Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Ceramiales
Family Rhodomelaceae
Placophora binderi (J.Agardh) J.Agardh 1863: 1138-1139
Plants epiphytic or epizoic, dark red to blackish, forming a foliose crust up to a few cm in diameter, with lobed margins. Structure of laterally fused polysiphonous branches arising usually from every segment, with two branches to the left and two to the right. Segments with five pericentral cells, two dorsal, three ventral. Fertile polysiphonous filaments up to 0.5 mm long, arising in usually dense tufts along thallus margins. Tetrasporangia ca 55 µm in diameter, in all but 3-4 most proximal segments of filaments up to 25 segments long. Spermatangial heads arranged radially on short free filaments , conical, ca 50 x 150 µm. Cystocarps globose to ovate, on short free filaments.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Recorded from the Cape Peninsula to northern KwaZulu-Natal (17-58). Epiphytic, usually on Codium species (e.g. C. platylobuim, C. duthiae), also on other larger algae including Zonaria subarticulata; epizoic on Pyura stolonifera.
Worldwide distribution: Also recorded from Inhaca Island (Mozambique), Japan, Australia, New Zealand, Indonesia, Peru and Tristan da Cunha (Guiry & Guiry 2013).
Type locality: Cape of Good Hope, South Africa (Silva et al. 1996).
Note: P. binderi is described in detail by Scagel (1953).
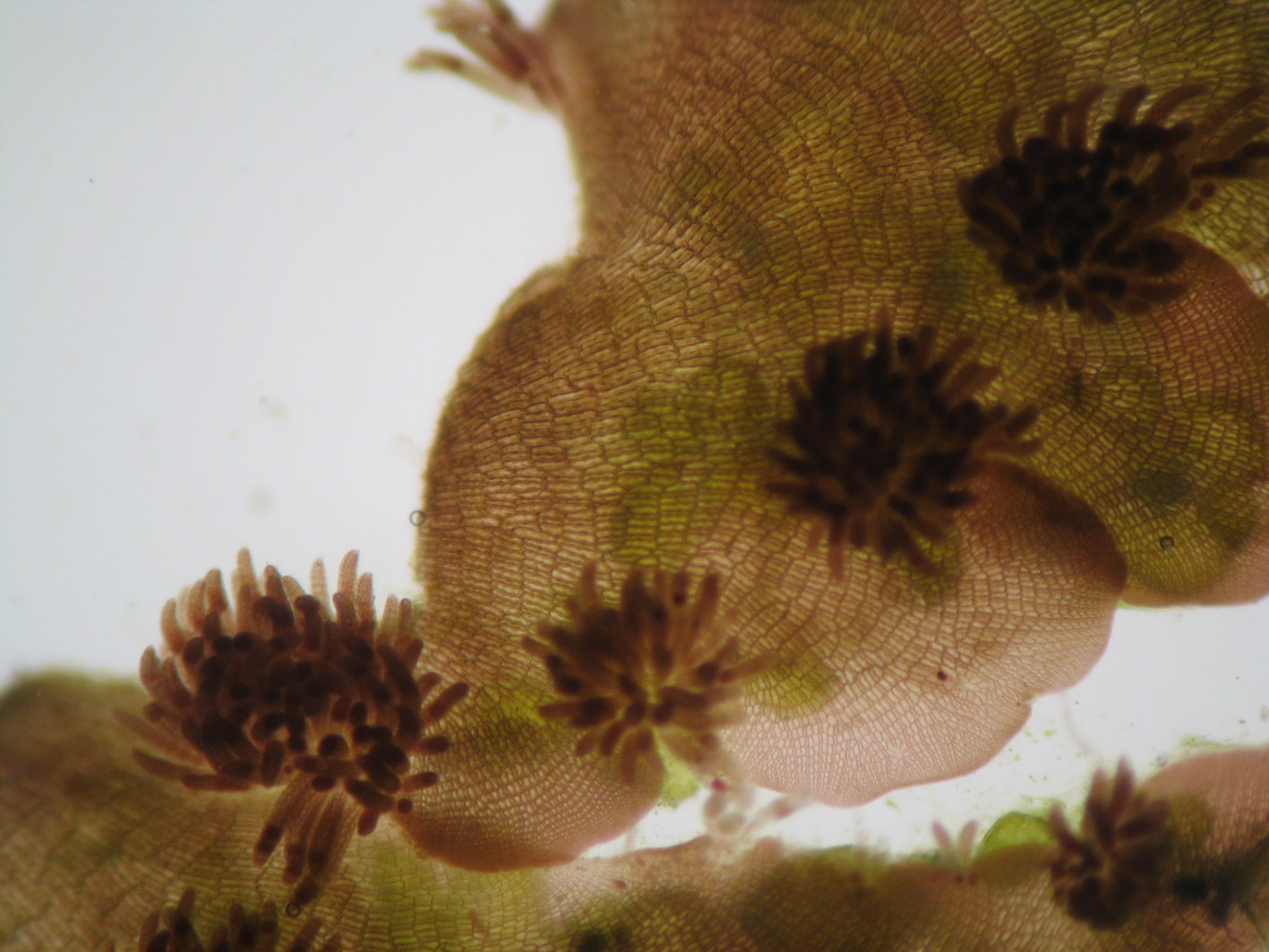

Placophora binderi: foliose thallus with tetrasporangial filaments. Removed from surface of a Codium sp., along with some of the (green) utricles.
