Seaweeds of the South African South Coast


Order Ceramiales
Family Wrangeliaceae
Tiffaniella cymodoceae (Børgesen) E.M.Gordon 1972: 121-123, figs. 39D-F, 40
Plants epiphytic on Codium spp., differentiated into creeping filaments, unicellular haptera and erect filaments up to 5 mm tall. Cells of the creeping filaments ca. 37 µm in diameter, about 4 or 5 times longer than broad, with one (or two) haptera on the proximal end and an erect filament on the distal end. Erect filaments ca. 37 µm in diameter basally, slightly tapering to the apex to about 30 µm, long-celled as the prostrate filaments are. Erect axes sparsely branched, reproductive laterals often more abundant.
Tetrasporangia arranged in up to four or five small cymose clusters on the proximal cells of the erect axes, measuring ca. 45 x 40 µm, tetrahedrally divided. Spermatangia in cylindrical to conical heads, with four- to five-celled axes, occurring on a number of subapical cells of the erect axes, measuring ca. 75 x 37 µm. Female fertile filament four-celled, often terminal on a one- or two-celled lateral. The subapical cell with one sterile cell and two fertile cells. Mature carposporophyte with a prominent central T-shaped cell consisting of the fused second and third cell of the fertile filament with the auxiliary cells (and proximal gonimolobe cells). Carposporophytes may grow to about 250 µm in diameter. Only the terminal cells of the gonimolobes ripen to carpospores measuring ca. 30 X 22 µm. There are no involucral filaments, but often the cell below the subhypogenous cell emits two or three filaments that continue growth after fertilization.
