Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Ceramiales
Family Spyridiaceae
Spyridia horridula F. Schmitz ex J. Agardh 1897: 15
Plants to 30 cm in height but usually 10-15 cm, rather stiff. Branching appears to be mainly in one plane, but near the apices four rows of laterals become apparent. Indeterminate branches generally alternating at intervals of 5-8 segments, the other segments with one determinate branchlet. Segments of the indeterminate branches with ca. 15 periaxial cells, each of which produces two derivatives that connect with the periaxials of the segment below. Main axis heavily corticated, increasing in diameter to over 1 mm, the segments becoming much wider than long. Determinate branchlets straight, consisting of 9-12 segments, with an incomplete cortication; cortical bands 2(-3) cells high, developing exclusively in acropetal and lateral direction from the periaxial cells. Apex of the determinate branchlets with (3)4 recurved stout spines. Reproductive stages not seen.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
Recorded from Goukamma to Cape Vidal in KwaZulu-Natal (29-56). Found in rock pools, sublittoral fringe and below.
World distribution: South African endemic.
Note: Superficially similar to S. hypnoides, but with a nearly distichous branching pattern and no straight terminal spine (De Clerck et al. 2005).
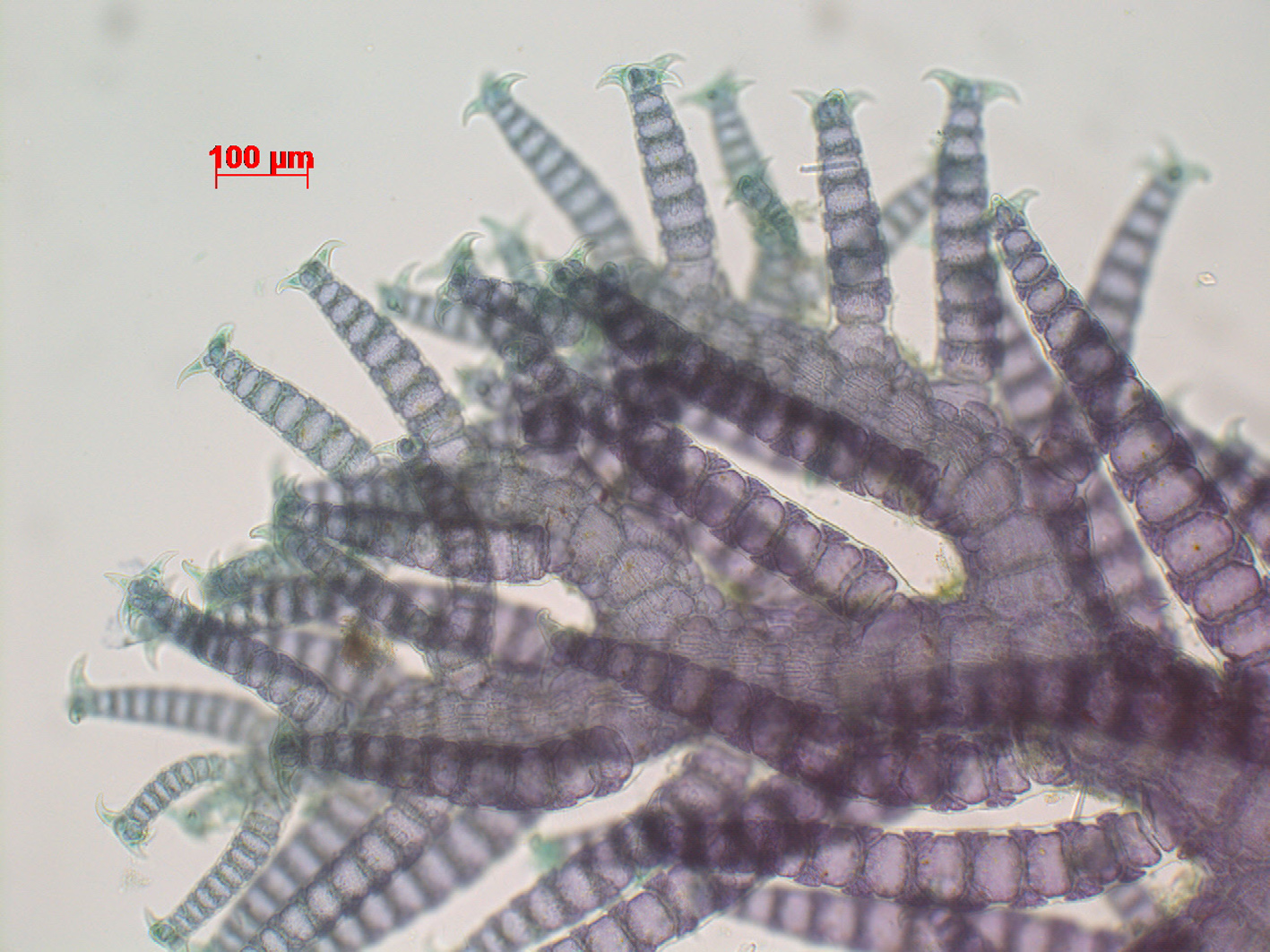
Spyridia horridula, determinate laterals with four recurved spines. Stained slide, Goukamma oyster beds.
