Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Ceramiales
Family Rhodomelaceae
Rhodomelopsis africana M.A.Pocock 1953: 34, fig. 1; pl. 5: figs A-F; pl. 6: figs A-C
Plants yellowish-brown to blackish, bushy, comprising prostrate basal system of rhizome-like branches with several erect axes up to about 10 (-20) cm tall. Segments with single axial filament surrounded by 7 pericentral cells, a layer of medullary cells and single-layered cortical cells of about 30 µm in diameter; cortication to very close behind apex, so that segmentation is obscured. Axes terete, up to 1 mm in diameter. Branching radial, laterals remaining unbranched and awl-shaped or developing into indeterminate branches. Trichoblasts absent in vegetative plants. Reproductive structures borne at apices of branches. Tetrasporangia in somewhat sickle-shaped stichidia, one per segment, about 80 µm in diameter, in single rows. Antheridial stands broadly sickle-shaped. Cystocarps globose, large (up to 1 mm in diameter), stalked, with short beak and ostiole.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Found from Brandfontein just west of Agulhas (Stegenga et al. 1997) along the south coast and east coasts (22-58). Often in sand-washed areas, in rock pools and the lower eulittoral and shallow sublittoral zones.
World distribution: Also recorded from Mozambique (Silva et al. 1996).
Type locality: Arniston, Western Cape, South Africa (Pocock, 1953).
Note: described in some detail by Pocock (1953).
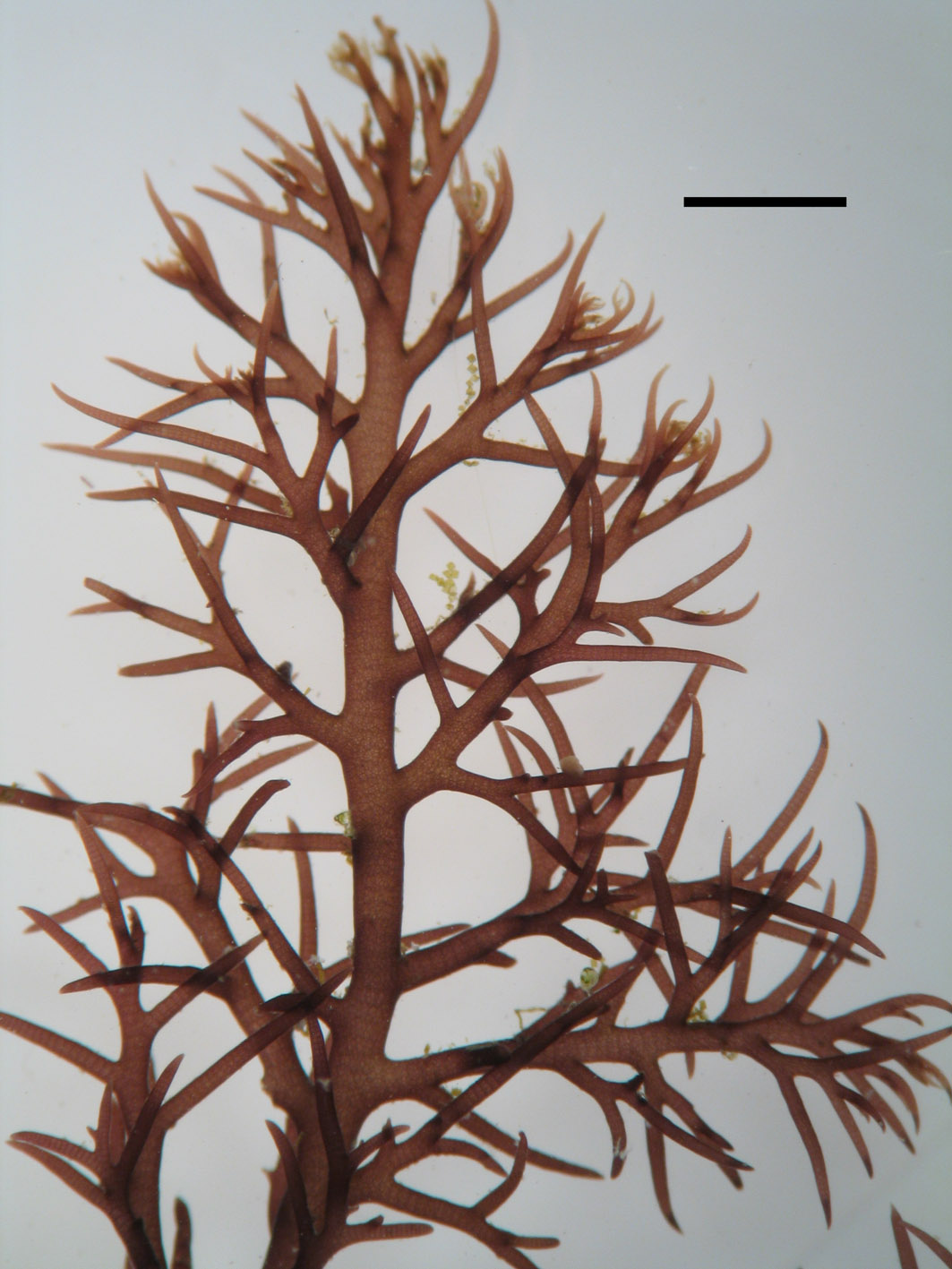

Rhodomelopsis africana (scale bar 2 mm)
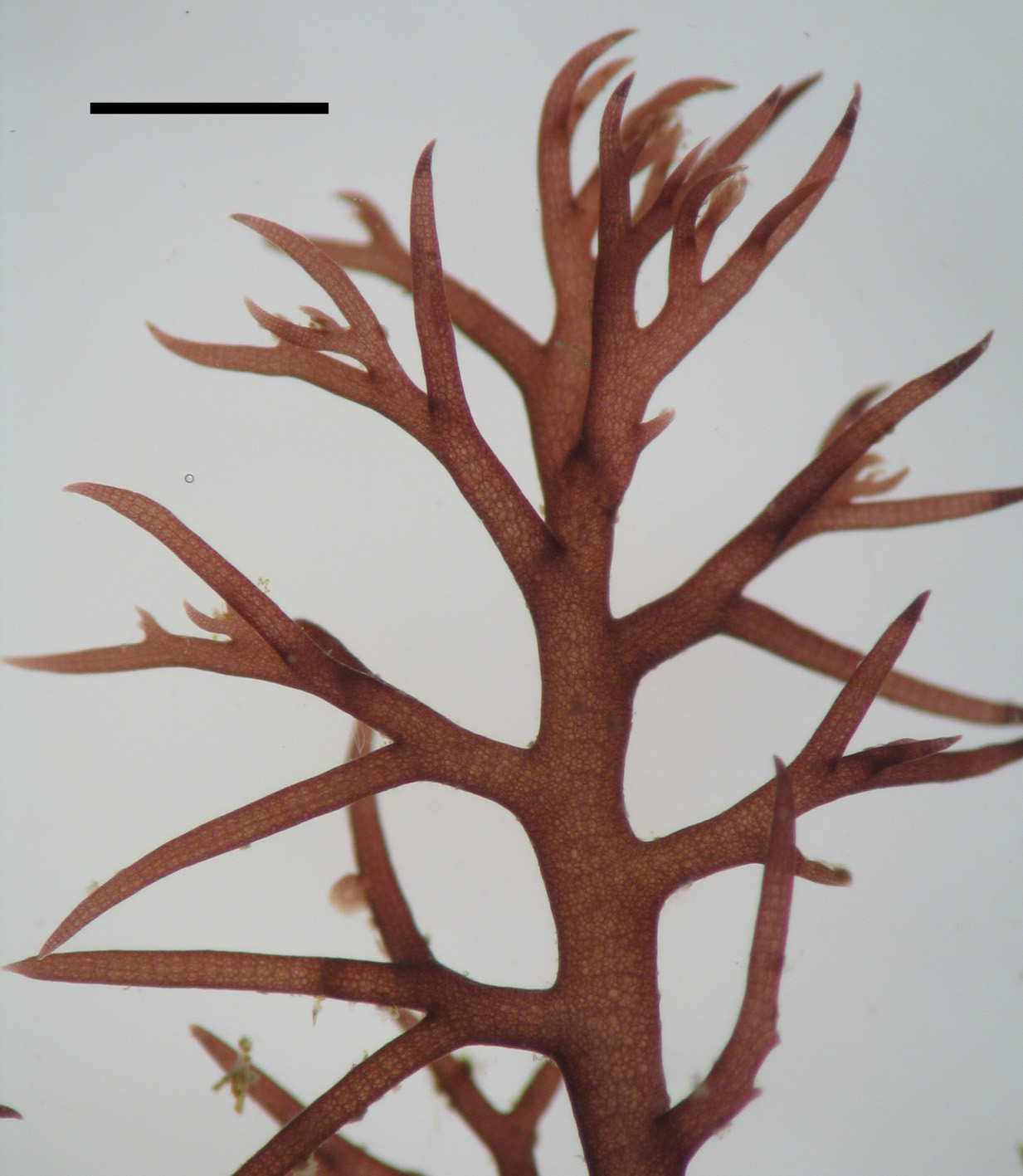

Rhodomelopsis africana, detail of apex (scale bar approximately 2 mm).
