Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Gigartinales
Family Plocamiaceae
Plocamium rigidum Bory de Saint-Vincent in Bélanger & Bory de Saint-Vincent 1834: 164
Plants red to reddish-brown, up to 20 cm tall, largely complanate, profusely branched, rather cartilaginous. Axes terete to slightly compressed, up to 1 mm wide. Groups of laterals comprising one simple and one or two compound branchlets; young laterals somewhat incurved, simple branchlets awl-shaped, up to 0.5 mm wide at the base. Tetrasporangial stichidia borne on ultimate or sometimes penultimate compound branchlets, simple and rather stout when young, with one or two bifurcations when mature, up to 100 µm in diameter.
Collections ecology and regional distribution
Recorded from Namibia, along the South African west and south coasts, to Palm Beach (Port Edward area) in southern Kwazulu-Natal (1-48). Common in the sublittoral fringe, rock pools and the shallow sublittoral zone.
World distribution: Also recorded from Namibia and from Amsterdam Island in the Indian Ocean (Silva et al. 1996).
Type locality: “Cape of Good Hope” (Silva et al. 1996).
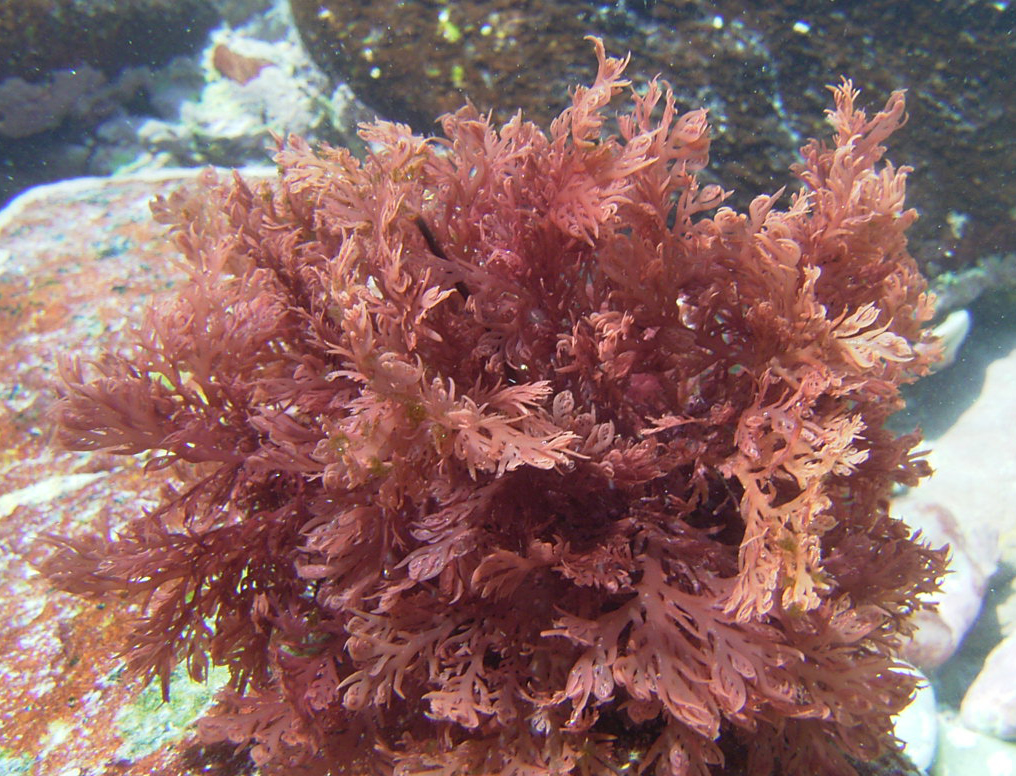

Plocamium rigidum, Struisbaai.