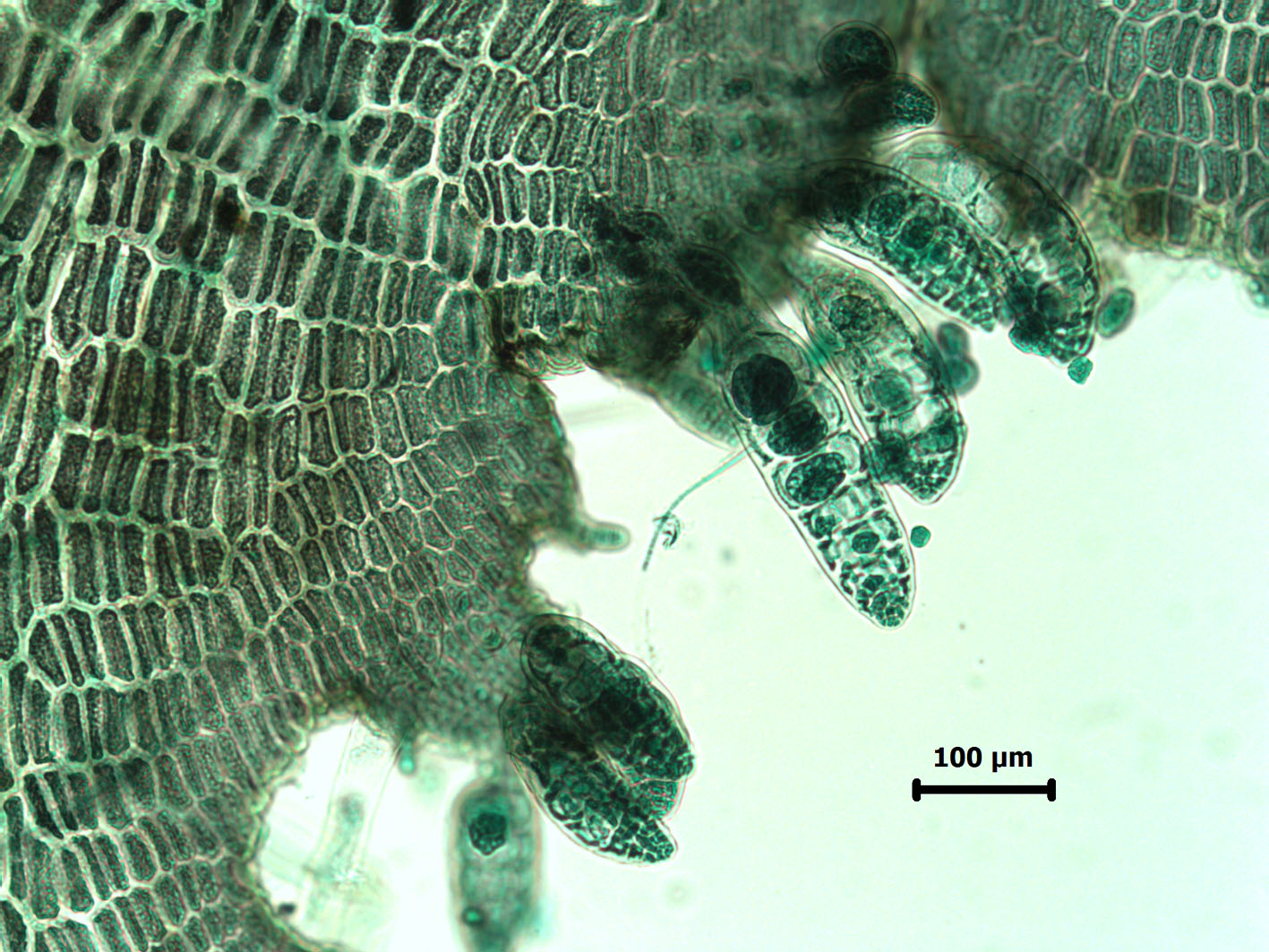

Placophora binderi: tetrasporangial filaments on thallus – stained slide material.