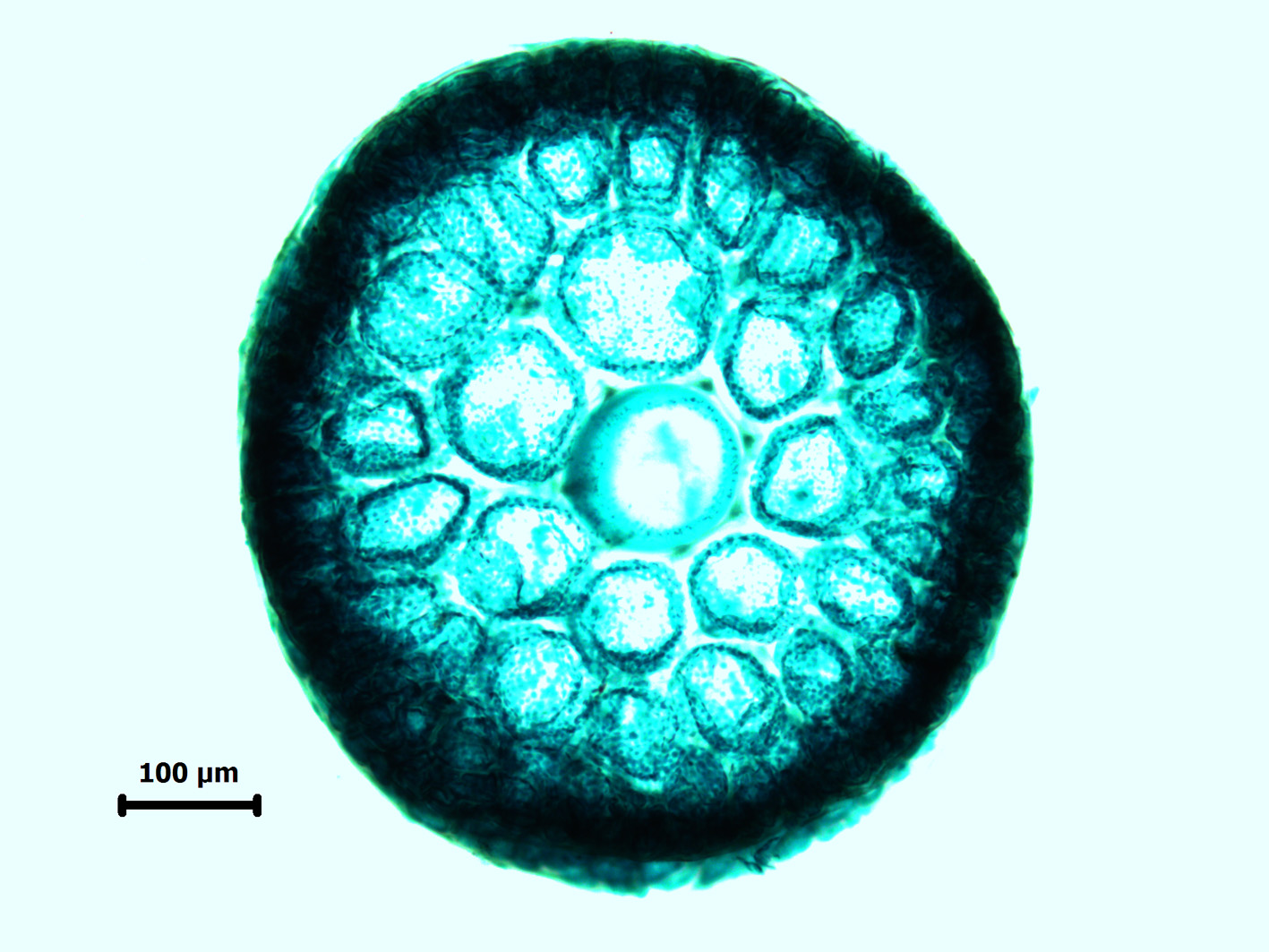
Rhodomelopsis africana, cross-section of axis showing axial filament and seven pericentral cells.