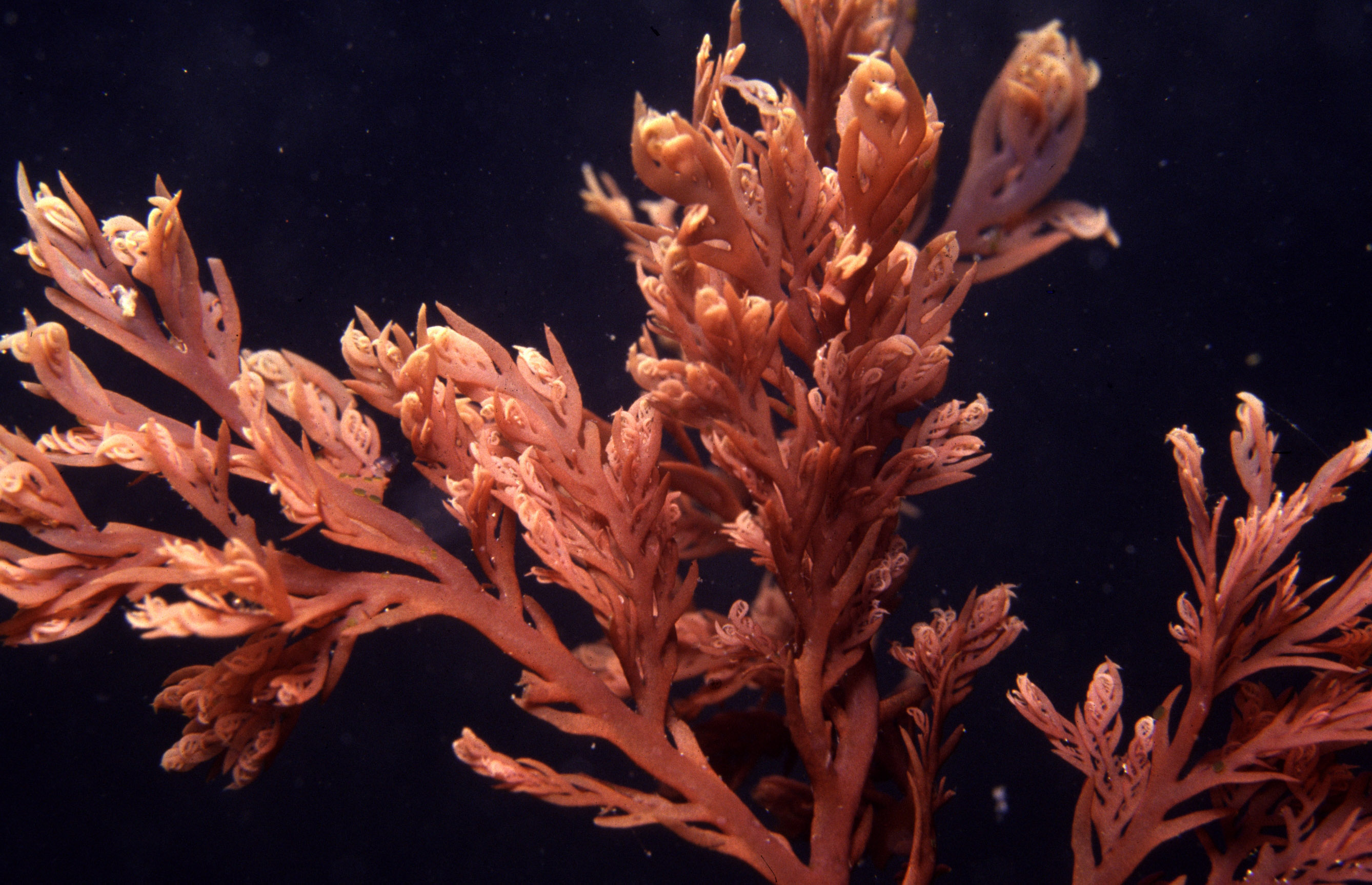

Plocamium rigidum.