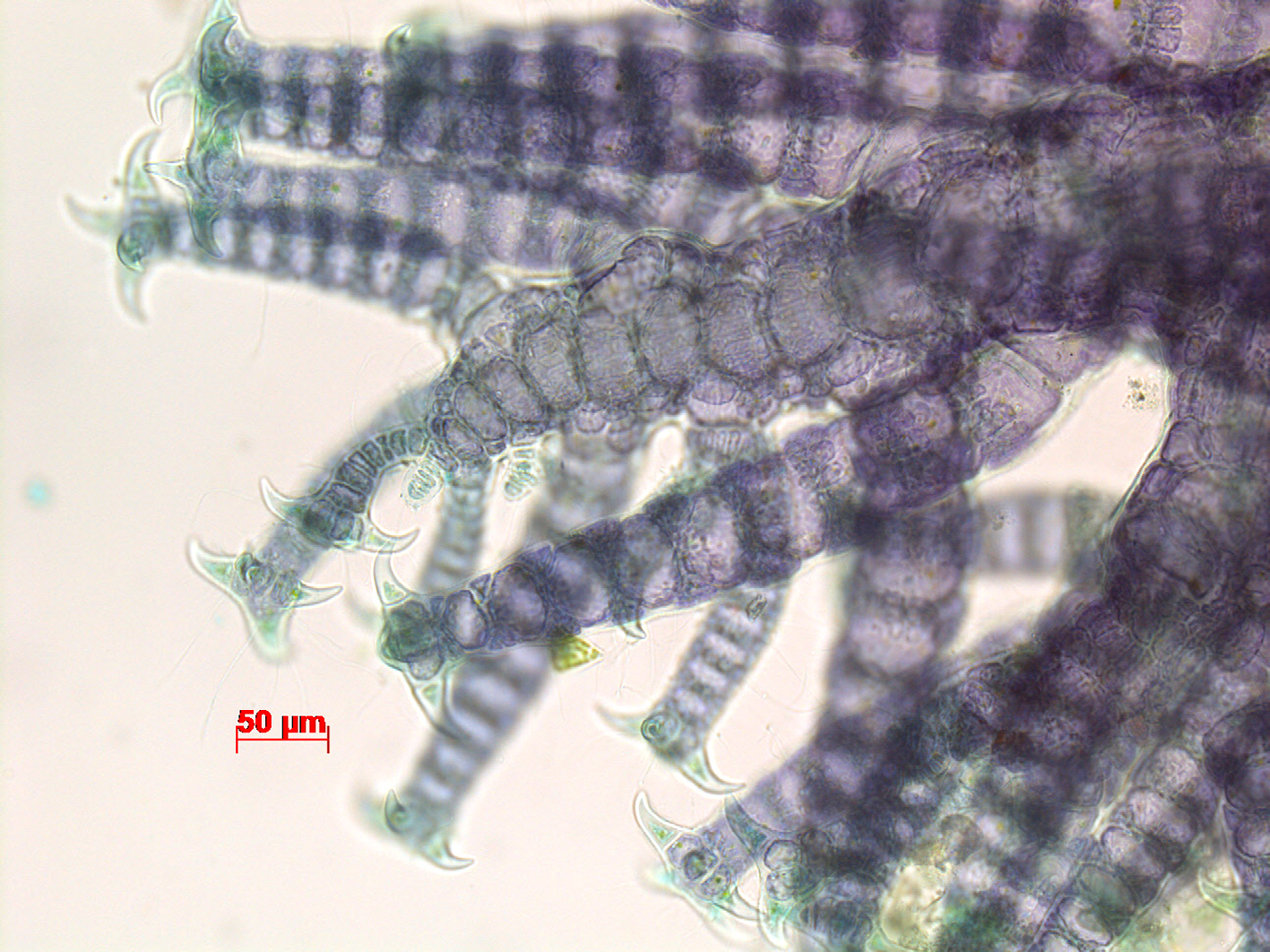

Spyridia horridula, detail of determinate laterals with four recurved spines. Stained slide, Goukamma oyster beds.