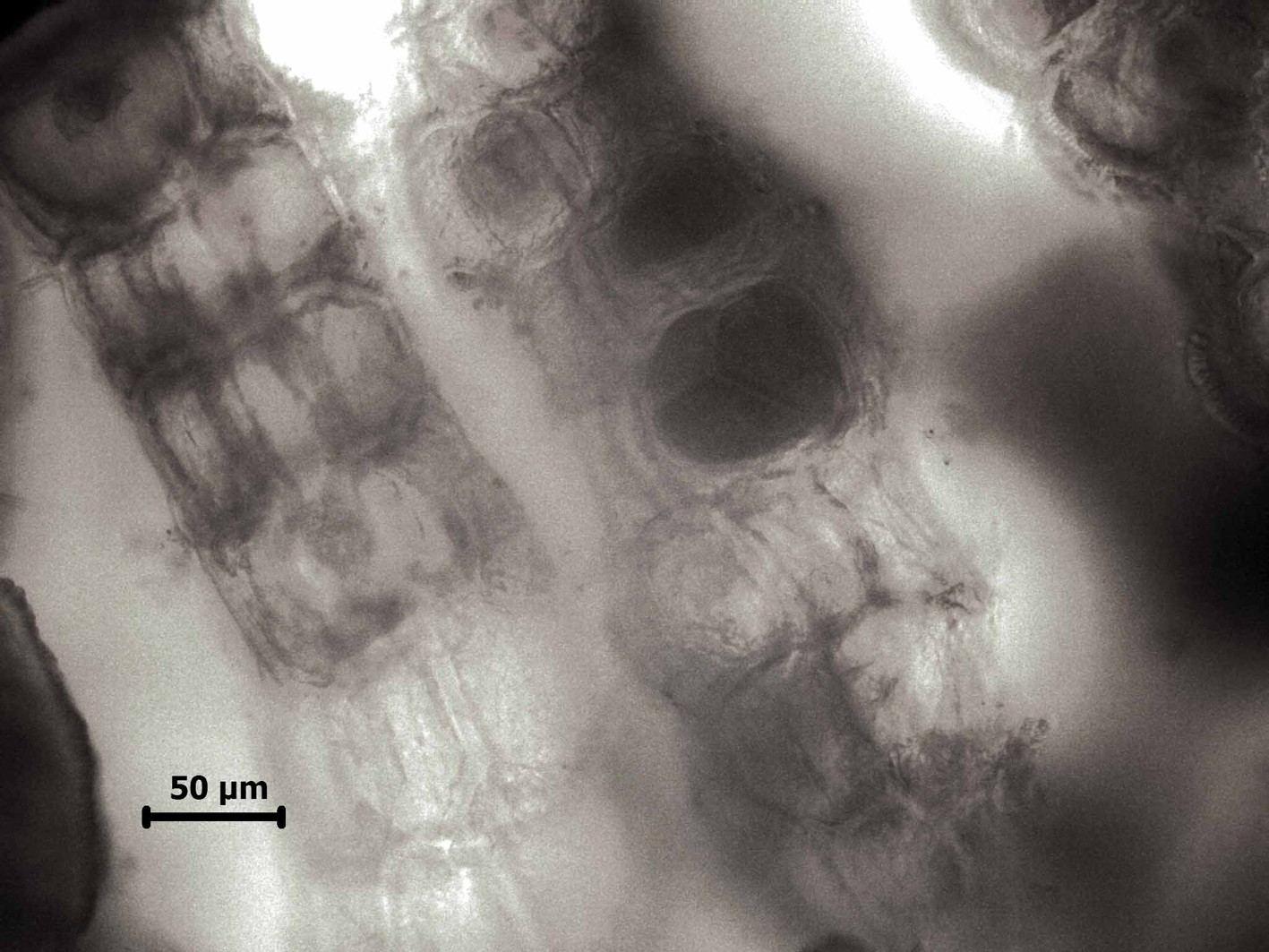

Rhodomelopsis africana, tetrasporangia.