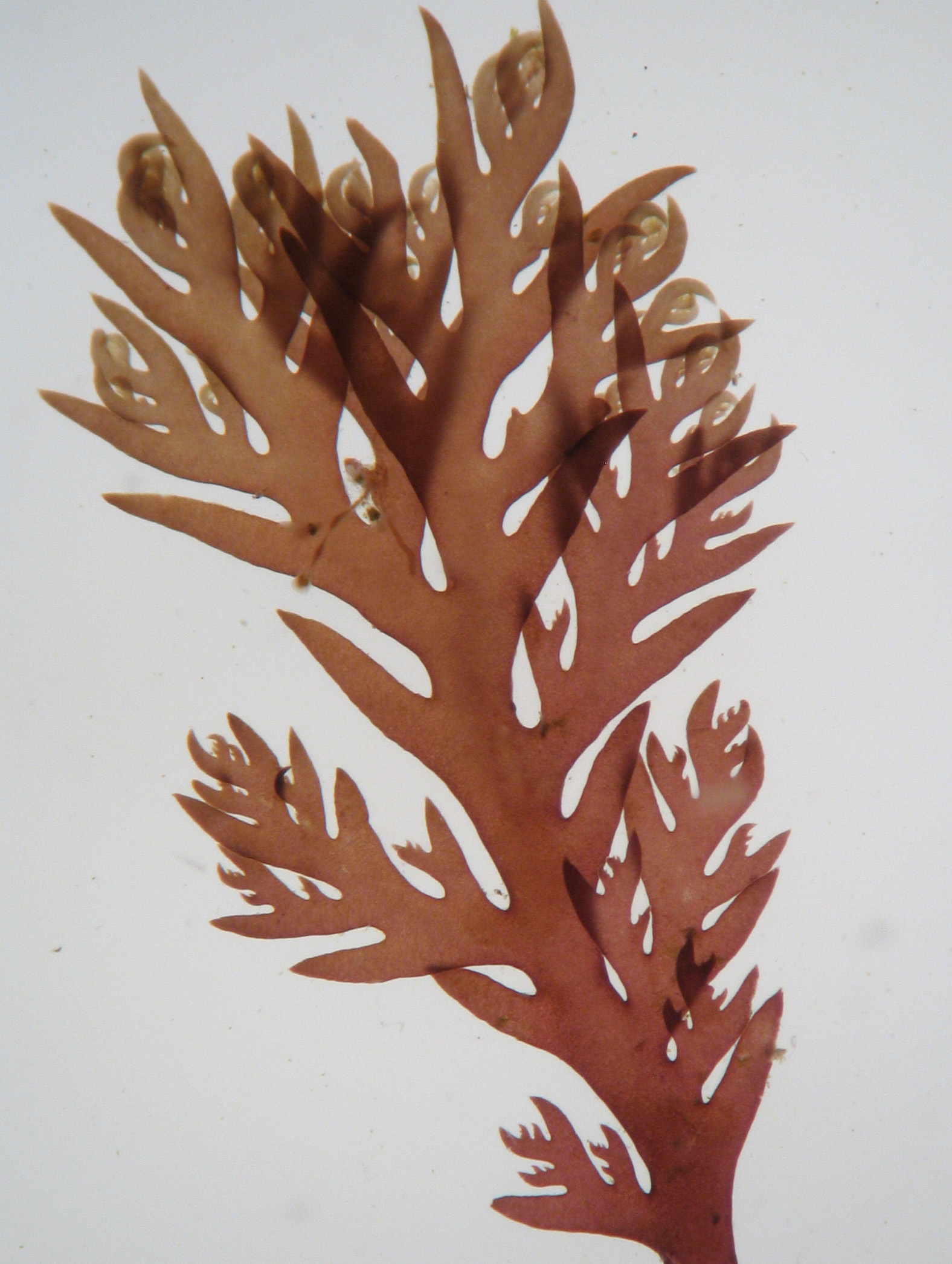

Plocamium rigidum, branch detail.
