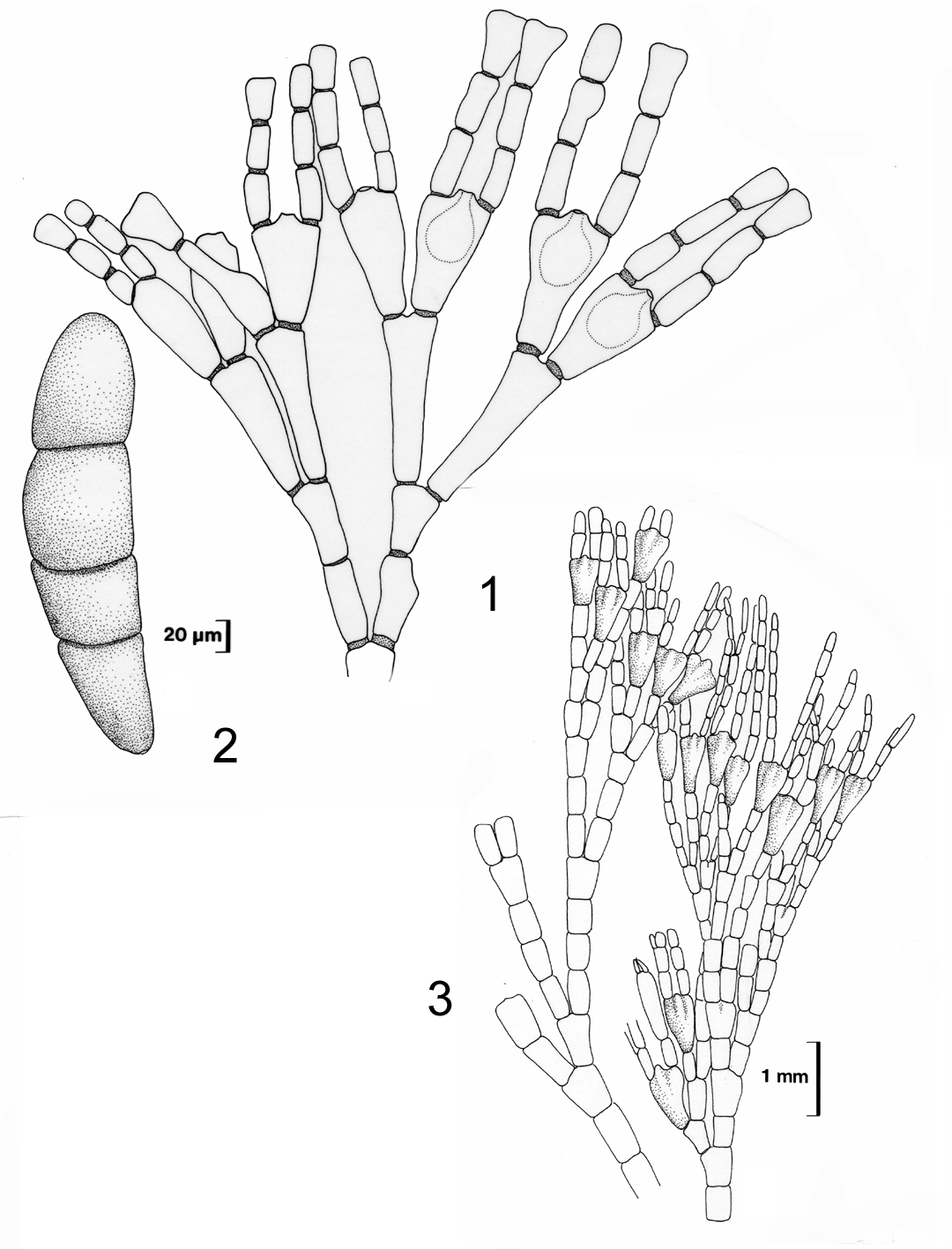
Jania verrucosa. 1. Detail of (small) plant with tetrasporangial conceptacles. 2. Tetrasporangium. 3. Habit of large plant (apex). Reproduced from Stegenga et al. (1997).
References Jania verrucosa
Guiry MD, in Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. 2016. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched on 10 October 2016.
Kogame, K., Uwai, S., Anderson, RJ., Choi, H.-G. & J.J. Bolton. 2017. DNA barcoding of South African geniculate coralline red algae (Corallinales, Rhodophyta). South African Journal of Botany 108: 337-341.
Lamouroux J. V. 1816. Histoires des polypieres coralligènes flexibles vulgairement nommés zoophytes. Caen, 559 pp., pl. 1-19.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. (1996). Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. and R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Woelkering, W.J., Harvey, A.S. & Reviers, B. de (2015). Jania pedunculata (Rhodophyta: Corallinaceae): Typification, nomenclature, and taxonomic status relative to J. crassa, J. verrucosa sensu Johansen & Womersley, and J. ungulata. Taxon 64(6): 1280-1293.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 09 March 2026.