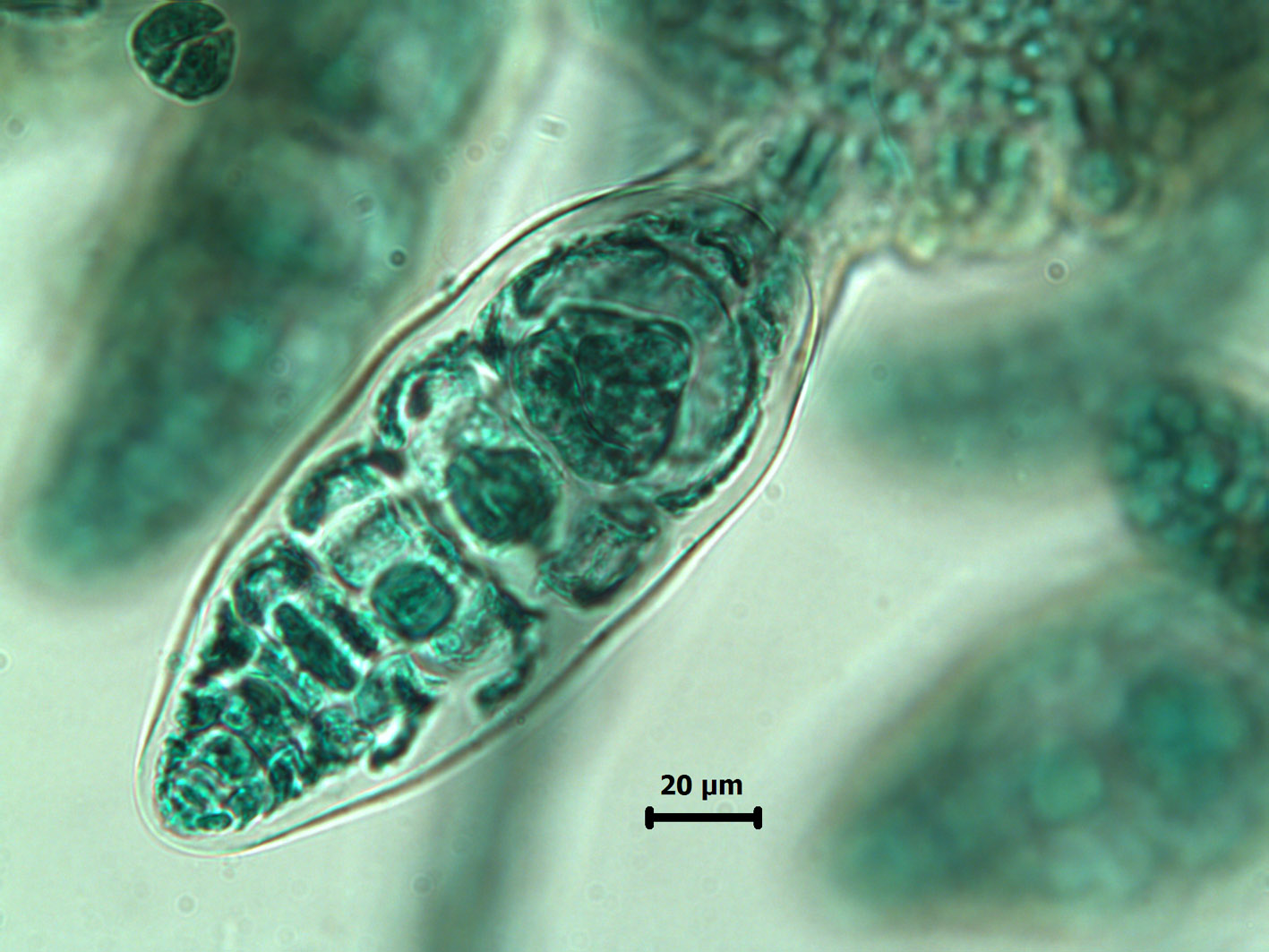
Placophora binderi: tetrasporangium – stained slide material.