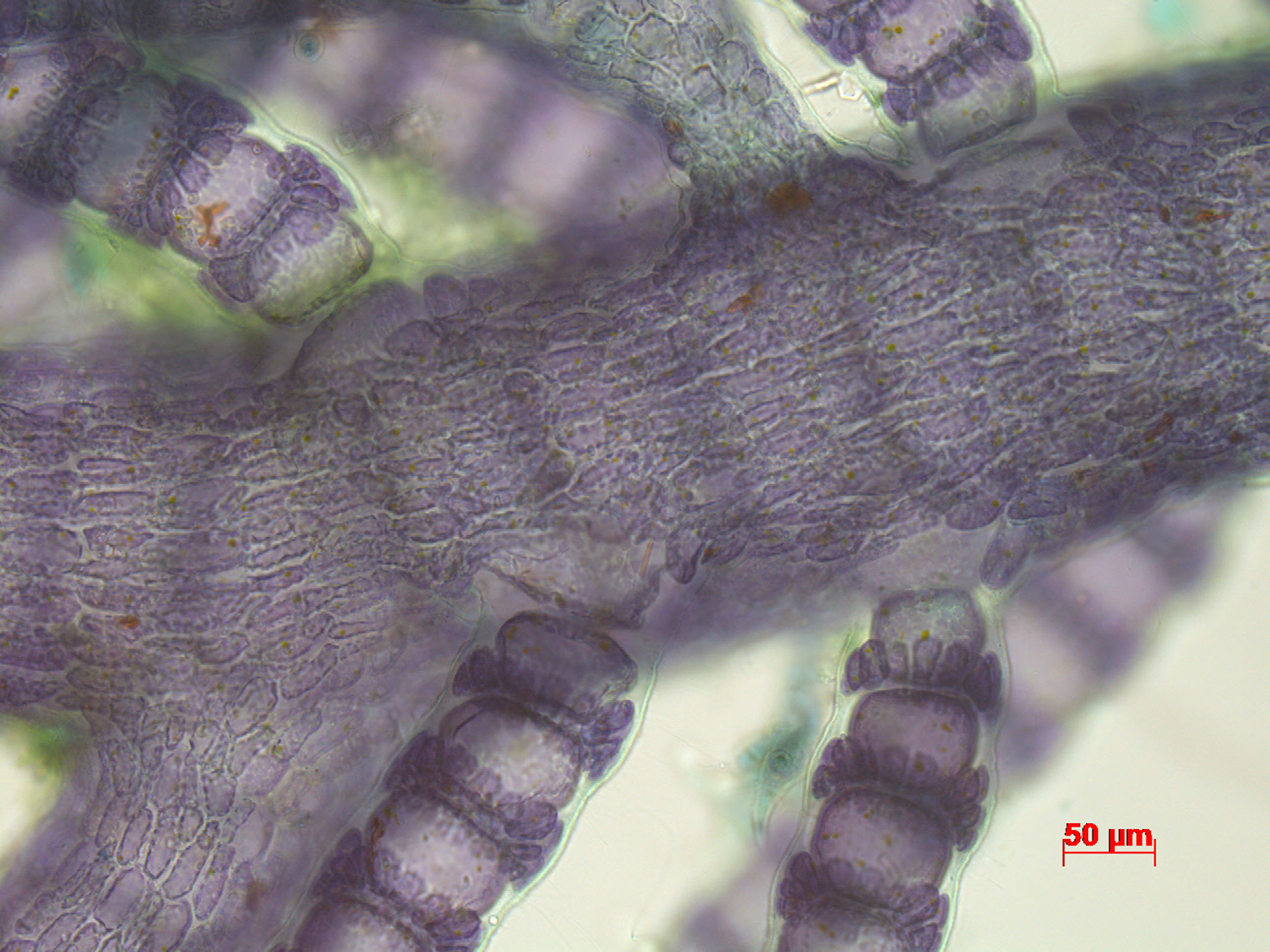
Spyridia horridula, indeterminate axes with determinate branchlets. Stained slide, Goukamma oyster beds.
References Spyridia horridula
Agardh, J.G. 1897. Analecta algologica. Continuatio IV. Lunds Universitets Års-Skrift, Andra Afdelningen, Kongl. Fysiografiska Sällskapets i Lund Handlingar 33(9): 106, 2 plates.
De Clerck, O, Tronchin, E. M., Schils, T. 2005. Red algae. In: De Clerck, O., J.J. Bolton, R. J. Anderson and E. Coppejans, 2005. Guide to the Seaweeds of Kwazulu-Natal. National Botanic Garden of Belgium, Brussels (Scripta Botanica Belgica), pp. 130-269.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 11 March 2026.