Collections, ecology and regional distribution
During the present study only found from Bird Island (Algoa Bay) eastward, but Stegenga et al. (1997) mentioned it from False Bay (17-58). It is reported to occur as far east as Mozambique. The type of T. cymodoceae is however described from the sea grass Cymodocea (from Mauritius), whereas all our material was found on Codium spp.
World distribution: Mauritius (type locality), Mozambique, and South and Western Australia, in the last locality also on Codium spp. (Womersley 1998).
Type locality: Riambel, near Souillac, Mauritius (Silva et al. 1996).

Tiffaniella cymodoceae. 1. Habit, tetrasporangial. 2 Tetrasporangia. 3. Spermatangial heads. 4. Carposporophyte. Reproduced from Stegenga et al. (1997).
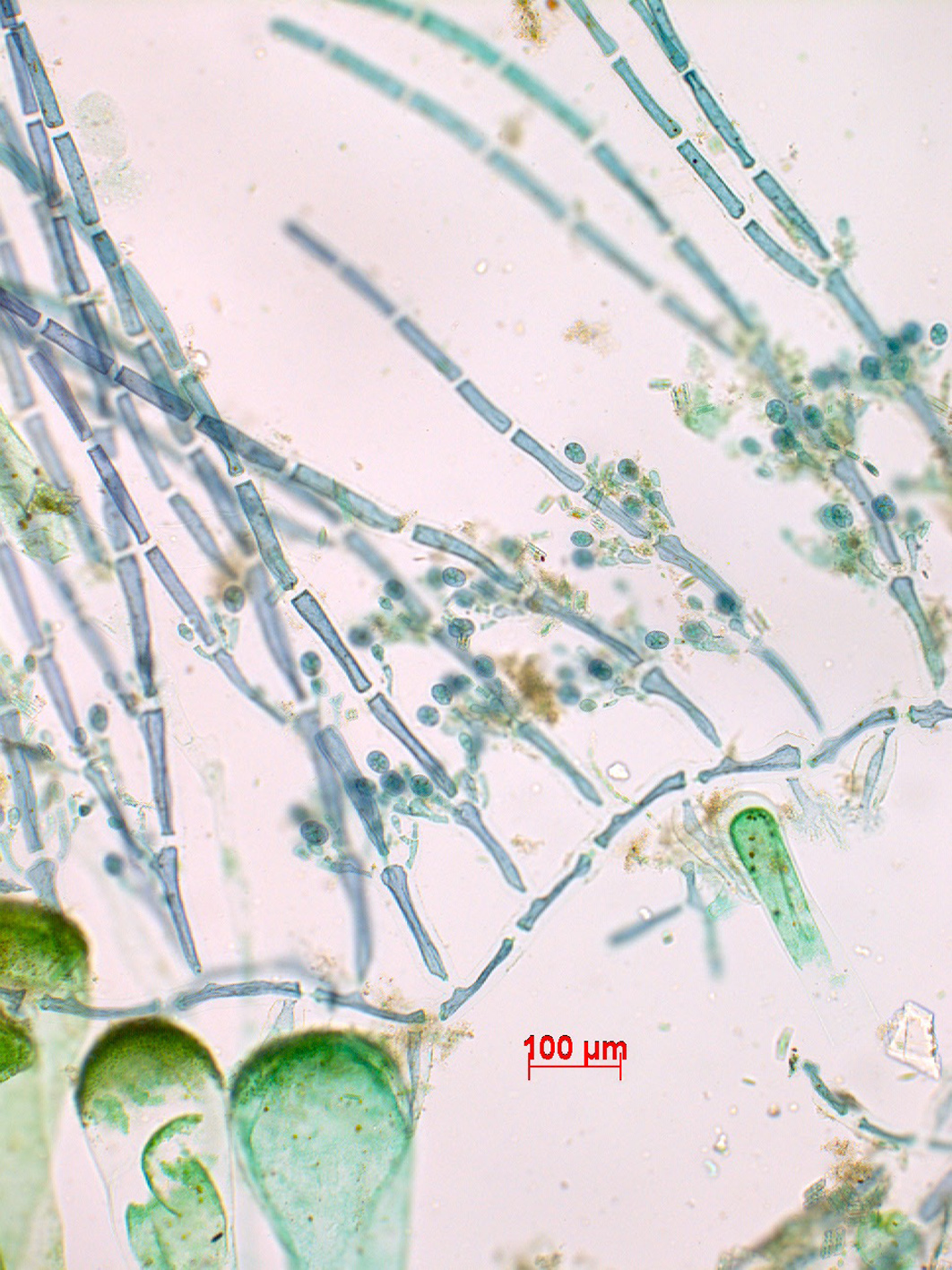