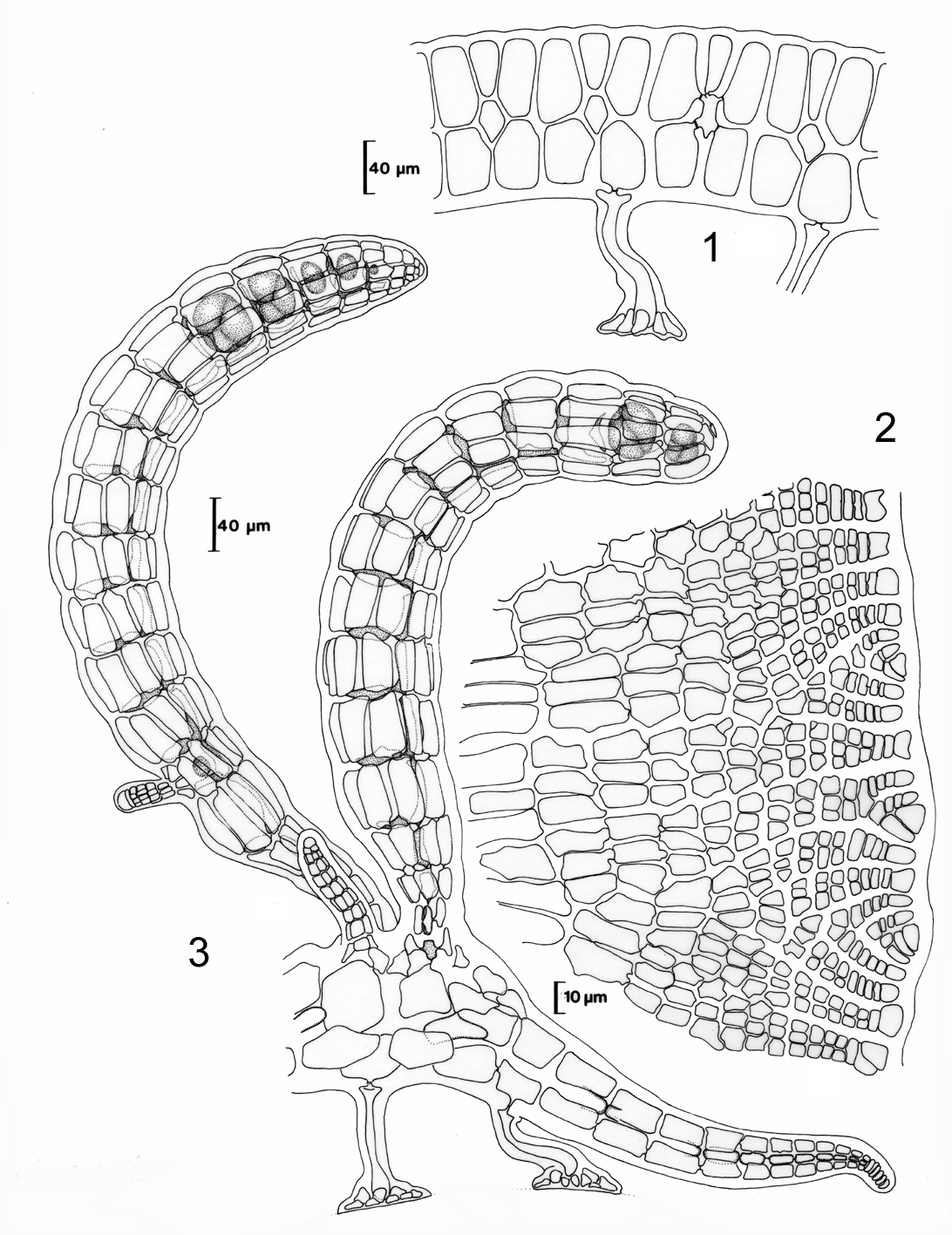
Placophora binderi. 1. Cross section of foliaceaous thallus. 2. Thallus margin in surface view. 3. Tetrasporiferous filaments (prostrate thallus in oblique section). Reproduced from Stegenga et al. (1997).
References Placophora binderii
Agardh, J.G. 1863. Species genera et ordines algarum, seu descriptiones succinctae specierum, generum et ordinum, quibus algarum regnum constituitur. Volumen secundum: algas florideas complectens. Part 2, fasc. 3. pp. 787-1138, 1158-1291. Lundae [Lund]: C.W.K. Gleerup.
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. 2013. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched on 20 May 2013.
Scagel R. F. 1953. A morphological study of some dorsiventral Rhodomelaceae. University of California Publications in Botany 27: 1-108.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. 1996. Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. & R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 11 March 2026.