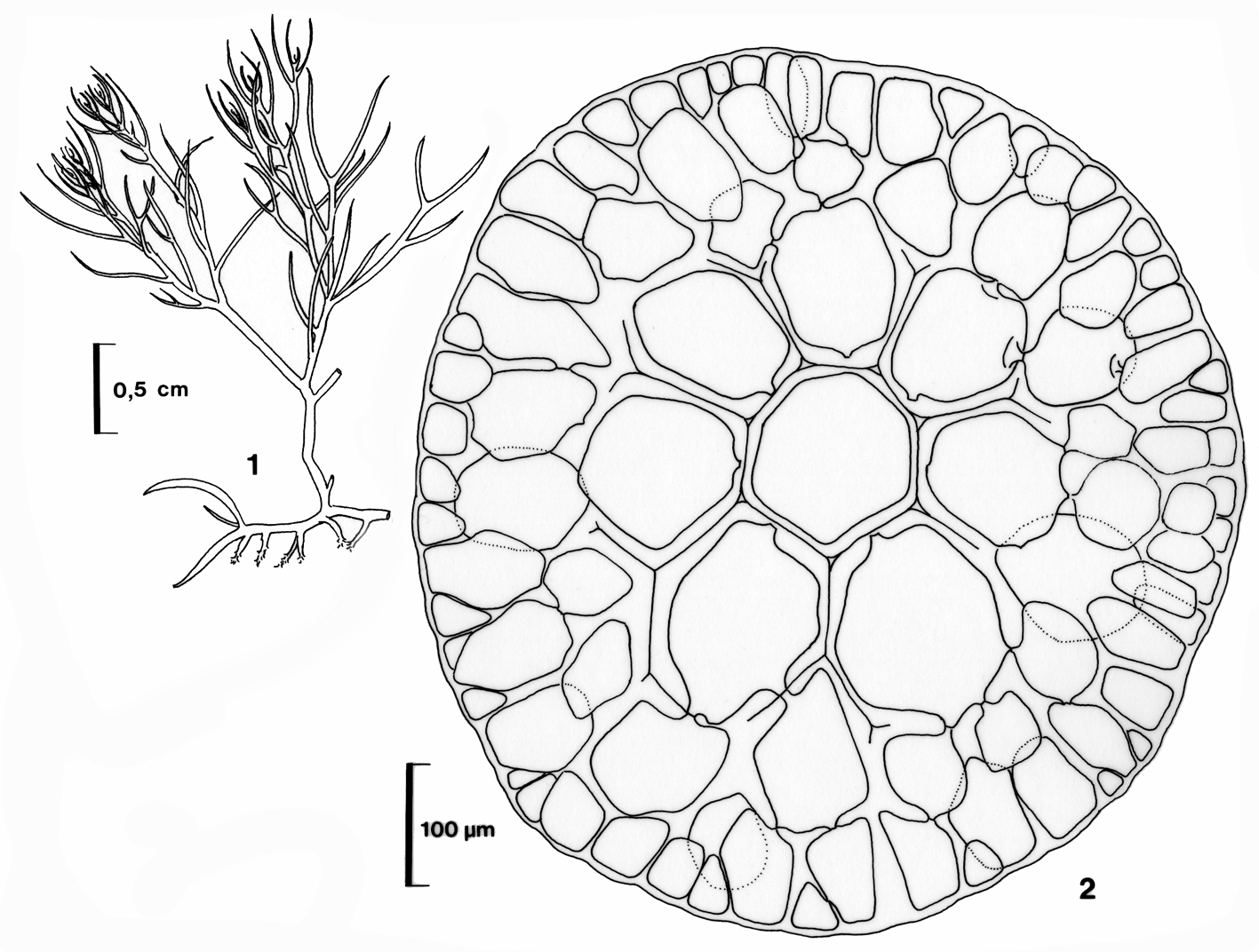
Rhodomelopsis africana. 1. Habit. 2. Cross section of main axis. Reproduced from Stegenga et al. (1997).
References Rhodomelopsis africana
Pocock, M.A. 1953. South African parasitic Florideae and their hosts. 1. Four members of the Rhodomelaceae which act as hosts for parasitic Florideae. Journal of the Linnean Society of London, Botany 55: 34-47, 9 figs, Plates 5-9.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. 1996. Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. & R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 09 March 2026.