Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Ceramiales
Family Rhodomelaceae
Microcolax africanus M.T.Martin & M.A.Pocock 1953: 56-58, fig. 5; pl. 12: figs a-c (as 'africana')
Parasitic on a species of Streblocladia, as small round pustules on the filaments of the host, comprising short branched axes radiating from the host tissue and attached by penetrating rhizoidal branches. Vegetative filaments with four pericentral cells, occasionally corticated basally. Free axes with short stalks and profuse distal branching. Tetrasporangia in cylindrical stichidia, usually developing from one row of pericentral cells and arranged in single row. For rurther details see Martin & Pocock (1953).
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Recorded from the type locality (Cove Rock, East London)(41).
World distribution: South African endemic.
Type locality: Cove Rock, near East London, South Africa (Martin & Pocock (1953).
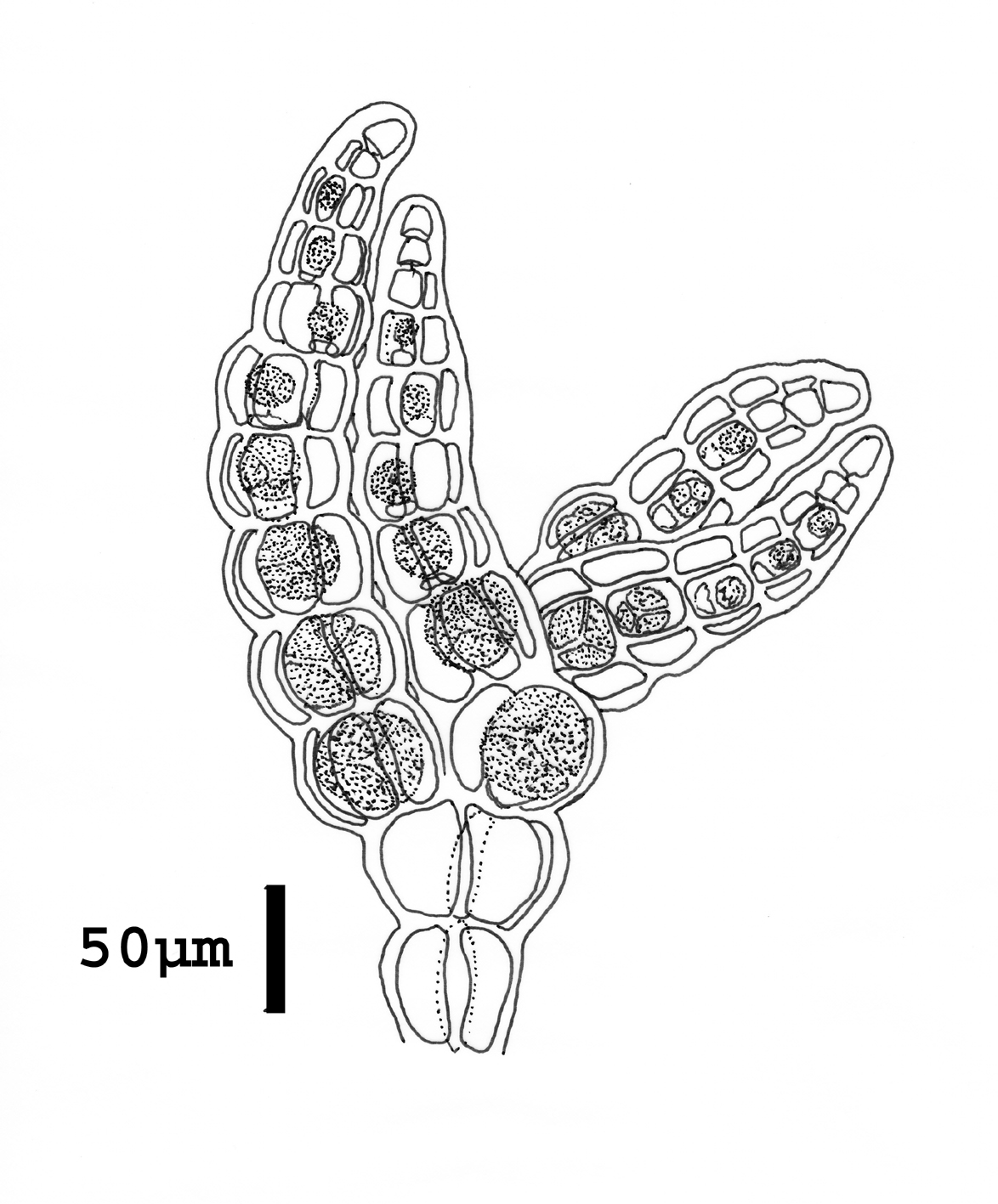
Microcolax africanus, tetrasporic stichidia. Re-drawn from Martin & Pocock (1953).