Tiffaniella cymodoceae. Microcopic habit, with tetrasporangia. Stained slide, Mntafufu (east of Port St Johns, Transkei).
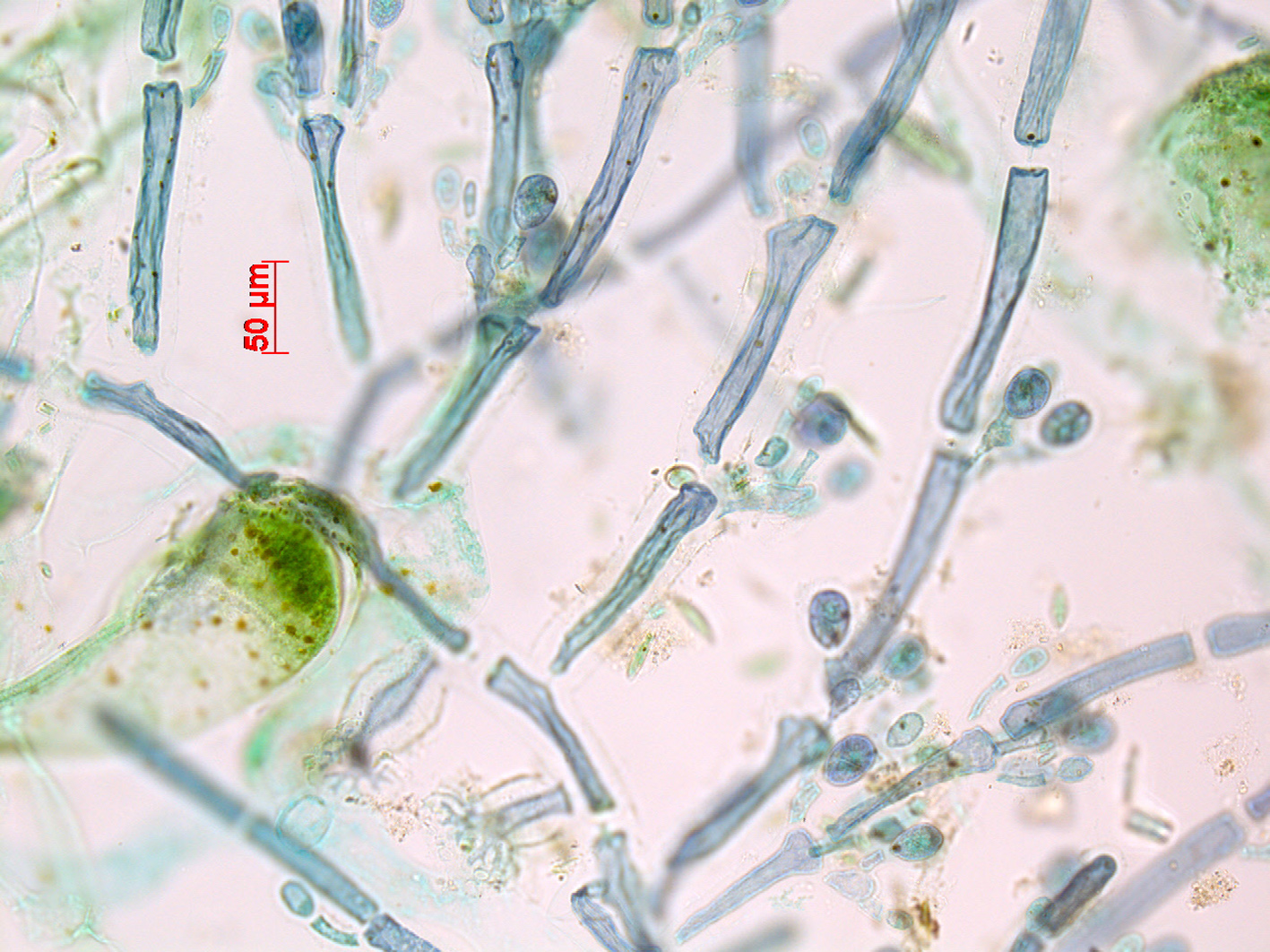
Tiffaniella cymodoceae. Detail of creeping filament with attachment structures and erect axes with tetrasporangia. Stained slide, Mntafufu.
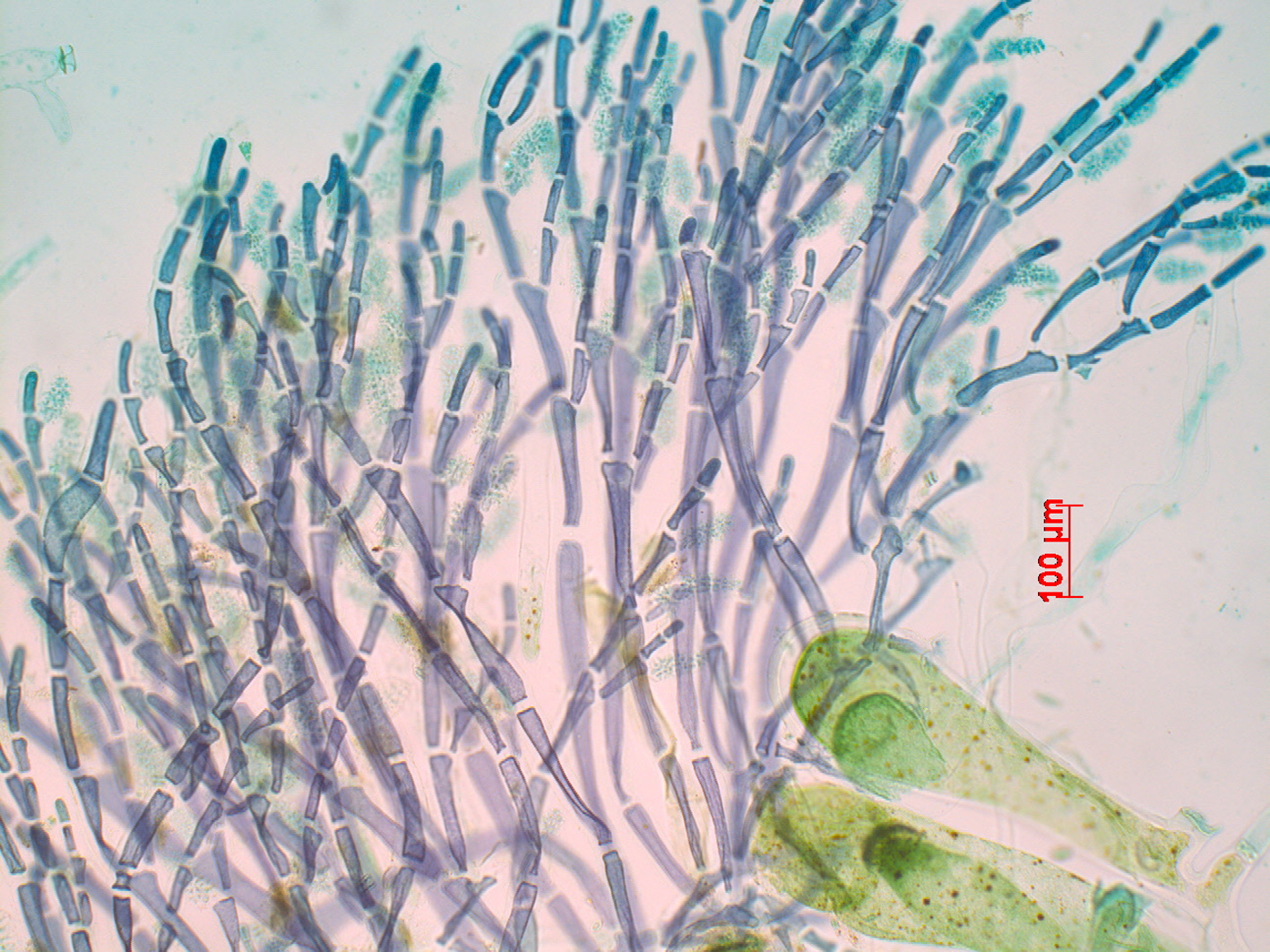
Tiffaniella cymodoceae. Male reproductive thallus. Stained slide, Mntafufu.
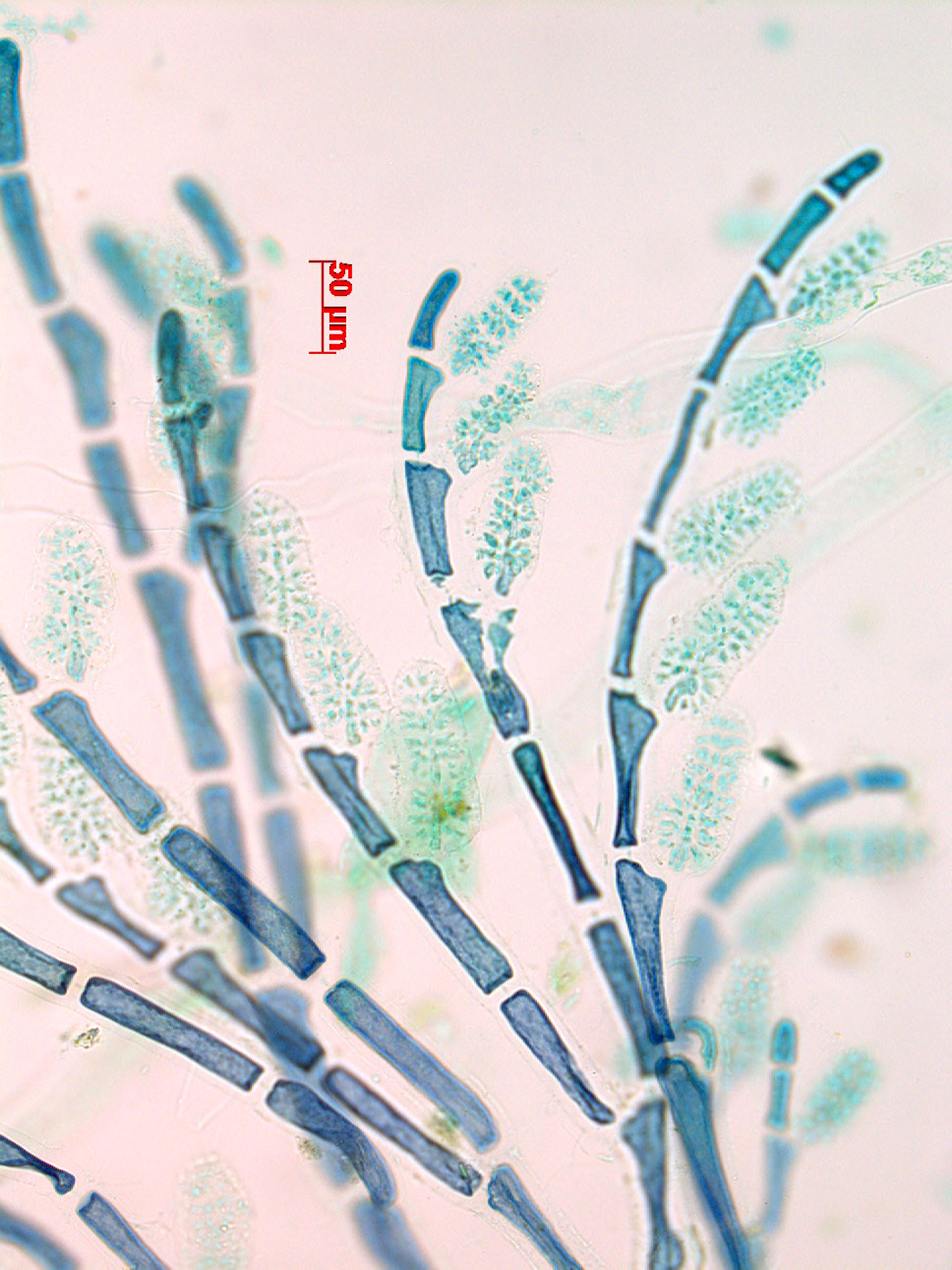
Tiffaniella cymodoceae. Detail of male reproductive thallus. Stained slide, Mntafufu.
References Tiffaniella cymodoceae
Gordon, E.M. 1972. Comparative morphology and taxonomy of the Wrangelieae, Sphondylothamnieae and Spermothamnieae (Ceramiaceae, Rhodophyta). Australian Journal of Botany Suppl. 4: 1-180, 63 figs, 3 tables.
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W. & Moe, R.L. 1996. Catalogue of the benthic marine algae of the Indian Ocean. University of California Publications in Botany 79: 1-1259.
Stegenga, H., Bolton, J.J. & R. J. Anderson. 1997. Seaweeds of the South African west coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium 18: 655 pp.
Womersley, H.B.S. 1998. The marine benthic flora of southern Australia - Part IIIC. Ceramiales - Ceramiaceae, Dasyaceae. pp. 535. Canberra & Adelaide: Australian Biological Resources Study & State Herbarium of South Australia.
Cite this record as:
Anderson RJ, Stegenga H, Bolton JJ. 2016. Seaweeds of the South African South Coast.
World Wide Web electronic publication, University of Cape Town, http://southafrseaweeds.uct.ac.za; Accessed on 09 March 2026.