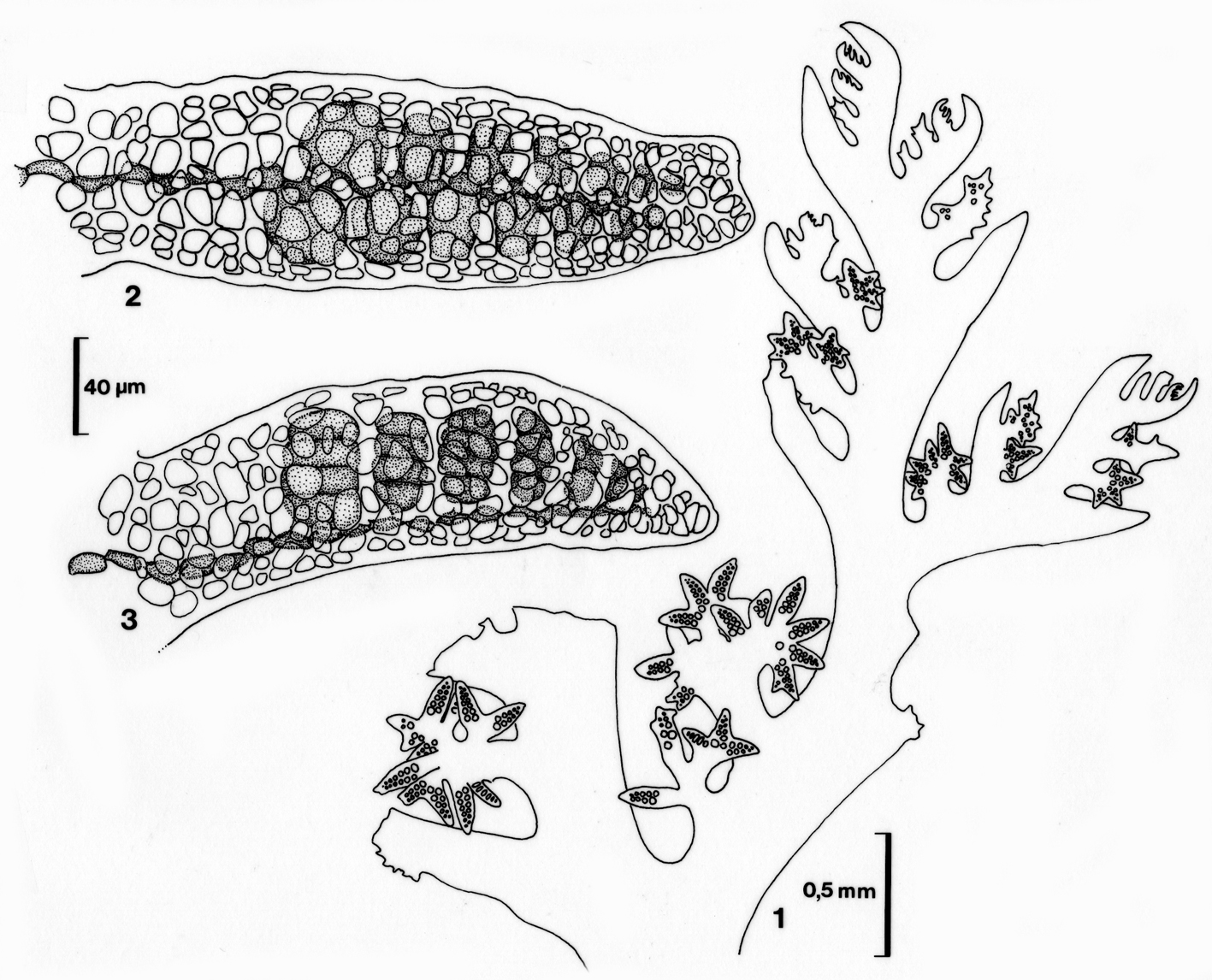
Plocamium rigidum. 1. Thallus apex with tetrasporangial stichidia. 2-3. Tetrasporangial stichidia, in ventral and lateral view respectively. Reproduced from Stegenga et al. (1997).