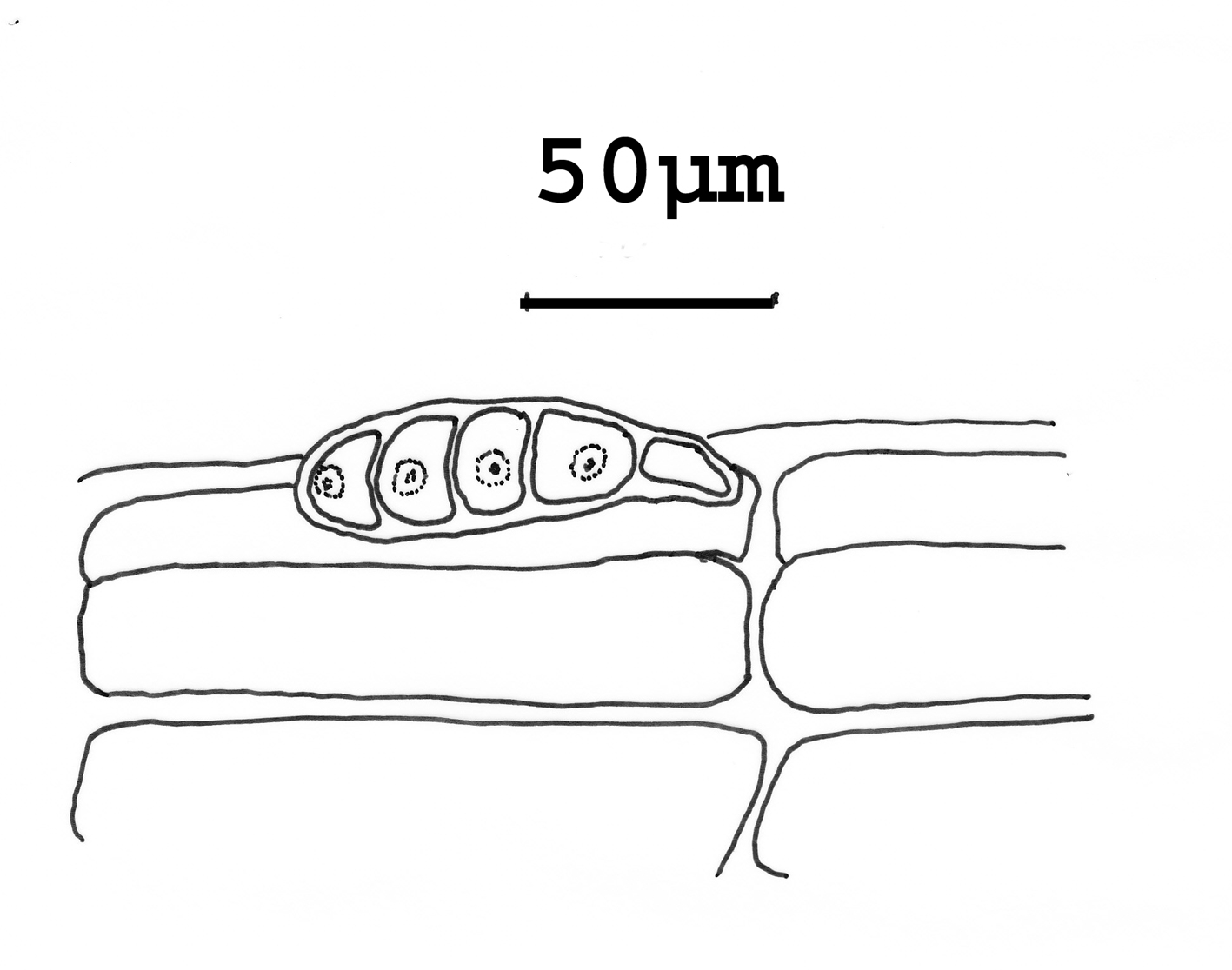
Microcolax africanus, germinating sporeling on Streblocladia tenuissima. Re-drawn from Martin & Pocock (1953) (as M. africanus).
References Microcolax africanus
Martin, M.T. & Pocock, M.A. 1953. South African parasitic Florideae and their hosts. 2. Some South African parasitic Florideae. Journal of the Linnean Society of London, Botany 55: 48-64, 7 figs, pls 10-12.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 11 March 2026.