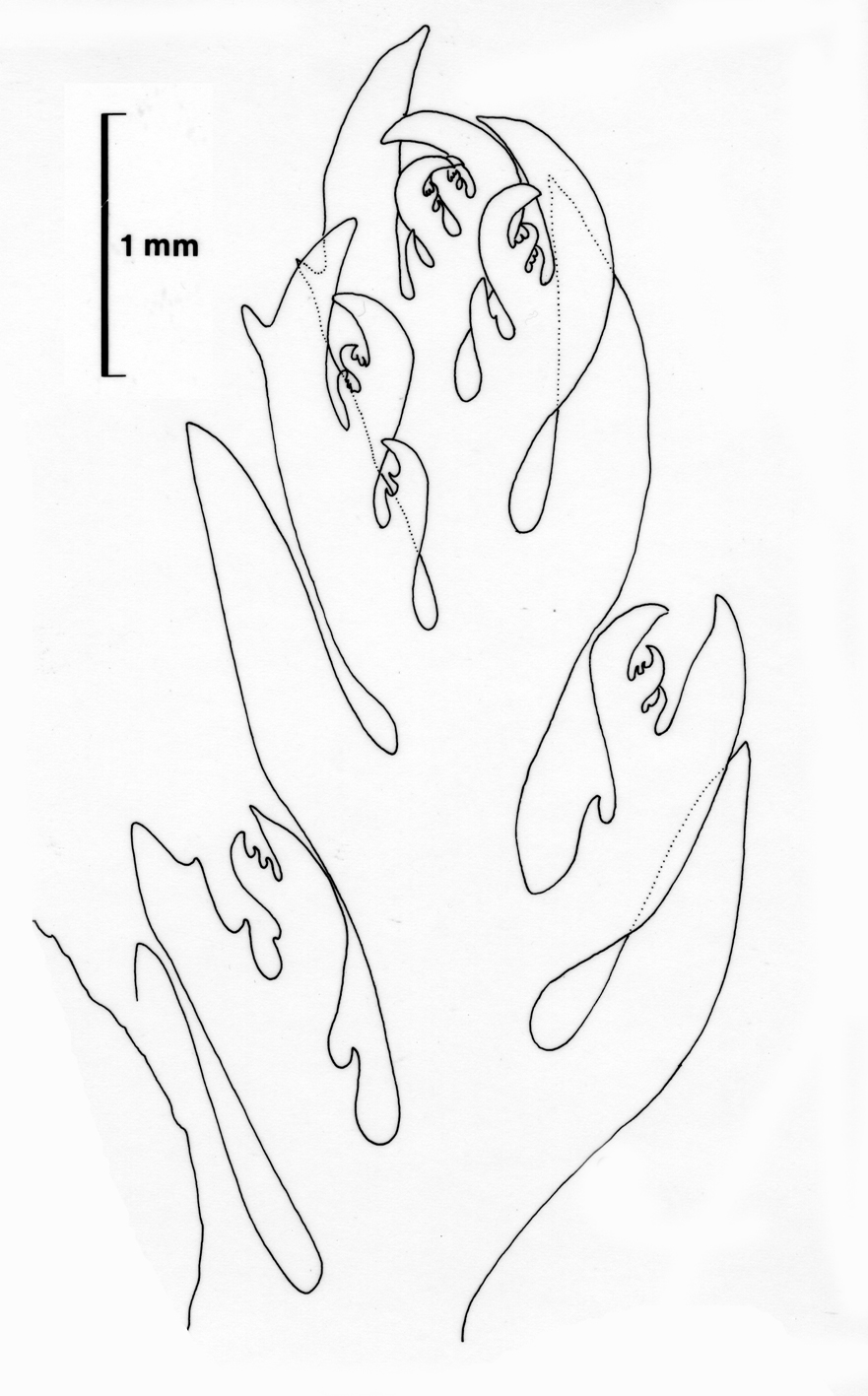

Plocamium rigidum, thallus apex, vegetative. Reproduced from Stegenga et al. (1997).
References Plocamium rigidum
Bélanger, C. & Bory de Saint-Vincent, J.B.G.M. 1834. Voyage aux Indes-Orientales. Botanique 2. Cryptogamie. Paris, 192 pp., 16 pls.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. 1996. Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. & R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 07 January 2026.